In essence, a tube furnace excels by providing a highly controlled and isolated environment for thermal processing. Its primary advantages are precise temperature uniformity, superior control over the internal atmosphere (from vacuum to specific gases), and an operational simplicity that makes it a versatile tool for both research and specialized production.
The core value of a tube furnace is not merely its ability to generate heat, but its capacity to create a contained, uniform, and atmospherically controlled environment. This makes it indispensable for processes where sample purity and reaction conditions are paramount.
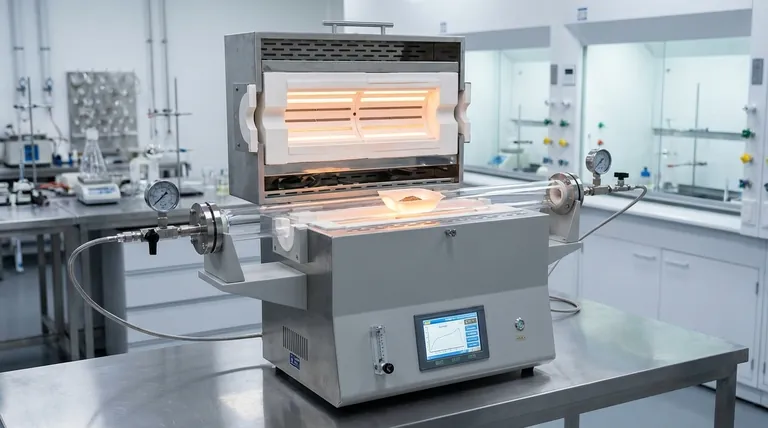

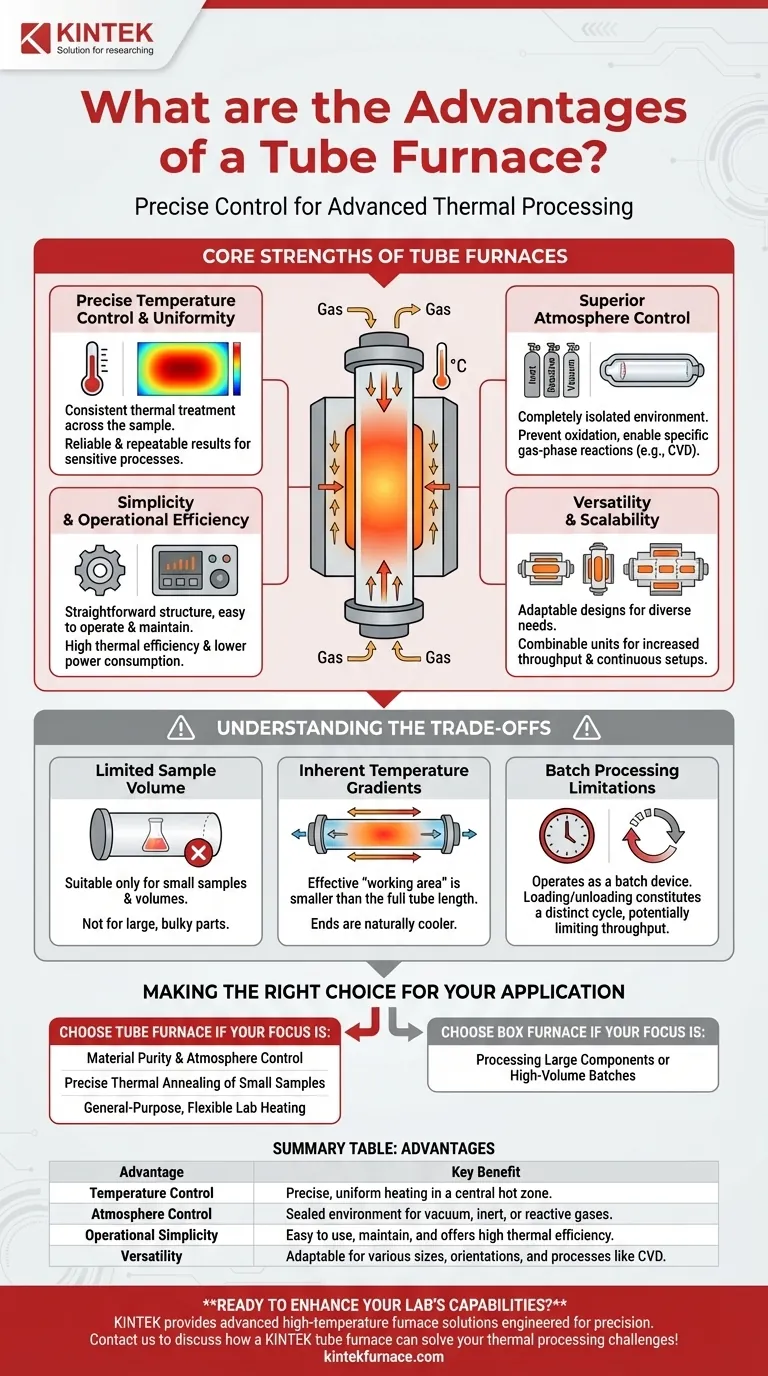
The Core Strengths of Tube Furnaces
A tube furnace is chosen for its unique combination of precision, control, and efficiency. Understanding these strengths is key to leveraging it correctly.
