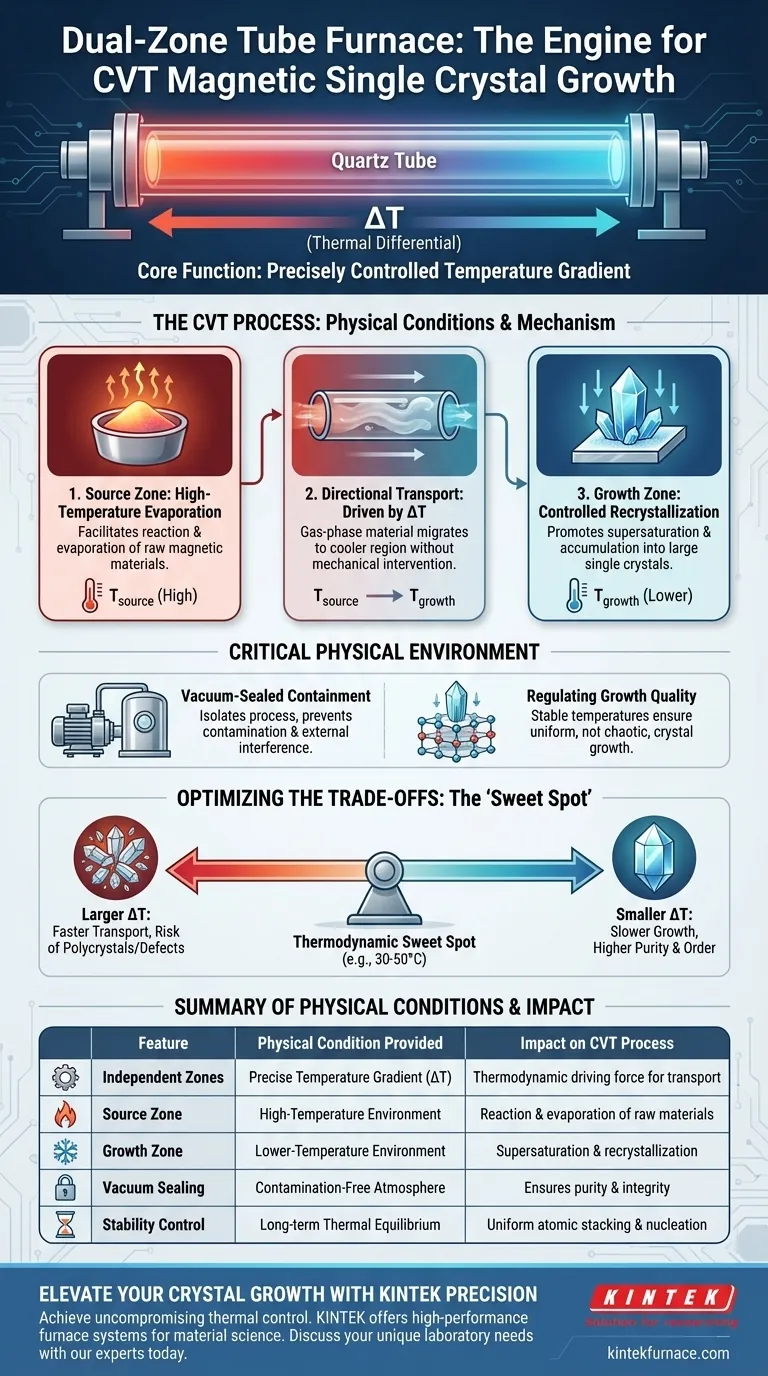
A dual-zone tube furnace primarily provides a precisely controlled temperature gradient within a vacuum-sealed environment. By utilizing independent temperature control systems, the furnace establishes a distinct high-temperature "source zone" and a lower-temperature "growth zone." This thermal difference acts as the necessary thermodynamic driving force to transport raw materials through the gas phase, allowing them to recrystallize into high-quality magnetic single crystals.
The core function of a dual-zone furnace is not merely heating, but the engineering of a specific thermal differential. This gradient is the engine that drives evaporation at one end and controlled crystallization at the other, determining the size and quality of the final magnetic crystal.

The Mechanism of Temperature Control
Independent Heating Zones
The defining feature of this equipment is the ability to control two distinct heating areas independently.
