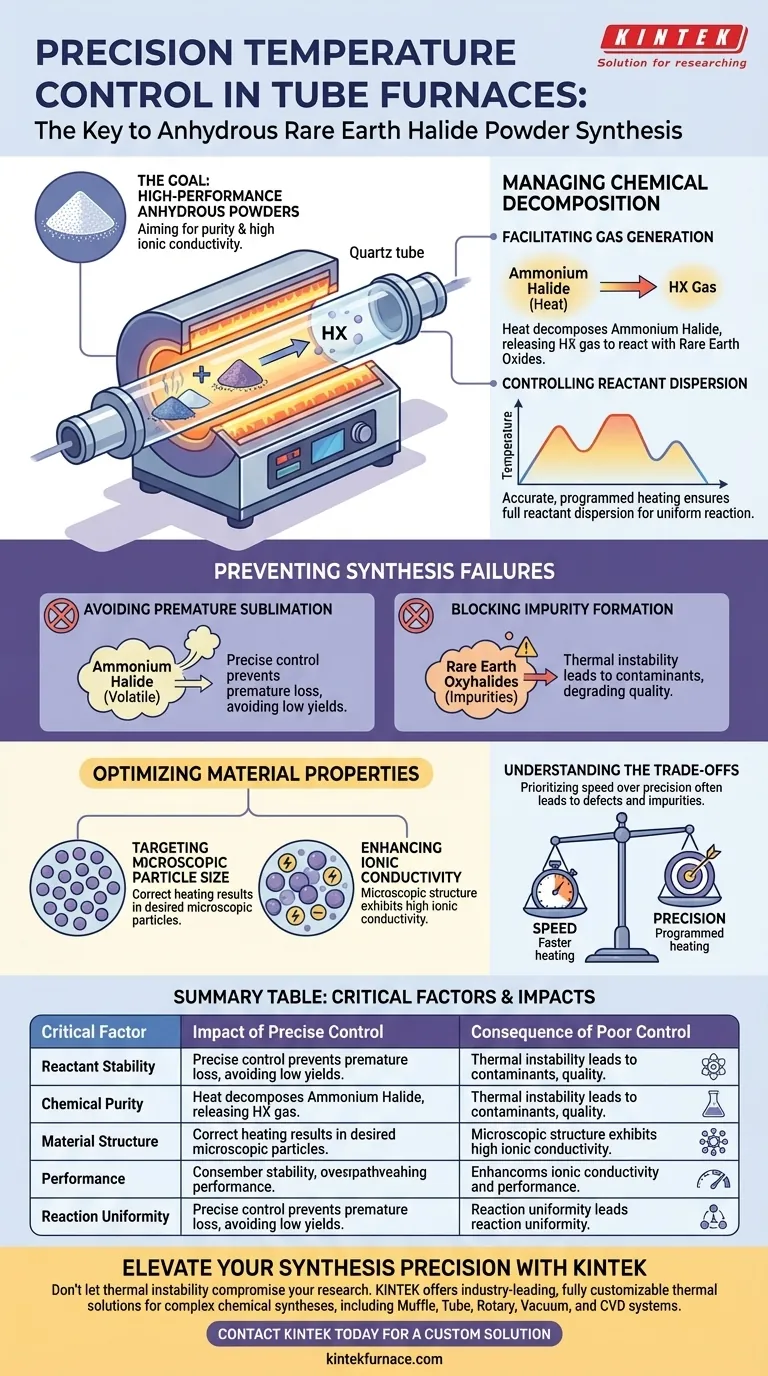
Precision is the dividing line between successful synthesis and wasted material. In the preparation of anhydrous rare earth halide powders, the tube furnace is not merely a heat source, but a critical control mechanism that governs the reaction between decomposing ammonium halide and rare earth oxides. Without exact thermal management, you risk losing reactants to sublimation or contaminating the final product with unwanted chemical byproducts.
Precise thermal regulation prevents the premature loss of reactants and the formation of impurities, ensuring the creation of microscopic particles with high ionic conductivity. It is the essential mechanism for facilitating the correct chemical decomposition and reaction sequence.

