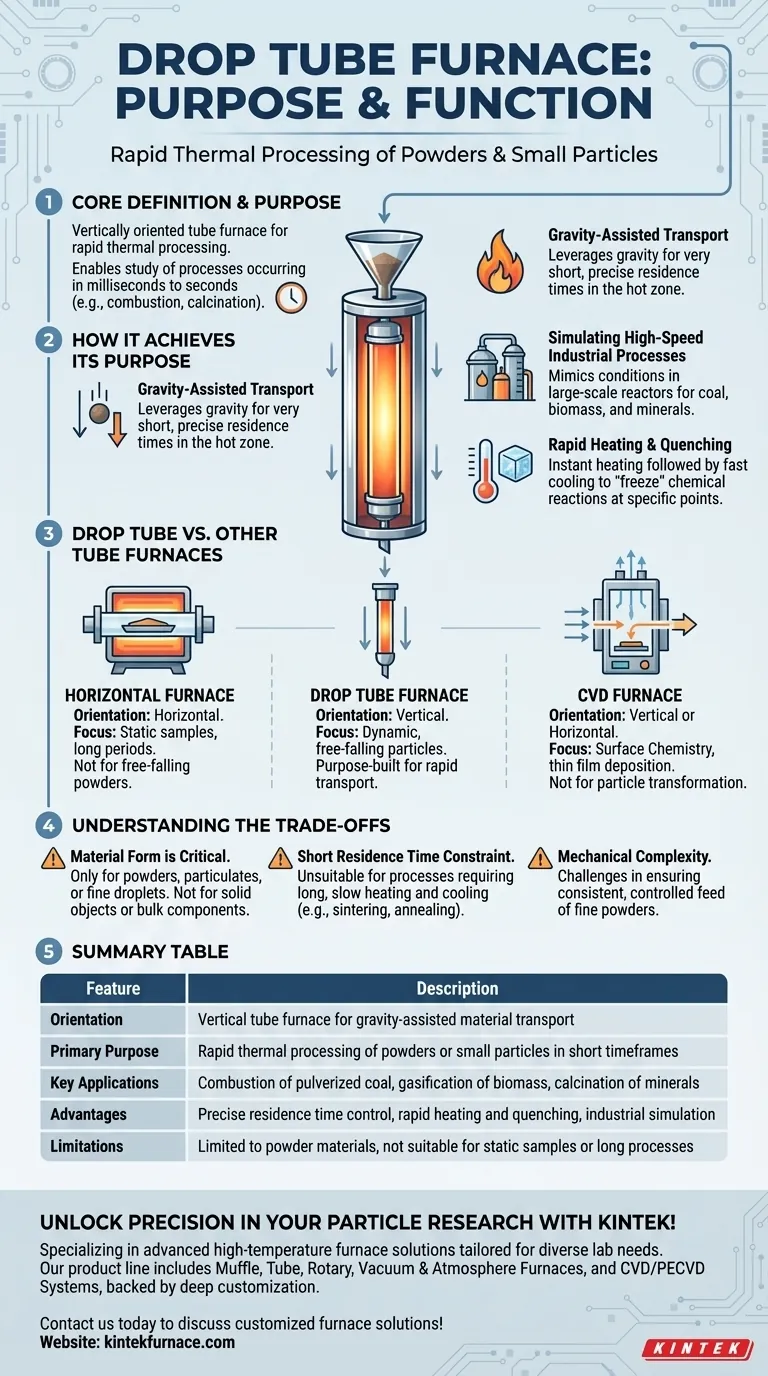
At its core, a drop tube furnace is a vertically oriented tube furnace specifically designed for the rapid thermal processing of materials, typically powders or small particles. Its primary purpose is to allow materials to be dropped through a precisely controlled high-temperature zone, enabling the study of processes that occur in very short timeframes, such as combustion or rapid calcination.
A drop tube furnace is not just a furnace turned on its side. Its vertical design is the key to its function, using gravity to precisely control the brief time a material spends at high temperature, making it an essential tool for simulating and studying rapid, particle-based industrial processes.

