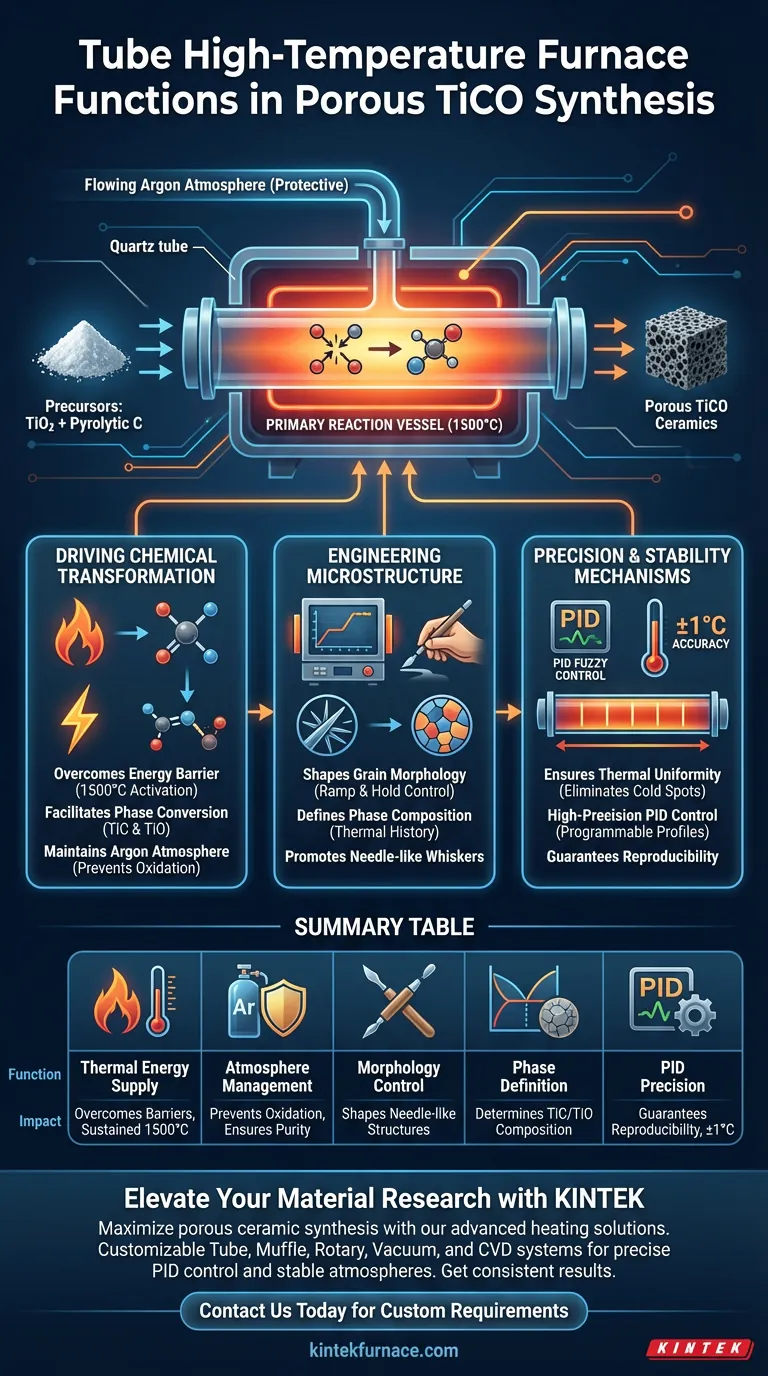
A tube high-temperature furnace functions as the primary reaction vessel for synthesizing porous TiCO ceramics, orchestrating the critical thermodynamic conditions required for in-situ carbothermal reduction. It supplies the necessary 1500°C thermal environment to drive the reaction between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and pyrolytic carbon, while simultaneously maintaining a flowing argon atmosphere to protect the material during synthesis.
The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a morphological tool. By precisely manipulating heating rates and holding times, it directly controls the transformation of raw precursors into specific grain structures, such as needle-like whiskers, and determines the final phase composition of the ceramic.

Driving the Chemical Transformation
Supplying Essential Thermal Energy
The primary function of the furnace is to overcome the energy barrier for the carbothermal reduction reaction.
It generates and sustains a 1500°C environment, which is the threshold required to activate the chemical interaction between TiO2 and pyrolytic carbon.
