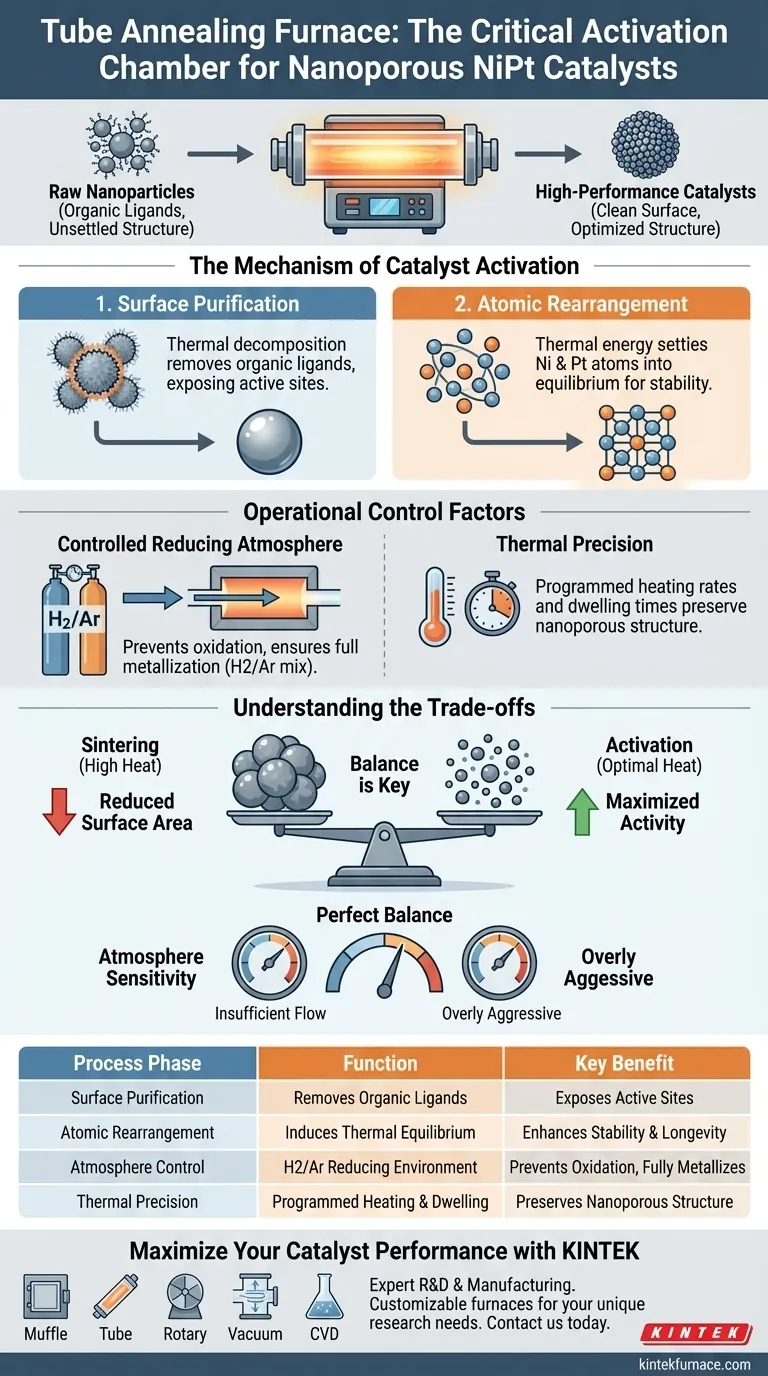
A tube annealing furnace serves as the critical activation chamber in the synthesis of nanoporous Nickel-Platinum (NiPt) catalysts. By providing a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment under a reducing atmosphere (typically Hydrogen/Argon), the furnace performs the dual function of cleaning the catalyst surface and finalizing its internal atomic structure.
Core Takeaway The tube annealing furnace transforms raw, synthesized nanoparticles into high-performance catalysts. It achieves this by stripping away residual organic impurities and inducing necessary atomic rearrangement, ensuring the catalyst is both chemically active and structurally stable.
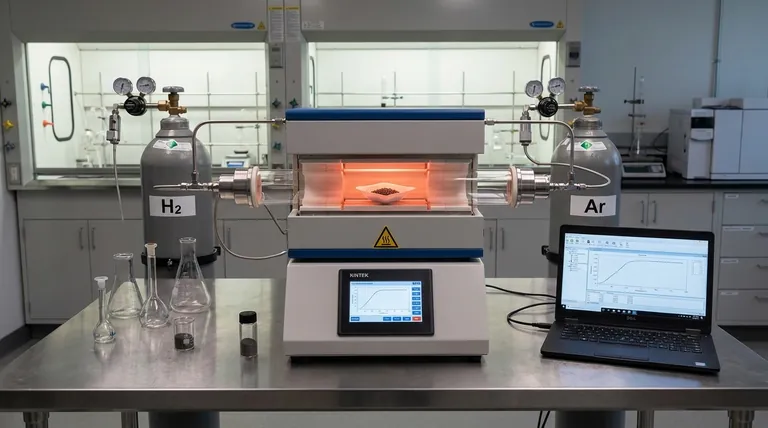

The Mechanism of Catalyst Activation
The preparation of NiPt catalysts does not end with chemical synthesis; the material must be "cured" to function correctly. The tube furnace facilitates two physical processes that are essential for performance.
