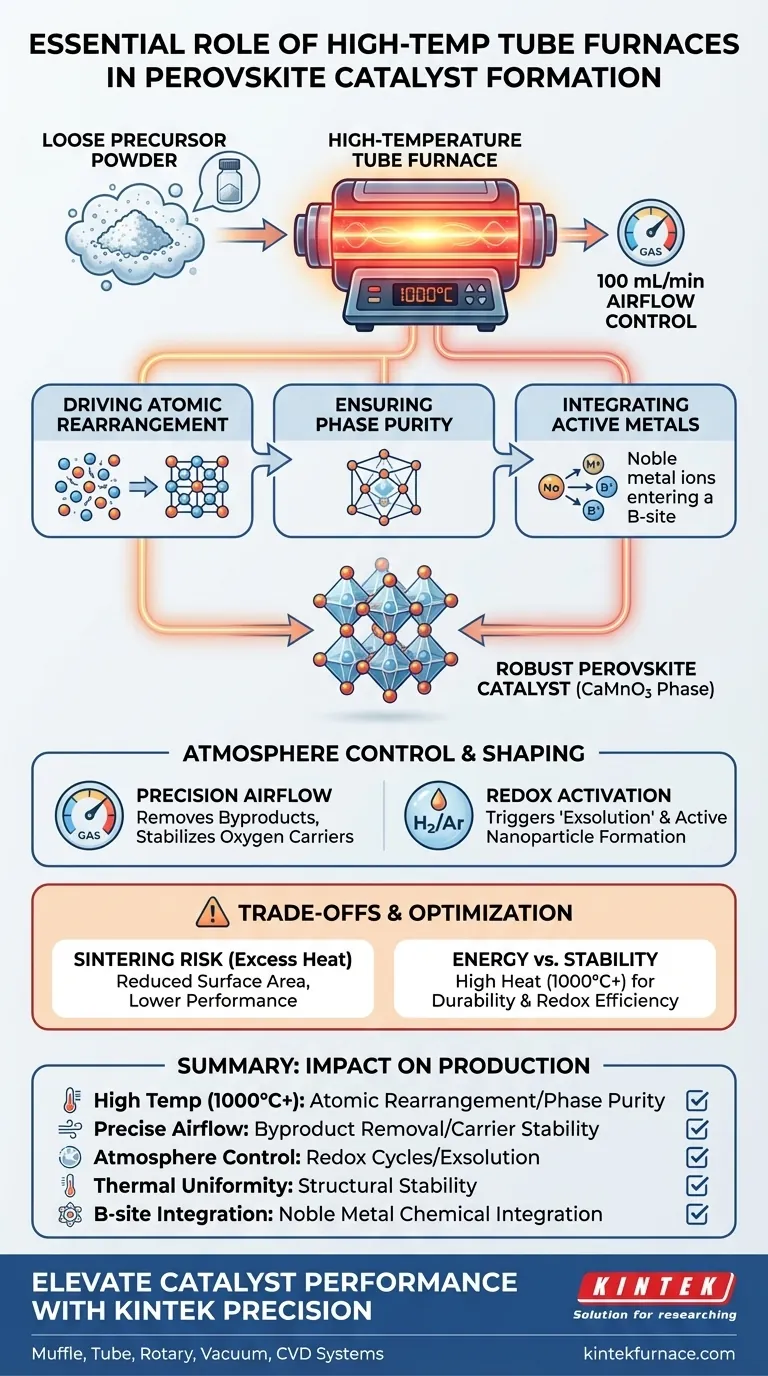
High-temperature tube furnaces are the critical mechanism required to transform loose precursor powders into robust, high-performance perovskite catalysts. They provide a sustained 1000°C environment combined with precise airflow control (e.g., 100 mL/min) to drive the atomic rearrangement necessary for forming the CaMnO3 perovskite phase. This process finalizes the crystal structure, ensuring the high crystallinity needed for structural stability and efficient lattice oxygen release.
Core Takeaway While low-temperature ovens remove solvents and muffle furnaces create porosity, the high-temperature tube furnace is the "finishing tool" that cements the catalyst's quality. It supplies the intense thermal energy required to lock atoms into their final lattice positions, directly determining the catalyst's durability and redox efficiency.

The Mechanics of Crystal Formation
Driving Atomic Rearrangement
The primary function of the tube furnace is to provide the activation energy required for lattice organization. At ultra-high temperatures (typically around 1000°C), the furnace promotes the rearrangement of lattice atoms. This movement is essential for converting disordered precursors into a highly ordered, crystalline perovskite structure.