Managing the Chemical Decomposition
Facilitating Gas Generation
The primary function of the tube furnace in this context is to drive a specific chemical reaction. The heat causes ammonium halide to decompose.
This decomposition releases HX gas. This gas is the critical agent required to react with the rare earth oxides to form the desired halide powder.
Controlling Reactant Dispersion
You must rely on accurate, programmed heating rather than a static temperature application.
This dynamic thermal profile ensures that the reactants are fully dispersed. Proper dispersion is necessary to ensure the reaction occurs uniformly throughout the material batch.
Preventing Synthesis Failures
Avoiding Premature Sublimation
One of the most significant risks in this process is the volatility of the ammonium halide.
If the temperature is not controlled precisely, the ammonium halide may undergo premature sublimation. This means the reactant turns to gas and escapes the system before it has time to react with the rare earth oxides, leading to low yields or incomplete reactions.
Blocking Impurity Formation
Inaccurate heating does more than just reduce yield; it actively degrades quality.
Thermal instability can lead to the formation of rare earth oxyhalides. These are specific impurities that contaminate the final powder, rendering it less effective for its intended application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Cost of Thermal Inaccuracy
It is important to recognize that this synthesis process has very low tolerance for error.
While faster heating rates might seem efficient, they often bypass the necessary windows for reactant dispersion. Prioritizing speed over programmed precision inevitably leads to the structural defects and impurities mentioned above.
Optimizing Material Properties
Targeting Microscopic Particle Size
The ultimate goal of the thermal process is to engineer the physical structure of the powder.
Correctly executed heating results in the formation of microscopic particles. Large or irregular particles are often a sign of thermal mismanagement during the synthesis phase.
Enhancing Ionic Conductivity
The physical structure of the powder directly dictates its performance properties.
The microscopic particles produced through precise temperature control exhibit high ionic conductivity. If the temperature fluctuates, you compromise this conductivity, reducing the utility of the rare earth halide powder.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
To ensure consistent quality in your rare earth halide powders, align your thermal strategy with your specific production goals.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity: Maintain strict thermal stability to prevent the formation of rare earth oxyhalide impurities.
- If your primary focus is material performance: Utilize accurate programmed heating to ensure reactant dispersion and maximize ionic conductivity.
Mastering the temperature profile is the single most effective step toward producing high-performance anhydrous powders.
Summary Table:
| Critical Factor | Impact of Precise Control | Consequence of Poor Control |
|---|---|---|
| Reactant Stability | Prevents premature sublimation of ammonium halide | Low yield and lost reactants |
| Chemical Purity | Blocks the formation of rare earth oxyhalides | Contaminated, low-quality product |
| Material Structure | Ensures formation of microscopic particles | Large, irregular, or defective particles |
| Performance | Maximizes ionic conductivity of the powder | Reduced material utility and efficiency |
| Reaction Uniformity | Facilitates full dispersion of HX gas agents | Incomplete or non-uniform synthesis |
Elevate Your Synthesis Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let thermal instability compromise your research or production yields. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions specifically designed for complex chemical syntheses. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which are fully customizable to meet the exacting temperature profiles required for high-performance rare earth halide powders.
Ready to optimize your material properties and eliminate impurities?
Contact KINTEK Today for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Zhichao Zeng, Yaping Du. Vacuum evaporation-assisted reaction: sustainable solution for application of rare earth-based halide solid-state electrolytes. DOI: 10.1039/d5sc00003c
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of production processes benefit from the thermal uniformity of tube furnaces? Enhance Precision in Material Processing
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in two-stage pyrolysis? Precision Thermal Control
- What materials are used as sealed containers in a vacuum tube experimental furnace? Optimize Your High-Temp Experiments
- What safety protection mechanisms are typically included in tube furnaces? Ensure Operator and Equipment Safety
- What precaution should be taken when moving a vacuum tube furnace? Avoid Costly Damage and Safety Risks
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- What changes occur in materials processed in a tube furnace? Discover Physical, Chemical, and Heat Treatment Transformations
- What are the key application features of a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace? Boost Efficiency and Uniformity



















