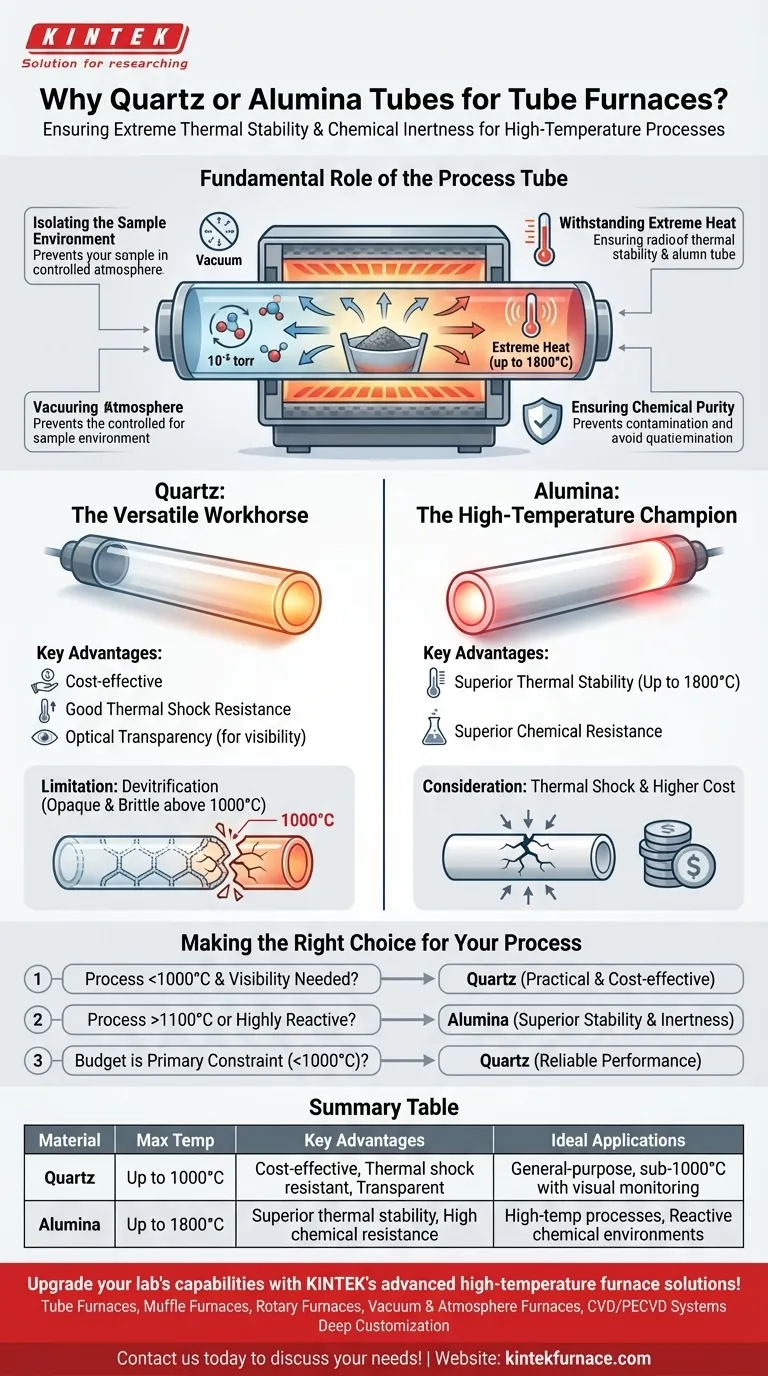
The choice of a process tube in a furnace is dictated by two non-negotiable requirements: extreme thermal stability and chemical inertness. Quartz and alumina are the industry standards because they can contain a sample within a controlled atmosphere at very high temperatures without breaking down or reacting with the process. This ensures the integrity and purity of the experiment or manufacturing process.
The core decision between quartz and alumina is a trade-off between temperature and cost. Quartz is the versatile and economical choice for most applications up to 1000°C, while high-purity alumina is required for processes demanding higher temperatures and maximum chemical resistance.
