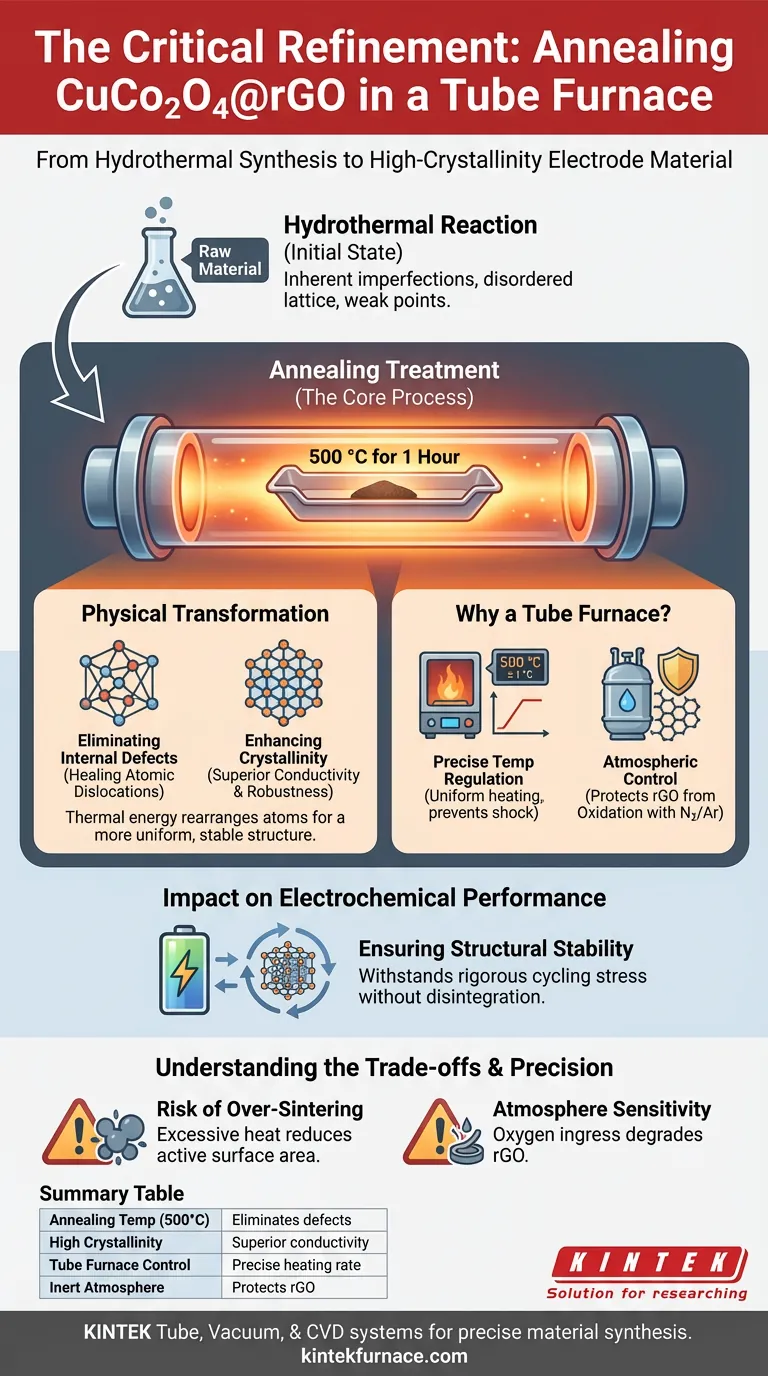
Annealing is the critical refinement phase in the synthesis of high-performance CuCo2O4@rGO. Following the initial hydrothermal reaction, the raw material contains inherent imperfections that must be corrected to ensure functionality. Placing the samples in a Tube Furnace at 500 °C for one hour is necessary to eliminate internal structural defects and drive the material toward high crystallinity.