Facilitating Phase Conversion
Under this intense heat, the furnace enables the conversion of precursors into the desired products.
Specifically, it facilitates the generation of Titanium Carbide (TiC) and Titanium Monoxide (TiO), forming the fundamental structure of the porous ceramic.
Maintaining a Protective Atmosphere
To prevent oxidation or unwanted side reactions, the furnace manages the environmental context of the synthesis.
It houses the reaction within a flowing argon protective atmosphere, ensuring the purity of the chemical reduction process.
Engineering Microstructure through Thermal Control
Shaping Grain Morphology
The furnace acts as a sculptor for the material's microstructure by strictly regulating the thermal profile.
By accurately controlling the heating rate and the specific holding time, the furnace influences how grains grow, specifically promoting the formation of needle-like whiskers.
Defining Phase Composition
The final makeup of the product is dictated by the thermal history provided by the furnace.
The precise duration and intensity of the heat treatment determine the ratios and stability of the final ceramic phases, ensuring the material meets specific property requirements.
Precision and Stability Mechanisms
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
Consistent material properties depend on the furnace's ability to eliminate cold spots.
The design ensures uniform thermal distribution along the length of the tube, reducing temperature gradients that could otherwise compromise the integrity of the experimental results.
High-Precision PID Control
To achieve complex morphologies, the furnace utilizes advanced control systems capable of maintaining temperatures within ±1°C.
This PID self-learning fuzzy control system allows for programmable heating profiles, including complex ramp rates and soak times, ensuring high reproducibility across experiments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Programmed Profiles
While the furnace provides high heat, "blasting" the material with thermal energy is insufficient and potentially detrimental.
Failure to utilize the programmable features—such as specific ramp rates and cooling curves—will result in uncontrolled grain growth and a failure to form the desired needle-like structures.
The Sensitivity of Reproducibility
The quality of the final ceramic is inextricably linked to the stability of the furnace's control system.
Even minor deviations in the heating profile or argon flow can significantly alter the phase composition, making reliance on the machine's stability and PID precision critical for consistent output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of a tube high-temperature furnace in TiCO synthesis, align your process controls with your specific material objectives.
- If your primary focus is Grain Morphology (Whiskers): Prioritize the programming of precise heating rates and holding times to direct specific grain growth patterns.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the furnace maintains a consistent 1500°C soak temperature and a strictly controlled flowing argon atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is Experimental Consistency: Utilize the advanced PID control features to standardize complex heating curves across multiple batches.
Mastering the thermal profile is the key to unlocking the structural potential of porous TiCO ceramics.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Function | Impact on TiCO Synthesis | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Energy Supply | Overcomes carbothermal reduction energy barriers | Sustained 1500°C heat |
| Atmosphere Management | Prevents oxidation and ensures chemical purity | Flowing Argon protection |
| Morphology Control | Shapes needle-like whisker structures | Precise heating/holding times |
| Phase Definition | Determines final ceramic composition (TiC/TiO) | Thermal profile & soak duration |
| PID Precision | Guarantees experimental reproducibility | ±1°C accuracy fuzzy control |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Maximize the potential of your porous ceramic synthesis with KINTEK’s advanced heating solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you require precise PID control for grain morphology or a stable protective atmosphere for phase purity, our lab high-temperature furnaces deliver the reliability your research demands.
Ready to optimize your TiCO production? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Xiaoyu Cao, Lei Feng. Microstructure, Mechanical Property and Thermal Conductivity of Porous TiCO Ceramic Fabricated by In Situ Carbothermal Reduction of Phenolic Resin and Titania. DOI: 10.3390/nano14060515
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key components of a tubular furnace? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- Why are high-temperature tube furnaces essential for perovskite catalysts? Precision Shaping & Crystallization
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the accuracy of microplastic thermal decomposition? Ensure Pyrolysis Precision
- How do laboratory-scale Tube Furnaces facilitate coal gasification? Precise Simulation for Industrial Success
- What is the role of a tube furnace during fuel cell feasibility studies? Optimize Your Thermal Control
- Why is tube furnace temperature control critical for anhydrous rare earth halide powders? Achieve Precise Synthesis
- How does a single-zone tube furnace facilitate the growth of Cu2Se thin films via CVD? Precision Thermal Control Guide
- Why are a split furnace and a PID temperature controller core in supercritical water gasification? Essential Guide



