How a Drop Tube Furnace Achieves Its Purpose
The unique design of a drop tube furnace is entirely driven by its specialized application. Unlike standard furnaces designed for static samples, every component is optimized for materials in free-fall.
The Principle of Gravity-Assisted Transport
The vertical orientation is the most significant feature. It leverages gravity to move material through the heating zone.
This allows for very short and highly reproducible residence times—the duration the particle is exposed to the high temperature—often on the order of seconds or even milliseconds.
Simulating High-Speed Industrial Processes
This capability is critical for accurately simulating conditions found in large-scale industrial reactors or combustion chambers.
Researchers use drop tube furnaces to study the behavior of individual particles under realistic conditions, such as the combustion of pulverized coal, the gasification of biomass, or the calcination of minerals.
Achieving Rapid Heating and Quenching
A particle entering the hot zone heats up almost instantly. After passing through the tube, it falls into a collection probe that is often cooled.
This rapid heating and subsequent quenching (fast cooling) "freezes" the chemical reaction at a specific point, allowing researchers to analyze the intermediate products and understand the reaction mechanism step-by-step.
Drop Tube vs. Other Tube Furnaces
While it shares components with other furnaces, the drop tube's purpose is distinct. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right tool for a given task.
The Role of Orientation: Vertical vs. Horizontal
Most standard lab furnaces are horizontal. They are ideal for processing static samples, such as substrates, wafers, or material batches held in a crucible, for extended periods.
The drop tube furnace's vertical design is purpose-built for dynamic experiments on free-falling powders and is generally unsuitable for processing static, bulk materials.
Process Focus: Material Transport vs. Chemical Deposition
A Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnace is defined by its process: depositing a thin film onto a substrate from gaseous precursors. While it can be vertical or horizontal, its primary function is surface chemistry.
A drop tube furnace, in contrast, is defined by its physical transport mechanism (dropping). Its focus is on the transformation of the particle itself as it passes through the hot zone, not on coating a surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The specialized nature of a drop tube furnace brings inherent limitations that make it unsuitable for general-purpose use.
Material Form is Critical
This method works almost exclusively with materials that can be fed and dropped as powders, particulates, or fine droplets.
It cannot be used for heat-treating solid objects, wafers, or large bulk components that cannot pass through the tube.
Short Residence Time is a Constraint
The rapid transit time is an advantage for studying fast reactions. However, it is a significant disadvantage for processes requiring long, slow heating and cooling cycles, such as sintering or annealing.
Mechanical Complexity
Ensuring a consistent and controlled feed rate of fine powder into the top of the furnace can be technically challenging. The feeding system is a critical component that requires careful calibration and operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace is a matter of matching the tool to the scientific question you are asking.
- If your primary focus is studying rapid reactions in free-falling particles (like combustion or pyrolysis): The drop tube furnace is the only tool specifically designed to simulate these conditions at a lab scale.
- If your primary focus is creating high-quality thin films on a static substrate: A dedicated CVD furnace provides the necessary control over gas flow and surface chemistry.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment, annealing, or sintering of solid samples: A standard horizontal tube furnace offers the simplicity and long processing times required for these tasks.
Ultimately, choosing a furnace requires a clear understanding of your material's form and the specific thermal process you need to execute.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Orientation | Vertical tube furnace for gravity-assisted material transport |
| Primary Purpose | Rapid thermal processing of powders or small particles in short timeframes |
| Key Applications | Combustion of pulverized coal, gasification of biomass, calcination of minerals |
| Advantages | Precise residence time control, rapid heating and quenching, simulation of industrial processes |
| Limitations | Limited to powder materials, not suitable for static samples or long processes |
Unlock Precision in Your Particle Research with KINTEK!
Are you working on rapid thermal processes like combustion or gasification and need reliable, high-performance equipment? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're studying particle behavior or optimizing industrial simulations, we can help you achieve accurate and efficient results.
Contact us today to discuss how our customized furnace solutions can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?



