You are not limited to a single ambient temperature; you can set a specific high temperature for the raw material and a specific lower temperature for the collection area.
Establishing the Driving Force
This temperature difference creates the physical conditions required for Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT).
The heat in the source zone causes the raw magnetic materials to react and evaporate into a gaseous state.
Directional Transport
Once in the gas phase, the material naturally migrates toward the cooler region due to the thermal gradient.
This ensures a continuous, unidirectional flow of material from the source to the growth zone without mechanical intervention.
The Physical Environment for Crystallization
Vacuum-Sealed Containment
The entire process occurs within a vacuum-sealed quartz tube.
This isolation prevents contamination and ensures that the vapor transport is governed strictly by the internal temperature gradient, not external atmospheric variables.
Controlled Recrystallization
When the gas-phase material reaches the lower-temperature growth zone, it becomes supersaturated.
This forces the material to precipitate and recrystallize, accumulating slowly to form large-sized magnetic single crystals, such as CrSBr.
Regulating Growth Quality
The precision of the "dual-zone" setup allows you to fine-tune the rate of this precipitation.
By stabilizing the temperatures, you ensure the crystals grow uniformly rather than chaotically, which is essential for maintaining magnetic properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gradient Magnitude
A larger temperature difference (${\Delta}T$) increases the transport rate, potentially speeding up production.
However, if the gradient is too steep, the transport rate may become too fast, leading to polycrystals or structural defects rather than a single, high-quality crystal.
The Challenge of Optimization
Finding the correct temperatures for specific magnetic materials requires trial and error.
While the furnace provides the conditions for control, the user must precisely determine the thermodynamic sweet spot—often a narrow window (e.g., a difference of 30°C to 50°C)—to avoid stalling the transport or crashing the material out too quickly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a dual-zone tube furnace for your specific magnetic crystal project, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Crystal Purity: Minimize the temperature difference to slow down the transport rate, allowing for ordered atomic stacking and fewer defects.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Size: Ensure the "growth zone" temperature is stable over long periods (often weeks) to allow the crystal to nucleate and expand without thermal fluctuations.
Precision in the thermal gradient is the single most important factor in translating raw powder into a functional magnetic single crystal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Condition Provided | Impact on CVT Process |
|---|---|---|
| Independent Zones | Precise Temperature Gradient ($\Delta$T) | Acts as the thermodynamic driving force for material transport. |
| Source Zone | High-Temperature Environment | Facilitates reaction and evaporation of raw magnetic materials. |
| Growth Zone | Lower-Temperature Environment | Promotes supersaturation and controlled recrystallization. |
| Vacuum Sealing | Contamination-Free Atmosphere | Ensures purity and prevents external atmospheric interference. |
| Stability Control | Long-term Thermal Equilibrium | Allows for uniform atomic stacking and large crystal nucleation. |
Elevate Your Crystal Growth with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect magnetic single crystal requires more than just heat—it requires uncompromising thermal control. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science.
Whether you need a specialized dual-zone setup for CVT or a custom high-temperature solution, our furnaces provide the stability and precision your research deserves.
Ready to optimize your thermal gradients? Contact our experts today to discuss your unique laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Chi Pang, Libo Ma. Optical Whispering‐Gallery Mode as a Fingerprint of Magnetic Ordering in Van der Waals Layered CrSBr. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202505275
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature quartz tube reactor facilitate the synthesis of PC-CNT microspheres? Expert Insights
- What metallurgical processes benefit from tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment and Material Control
- Why is an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace required for NC substrate preparation? Essential for carbonization.
- How is a tube furnace utilized to construct DTB sites for Co/Co0.85Se@NC? Mastering Phase Engineering
- What essential experimental conditions does a laboratory horizontal tube furnace provide for wood chip pyrolysis?
- What is the primary function of introducing high-purity argon into the tube furnace? Expert Pyrolysis Solutions
- How are tubular furnaces utilized in semiconductor manufacturing? Precision Thermal Processing for High-Yield ICs
- What is the importance of segmented temperature control in a tube furnace for Cu/Zn-SAN? Master Atomic Dispersion



