Surface Purification
During the initial chemical synthesis of nanoparticles, organic ligands are often used as stabilizing agents. While necessary for formation, these ligands coat the surface of the particles.
If left in place, these organics block the active sites where catalytic reactions occur. The tube furnace uses high heat to thermally decompose and remove these residual organic ligands, exposing the reactive metal surface.
Atomic Rearrangement
Raw nanoparticles often possess an unsettled or randomized atomic structure. The thermal energy provided by the furnace induces atomic rearrangement within the NiPt alloy.
This process optimizes the crystal structure. It settles the Nickel and Platinum atoms into a more thermodynamic equilibrium, which significantly enhances the material's chemical stability and longevity during actual operation.
Operational Control Factors
To achieve the desired nanoporous structure, the furnace must offer more than just heat; it must offer precision.
Controlled Reducing Atmosphere
The furnace chamber allows for the introduction of specific gases, most notably a mixture of Hydrogen and Argon (H2/Ar).
This reducing atmosphere prevents the metals from oxidizing (rusting) at high temperatures. Furthermore, it facilitates the reduction of any metal precursors that haven't fully metallized, ensuring the final product is composed of active metal nanoparticles rather than inactive oxides.
Thermal Precision
The furnace allows for programmed annealing. This involves accurately managing the heating rate and the dwelling time (how long it stays at the target temperature).
Precise thermal control ensures that the removal of surface groups and the adjustment of chemical properties occur physically without collapsing the delicate pore structure of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While annealing is necessary, it introduces specific risks that must be balanced.
Sintering vs. Activation
The most critical trade-off in furnace operation is temperature selection. Higher temperatures are excellent for removing ligands and solidifying the crystal structure.
However, excessive heat leads to sintering, where small nanoparticles clump together to form larger masses. This drastically reduces the surface area and, consequently, the catalytic activity.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The reducing atmosphere must be perfectly balanced. An insufficient flow of reducing gas may leave behind unreduced precursors or allow oxidation. Conversely, overly aggressive reduction conditions at high temperatures can alter the surface faceting of the metal unexpectedly, changing how it interacts with reactants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a tube annealing furnace for NiPt catalyst preparation, your parameters should shift based on your specific performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Activity: Prioritize a lower temperature range that is just sufficient to remove organic ligands, preserving the smallest possible particle size and highest surface area.
- If your primary focus is Long-term Stability: Utilize a slightly higher annealing temperature to encourage a more complete atomic rearrangement and alloying, creating a robust crystal structure that resists degradation over time.
Ultimately, the tube furnace acts as the final quality control step, determining whether your synthesized material behaves as a loose collection of atoms or a unified, high-performance catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Function of Tube Furnace | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Purification | Thermal decomposition of organic ligands | Exposes active sites for catalytic reactions |
| Atomic Rearrangement | Induced thermal equilibrium of NiPt alloy | Enhances chemical stability and structural longevity |
| Atmosphere Control | Hydrogen/Argon (H2/Ar) reducing environment | Prevents metal oxidation and ensures full metallization |
| Thermal Precision | Programmed heating rates and dwelling times | Preserves delicate nanoporous structures while activating |
| Quality Tuning | Controlled temperature & sintering management | Balances maximum surface activity with long-term stability |
Maximize Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal processing is the difference between raw materials and high-performance catalysts. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the rigorous demands of nanomaterial synthesis. Whether you are targeting maximum surface activity or long-term structural stability, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ready to optimize your annealing process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Yawei Li, Joshua Snyder. Unveiling the Origin of Morphological Instability in Topologically Complex Electrocatalytic Nanostructures. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c07842
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the use of a tube furnace for nitrogen-protected annealing affect tin oxide catalysts? Unlock Superior Activity
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab Needs
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What core functions does a tube high-temperature furnace perform? Mastering In-situ Carbothermal Reduction
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise, Controlled Thermal Processing
- How can the purity of the atmosphere inside a vacuum tube experimental furnace be increased? Master Vacuum Purging for Pristine Results
- How does a laboratory horizontal tube furnace contribute to TiO2@C synthesis? Master Thermal Treatment Stages
- What is the mechanism of the drive-in process in a tube furnace? Master Dopant Redistribution with Nitrogen Shielding



















