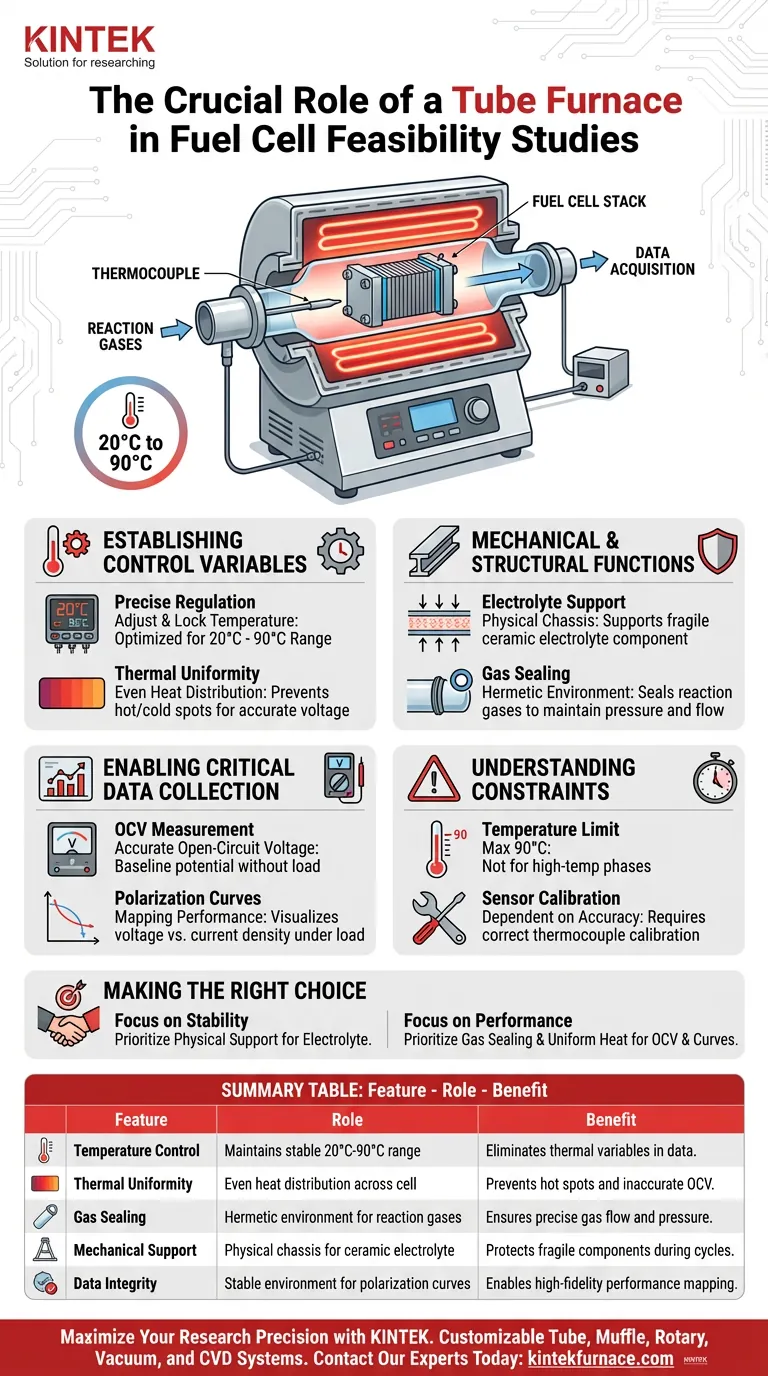
The primary role of a tube furnace or specialized heating fixture in fuel cell feasibility studies is to establish a strictly controlled thermal and mechanical environment. By utilizing heating elements and thermocouples, this equipment maintains a stable temperature range—specifically between 20°C and 90°C—while physically supporting the cell's ceramic electrolyte and sealing essential reaction gases.
The core value of this equipment lies in variable isolation: by ensuring uniform temperature and gas sealing, it allows for the accurate measurement of Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV) and polarization curves, ensuring data reflects true cell performance rather than environmental inconsistencies.
Establishing Control Variables
To determine if a fuel cell design is feasible, you must eliminate external variables that could skew performance data. The tube furnace serves as the baseline control mechanism.