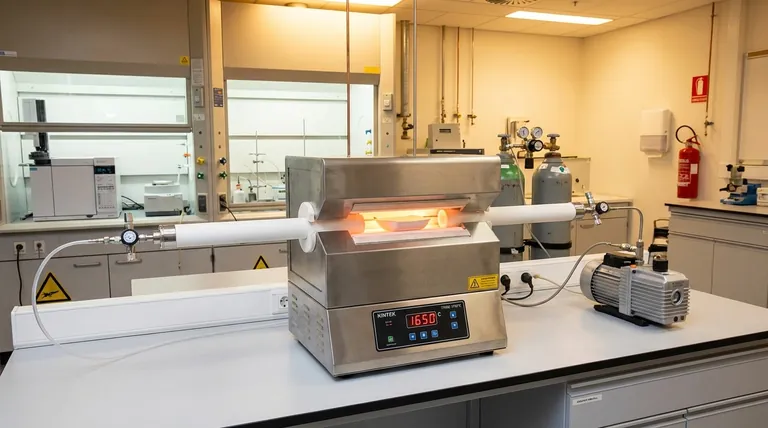

The Fundamental Role of the Process Tube
A tube furnace is designed to precisely heat a sample, but the process tube is the vessel that makes this process meaningful. Its role extends far beyond simply holding the material.
Isolating the Sample Environment
The primary function of the tube is to create a hermetically sealed environment. This allows you to work under a high vacuum (down to 10⁻⁵ torr) or introduce specific gases, creating a controlled atmosphere that is essential for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or annealing reactive materials.
Withstanding Extreme Heat
The furnace's heating elements operate at temperatures that can exceed 1700°C. The process tube must endure this intense, continuous heat without melting, sagging, or degrading. This thermal stability is the first criterion for material selection.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
At high temperatures, materials become much more reactive. The process tube must be chemically inert, meaning it won't react with the sample, precursor gases, or any byproducts. This prevents contamination, which is critical for applications in semiconductor fabrication and materials science research.
A Tale of Two Materials: Quartz vs. Alumina
While both materials serve the same fundamental purpose, their properties make them suitable for different operational windows.
Quartz: The Versatile Workhorse
Quartz (fused silica) is the most common choice for general-purpose tube furnace applications. It offers an excellent balance of properties and is relatively cost-effective.
Its key advantages are good thermal shock resistance, meaning it can handle relatively fast temperature changes, and optical transparency at lower temperatures, allowing for visual monitoring of the process.
Alumina: The High-Temperature Champion
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is a high-performance ceramic used when the limits of quartz are exceeded. Its primary advantage is a significantly higher maximum operating temperature, making it suitable for processes running up to 1700°C or even 1800°C.
It also offers superior chemical resistance against certain aggressive or alkaline compounds that might etch quartz at high temperatures. However, alumina is opaque, preventing any visual observation of the sample during the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Choosing the wrong material can lead to failed experiments, damaged equipment, and contaminated samples. Understanding the limitations of each is crucial.
The Quartz Limitation: Devitrification
The most significant drawback of quartz is a process called devitrification. Above approximately 1000°C, the amorphous glass structure of quartz begins to crystallize, causing it to become opaque and brittle.
This is not a defect but an inherent property of the material. Operating a quartz tube consistently above this temperature will drastically shorten its lifespan and increase the risk of mechanical failure.
The Alumina Consideration: Thermal Shock and Cost
While thermally stable, alumina and other ceramics can be more susceptible to thermal shock than quartz. Rapid heating or cooling can cause cracks, so controlled temperature ramps are essential.
Furthermore, high-purity alumina tubes are significantly more expensive than quartz tubes, making them a specific investment for processes that absolutely require their superior performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific application will determine the ideal tube material. Base your decision on the single most demanding parameter of your process.
- If your process operates below 1000°C and you value visibility: Quartz is your most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your process consistently exceeds 1100°C or involves highly reactive chemicals: Alumina is the necessary upgrade for its superior thermal stability and chemical inertness.
- If your budget is the primary constraint for a sub-1000°C process: Quartz provides reliable performance without the high cost of advanced ceramics.
Selecting the correct process tube is the foundation for achieving repeatable and reliable high-temperature results.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1000°C | Cost-effective, thermal shock resistant, transparent for visibility | General-purpose, sub-1000°C processes with visual monitoring |
| Alumina | Up to 1800°C | Superior thermal stability, high chemical resistance | High-temperature processes, reactive chemical environments |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need quartz or alumina tubes for optimal performance. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