Precise Temperature Control and Uniformity
The cylindrical design naturally promotes a uniform temperature zone in the center of the tube. This is critical for processes that demand consistent thermal treatment across the entire sample.
Modern tube furnaces offer exceptional temperature accuracy, ensuring that experimental or production results are reliable and repeatable. This precision is essential for developing and validating sensitive processes.
Superior Atmosphere Control
Perhaps its most significant advantage is the ability to completely control the atmosphere surrounding the sample. The sealed tube can be evacuated to create a vacuum or filled with specific inert or reactive gases.
This capability is vital for preventing oxidation of sensitive materials or for facilitating chemical reactions, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), that require a specific gaseous environment.
Simplicity and Operational Efficiency
Tube furnaces are designed with a straightforward structure. They are relatively easy to operate, control, and maintain, which lowers the barrier to entry for complex thermal processes.
This simplicity, combined with their high thermal efficiency and lower power consumption compared to larger furnaces, makes them a cost-effective choice for many laboratories and production lines.
Versatility and Scalability
The basic design is highly adaptable. Tube furnaces come in various sizes, orientations (horizontal or vertical), and configurations (single-zone or multi-zone) to meet diverse application needs.
For larger-scale needs, the principle allows for continuous production setups in certain industries. Multiple furnaces can also be combined to increase throughput while maintaining the benefits of individual process control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a tube furnace is not universally superior. Its focused design comes with inherent limitations.
Limited Sample Volume
The defining characteristic—the tube—is also its main constraint. By design, a tube furnace can only accommodate small sample sizes and volumes compared to a box furnace of similar power.
This makes it unsuitable for applications requiring the thermal processing of large, bulky parts or high-volume batches in a single run.
Inherent Temperature Gradients
While the central zone is highly uniform, the ends of the tube are naturally cooler. This temperature gradient is unavoidable and means the effective "working area" is smaller than the full length of the tube.
For processes that require a very long, uniform hot zone, a more expensive multi-zone furnace or a different type of heating system may be necessary.
Batch Processing Limitations
For most laboratory applications, a tube furnace operates as a batch-processing device. Loading, processing, and unloading constitute a distinct cycle, which can limit overall throughput.
While some industrial applications are configured for continuous flow, this is a specialized setup and not a standard feature of most general-purpose lab furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right thermal equipment depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is material purity and atmosphere control: The tube furnace is the ideal choice for preventing contamination and enabling gas-phase reactions.
- If your primary focus is precise thermal annealing of small samples: Its excellent temperature uniformity in the central zone ensures consistent and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is processing large components or high-volume batches: A box furnace is almost certainly a more practical and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, flexible lab heating: The versatility and lower cost of a tube furnace make it a foundational piece of equipment for many research needs.
Ultimately, choosing a tube furnace is a decision to prioritize environmental control and thermal precision for small-scale applications.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Precise, uniform heating in a central hot zone. |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed environment for vacuum, inert, or reactive gases. |
| Operational Simplicity | Easy to use, maintain, and offers high thermal efficiency. |
| Versatility | Adaptable for various sizes, orientations, and processes like CVD. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a high-performance tube furnace?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our tube furnaces are engineered for precision and reliability, and our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you need a standard model or a fully customized system, our product line—including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed to deliver superior results.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK tube furnace can solve your thermal processing challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