Precise Temperature Regulation
The fixture allows researchers to adjust and lock in specific operating temperatures. According to your reference specifications, this equipment is optimized for a range of 20°C to 90°C.
Achieving Thermal Uniformity
It is not enough to simply heat the environment; the heat must be evenly distributed. The fixture ensures uniform temperature distribution across the entire cell, preventing hot spots or cold zones that could lead to inaccurate voltage readings.
Mechanical and Structural Functions
Beyond temperature, the fixture acts as the physical chassis for the test subject during the study.
Supporting the Electrolyte
The fixture provides the necessary mechanical support for the fuel cell's core component, specifically the ceramic electrolyte. This ensures the fragile components remain stable during the testing process.
Sealing Reaction Gases
Feasibility studies rely on precise gas flow rates. The fixture creates a hermetic environment that seals reaction gases within the cell, preventing leaks that would lower pressure and artificially degrade performance metrics.
Enabling Critical Data Collection
The ultimate goal of the heating fixture is to facilitate the capture of high-fidelity data.
Measuring Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV)
By maintaining a stable environment, the fixture allows researchers to accurately measure OCV. This is the baseline voltage of the fuel cell when no current is flowing, a critical indicator of the cell's theoretical potential.
Generating Polarization Curves
The controlled environment is essential for mapping polarization curves. These curves show the relationship between voltage and current density, visualizing how well the fuel cell performs under actual load conditions.
Understanding the Constraints
While these fixtures are vital, it is important to recognize their operational boundaries to interpret your data correctly.
Temperature Range Limitations
The specific fixture described is limited to a maximum of 90°C. It is not suitable for high-temperature testing phases that might exceed this threshold, limiting its use to low-to-medium temperature feasibility windows.
Dependence on Sensor Calibration
The accuracy of the "stable environment" is entirely dependent on the embedded thermocouples. If these sensors are not calibrated correctly, the feedback loop will fail, and the temperature uniformity described above will be compromised.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When incorporating a tube furnace or heating fixture into your study, align its capabilities with your specific testing objectives.
- If your primary focus is component stability: Ensure the fixture provides adequate physical support for the ceramic electrolyte to prevent mechanical failure during heating cycles.
- If your primary focus is electrochemical performance: Prioritize the fixture's ability to seal reaction gases and maintain uniform heat to guarantee accurate OCV and polarization curve data.
By strictly controlling the thermal and mechanical variables, you transform a theoretical fuel cell concept into a measurable, verifiable reality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Feasibility Study | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Maintains stable 20°C to 90°C range | Eliminates thermal variables in data |
| Thermal Uniformity | Even heat distribution across cell | Prevents hot spots and inaccurate OCV |
| Gas Sealing | Hermetic environment for reaction gases | Ensures precise gas flow and pressure |
| Mechanical Support | Physical chassis for ceramic electrolyte | Protects fragile components during cycles |
| Data Integrity | Stable environment for polarization curves | Enables high-fidelity performance mapping |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Don't let environmental inconsistencies compromise your fuel cell data. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the unique thermal and mechanical demands of your lab. Whether you need precise temperature uniformity for feasibility studies or high-temp performance testing, our laboratory furnaces provide the reliability you need.
Ready to elevate your testing accuracy? Contact our experts today to find the perfect customized heating solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Peimiao Zou, Shanwen Tao. A fast ceramic mixed OH−/H+ ionic conductor for low temperature fuel cells. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45060-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an industrial monitoring camera necessary for measuring aluminum powder ignition delay in a tube furnace?
- What are the advantages of combining an online mass spectrometer with a fixed-bed reactor? Boost Kinetic Precision
- What features enable precise temperature control in a vertical tube furnace? Unlock Superior Thermal Accuracy for Your Lab
- How does an atmosphere tube furnace work? Master Precise Heat and Gas Control for Your Lab
- What is the future potential of fluidized bed vertical tube furnaces? Unlock Efficiency and Growth in Your Industry
- What are the key components of a drop tube furnace? Discover the 5 Essential Parts for High-Temperature Success
- What critical process conditions does a tube atmosphere furnace provide for Sr2CuWO6? Control Atmosphere & Temperature
- What are the objectives of using a tube furnace for dual-layer nanocomposite heat treatment? Maximize Coating Stability



