Core Insight: While hydrothermal synthesis creates the chemical composition, the annealing treatment defines the physical quality. This step serves as a structural "hardening" process, removing atomic defects to ensure the electrode remains stable during the rigorous stress of electrochemical cycling.

The Physical Transformation Mechanism
Eliminating Internal Defects
The product emerging from a hydrothermal reaction often possesses a disordered or "imperfect" lattice structure.
These internal defects act as weak points that can degrade performance.
Annealing provides the thermal energy required to heal these atomic dislocations, resulting in a more uniform material.
Enhancing Crystallinity
The primary goal of this treatment is to maximize the crystallinity of the CuCo2O4 nanoparticles.
High temperatures allow atoms to rearrange themselves into a highly ordered lattice structure.
This ordering is essential because high-crystallinity materials generally offer superior electronic conductivity and mechanical robustness compared to amorphous or semi-crystalline counterparts.
Why a Tube Furnace is Required
Precise Temperature Regulation
The specific protocol calls for a sustained temperature of 500 °C.
A tube furnace is designed to maintain this temperature with high precision, often controlling heating rates (e.g., 5 °C per minute) to prevent thermal shock.
This stability ensures that the crystallization process occurs uniformly throughout the entire sample batch.
Atmospheric Control (Protection of rGO)
While the primary focus is on the metal oxide, the composite includes Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO).
Tube furnaces allow for the introduction of inert atmospheres, such as Nitrogen (N2) or Argon.
This is critical because heating carbon-based materials like rGO to 500 °C in an uncontrolled (oxygen-rich) environment would lead to oxidation or combustion, destroying the conductive carbon backbone.
Impact on Electrochemical Performance
Ensuring Structural Stability
The ultimate purpose of this treatment is to prepare the material for use as an electrode.
Electrodes undergo significant mechanical stress during electrochemical cycling (charging and discharging).
By removing defects and increasing crystallinity, the annealing process ensures the CuCo2O4@rGO has the structural integrity to withstand these cycles without disintegrating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Over-Sintering
While heat removes defects, excessive heat or prolonged exposure can cause nanoparticles to merge (sinter).
This reduces the active surface area, which is detrimental to electrochemical performance.
Adhering strictly to the 500 °C for one hour limit is a balance between removing defects and maintaining the nanostructure.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The effectiveness of the tube furnace relies heavily on the integrity of the inert environment.
If the tube seal is compromised, even slightly, oxygen ingress at 500 °C will degrade the rGO component.
This creates a dependency on equipment maintenance that does not exist with simple air ovens.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the potential of your CuCo2O4@rGO, align your processing parameters with your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is Cycle Life: Strictly adhere to the 500 °C annealing temperature to maximize crystallinity, as ordered structures resist degradation during repetitive cycling.
- If your primary focus is Compositional Purity: Ensure your tube furnace utilizes a verified inert gas flow (N2 or Ar) to protect the rGO lattice from oxidation during the heating phase.
Summary: The annealing step is not merely a drying process; it is a structural reorganization that dictates the final longevity and reliability of your electrode material.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Role in CuCo2O4@rGO Synthesis | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing Temp (500°C) | Eliminates internal lattice defects | Enhanced structural stability |
| High Crystallinity | Drives atomic rearrangement | Superior electronic conductivity |
| Tube Furnace Control | Precise heating rate (e.g., 5°C/min) | Prevents thermal shock & sintering |
| Inert Atmosphere | Protects rGO from oxidation | Maintains conductive carbon backbone |
Precision is the difference between a failing electrode and a high-performance battery. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the exact thermal profiles required in advanced material synthesis. Whether you need customizable atmospheric control or precise temperature uniformity for your research, our lab high-temp furnaces ensure your CuCo2O4@rGO achieves maximum crystallinity. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Xue Fang, Jiali Yu. Introducing CuCo2S4 Nanoparticles on Reduced Graphene Oxide for High-Performance Supercapacitor. DOI: 10.3390/nano14020182
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















