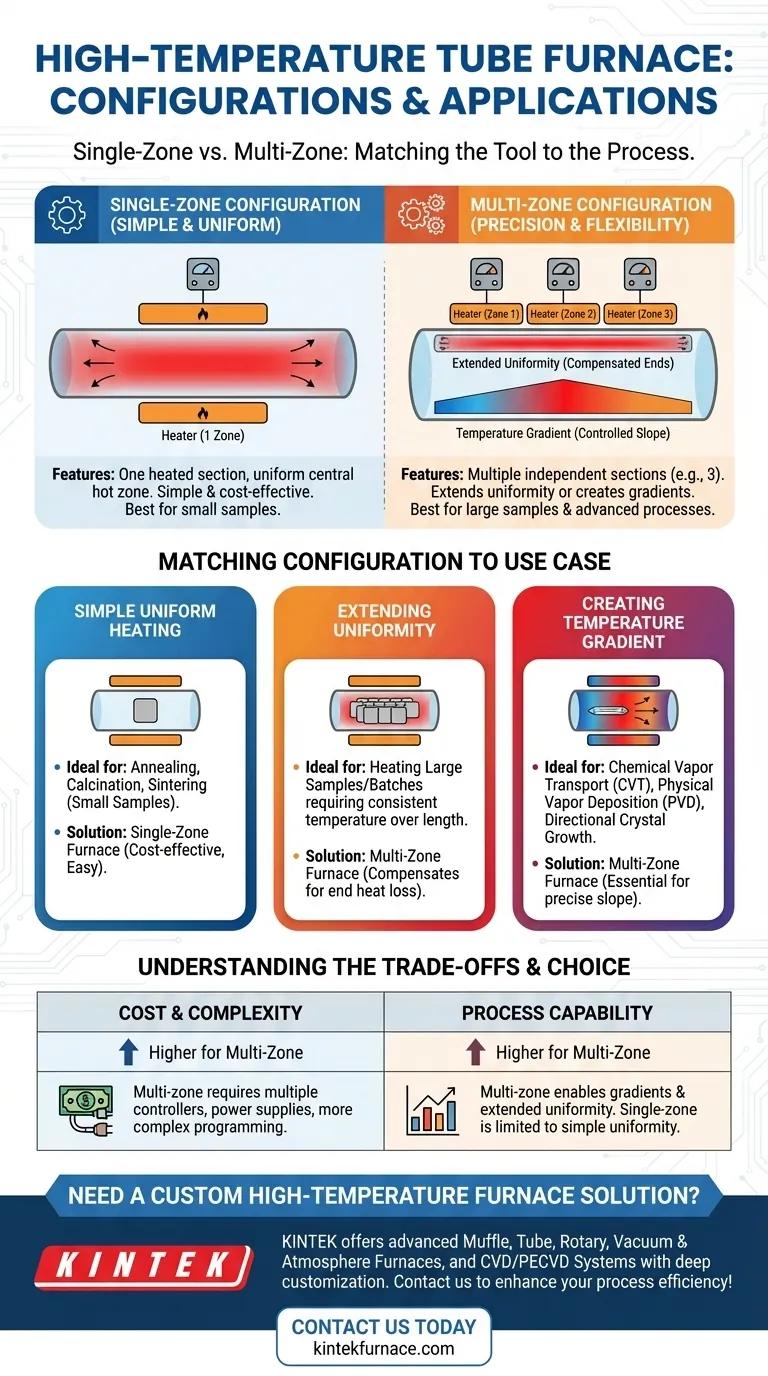
At its core, a high-temperature tube furnace can be configured with either a single heated section or multiple, independently controlled heated sections. The primary configurations are single-zone and multi-zone (most commonly three-zone), with the choice depending entirely on the specific heating requirements of your process, such as the need for a uniform temperature over a long area or a controlled temperature gradient.
The decision between a single-zone and a multi-zone furnace is not about which is superior, but about which tool is right for the job. Single-zone furnaces provide simple, uniform heat for smaller samples, while multi-zone furnaces offer precise control to either extend that uniformity or create intentional temperature differences along the tube.

The Fundamental Configurations: Single vs. Multi-Zone
The configuration of the heating zones is the most critical factor defining a tube furnace's capability. It dictates the temperature profile you can achieve along the length of the process tube.
The Single-Zone Furnace
A single-zone furnace is the most fundamental design. It features one set of heating elements managed by a single temperature controller and thermocouple.
This configuration is designed to create one stable, uniform hot zone, which is typically located in the very center of the furnace's heated length.
While simple and effective, the temperature naturally drops off towards the ends of the tube due to heat loss to the ambient environment. The actual uniform zone is therefore shorter than the total heated length.
The Multi-Zone Furnace
A multi-zone furnace divides the heated length into several sections, each with its own independent heating elements, thermocouple, and controller.
The most common arrangement is a three-zone furnace, featuring a main center zone and two smaller end zones. However, configurations with two, five, or more zones exist for highly specialized applications.
This design allows for precise temperature manipulation along the tube, enabling two distinct operational modes: extending uniformity or creating a gradient.
How Each Configuration Solves a Different Problem
Understanding the intended application of each configuration is key to selecting the right furnace for your work. The goal is to match the furnace's capability to your process requirements.
Use Case: Simple, Uniform Heating
For processes like annealing, calcination, or sintering of small samples, a single-zone furnace is often the ideal choice.
Its primary strength is providing a cost-effective and easy-to-operate solution when your sample can fit entirely within the central uniform hot zone.
Use Case: Extending Temperature Uniformity
A three-zone furnace is superior for heating larger samples or batches that require a consistent temperature across a significant length.
By setting the two end zones to a slightly higher temperature, you can actively compensate for the natural heat loss at the ends. This creates a much longer and more stable uniform hot zone than is possible with a single-zone furnace of the same physical length.
Use Case: Creating a Temperature Gradient
The true power of a multi-zone furnace lies in its ability to create a controlled temperature gradient.
By setting each zone to a different temperature, you can establish a precise temperature slope along the process tube. This capability is essential for advanced applications like chemical vapor transport (CVT), physical vapor deposition (PVD), and certain types of directional crystal growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace configuration involves balancing performance needs with practical constraints like budget and operational complexity.
Cost and Complexity
A multi-zone furnace is inherently more expensive and complex than a single-zone model. It requires multiple PID controllers, power supplies, and thermocouples, increasing both the initial investment and the complexity of programming a temperature profile.
Process Capability
A single-zone furnace simply cannot create a temperature gradient. If your process requires this, a multi-zone furnace is mandatory.
Likewise, achieving a high degree of temperature uniformity over a long length is only practical with a multi-zone furnace configured to compensate for end losses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven entirely by the thermal profile your experiment or process demands.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness for small samples: A single-zone furnace is the most direct and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is processing large samples or batches with maximum temperature consistency: A three-zone furnace, configured to extend the uniform hot zone, is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is a specialized process requiring a controlled temperature slope: A multi-zone furnace is essential for creating the required temperature gradient.
Ultimately, understanding these configurations empowers you to select a furnace that serves as a precise tool for your specific scientific or industrial objective.
Summary Table:
| Configuration | Key Features | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Zone | One heated section, uniform central hot zone, simple and cost-effective | Annealing, calcination, sintering of small samples |
| Multi-Zone (e.g., Three-Zone) | Multiple independently controlled sections, enables extended uniformity or gradients | Large sample heating, chemical vapor transport, crystal growth |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