Ensuring Phase Purity
Achieving the specific CaMnO3 perovskite phase requires more than just heat; it requires heat applied uniformly over time. The tube furnace maintains a constant thermal environment that facilitates atomic diffusion. This diffusion allows the material to achieve the correct crystallographic geometry (such as a stable rhombohedral structure) and eliminates organic residues that might interfere with phase purity.
Integrating Active Metals
For complex catalysts, the final heating stage is where chemical integration occurs. The thermal energy allows noble metal ions (like Pd, Rh, or Ru) to successfully integrate into the B-sites of the crystal lattice. This precise integration is what "shapes" the chemical potential of the catalyst, enabling specific reactions like hydrogen evolution or oxidation.
The Role of Atmosphere Control
Precision Airflow
Unlike standard muffle furnaces, tube furnaces allow for the strict regulation of gas flow. By maintaining a specific flow rate (e.g., 100 mL per minute), the furnace ensures the consistent removal of reaction byproducts. This controlled flow is vital for stabilizing the oxygen carrier capabilities of the material.
Enabling Redox Activation
Tube furnaces can support specialized atmospheres, such as reducing environments (H2/Ar), which are crucial for certain shaping mechanisms. For example, high-temperature redox cycles in these furnaces can trigger "exsolution," where metal cations migrate from inside the lattice to the surface to form active nanometer-sized particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Sintering
While high heat promotes crystallization, excessive heat or uncontrolled duration can lead to agglomeration. If grains fuse together (sinter) too much, the active surface area decreases, potentially lowering catalytic performance. Precise temperature regulation is the only defense against this.
Energy vs. Stability
Operating at 1000°C or higher (some furnaces reach 1900°C) is energy-intensive. However, attempting to crystallize perovskites at lower temperatures often results in a "loose" structure with poor lattice oxygen release capability, rendering the catalyst unstable during actual operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of your perovskite catalysts, align your furnace parameters with your specific structural requirements:
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Prioritize temperatures around 1000°C to maximize crystallinity, which ensures the lattice can withstand repeated expansion and contraction during redox cycles.
- If your primary focus is Doping Efficacy: Focus on the duration of the heat treatment to allow sufficient time for atomic diffusion and the integration of noble metals into the B-site of the lattice.
- If your primary focus is Surface Activation: Utilize the tube furnace's atmospheric control to run redox cycles (e.g., at 1073 K) to trigger exsolution and precipitate active metal nanoparticles onto the support surface.
The high-temperature tube furnace is not merely a heating device; it is a precision instrument that dictates the ultimate geometry and longevity of your catalyst's crystal lattice.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Perovskite Catalyst Production |
|---|---|
| High Temp (1000°C+) | Provides activation energy for atomic rearrangement and phase purity. |
| Precise Airflow | Ensures consistent removal of byproducts and stabilizes oxygen carriers. |
| Atmosphere Control | Supports redox cycles and exsolution of active metal nanoparticles. |
| Thermal Uniformity | Prevents disordered structures and ensures long-term structural stability. |
| B-site Integration | Facilitates the chemical integration of noble metals into the crystal lattice. |
Elevate Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the structural stability and redox efficiency of your perovskite materials with KINTEK’s high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production needs.
Whether you require 1000°C stability for lattice oxygen release or precise atmosphere control for metal exsolution, KINTEK provides the reliability your lab demands. Contact us today to find your perfect high-temperature furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Shaowei Yao, Tengwei Chen. Tandem catalysis of zeolite and perovskite for light olefins production in dehydrogenation cracking of naphtha. DOI: 10.1039/d5ra02427g
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in cigarette waste pyrolysis? Optimize Carbon Material Conversion
- What is a drop tube furnace and what is its primary purpose? Master Rapid Thermal Processing for Particle Studies
- How are tube furnaces utilized in environmental testing? Key Applications for Analysis and Remediation
- What is the necessity of using sealed silica tubes in the BCM reduction method? Ensuring High-Purity Synthesis
- What physical conditions does a dual-zone tube furnace provide for CVT? Master Precision Thermal Gradient Control
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate Fe-Nx-C electrocatalyst formation? Expert Synthesis Insights
- What are the advantages of using a high-temperature tube furnace for rGO sensor fabrication? Precision & Performance
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for AlPO4 calcination? Ensure Safety in Molten Salt Electrolysis



















