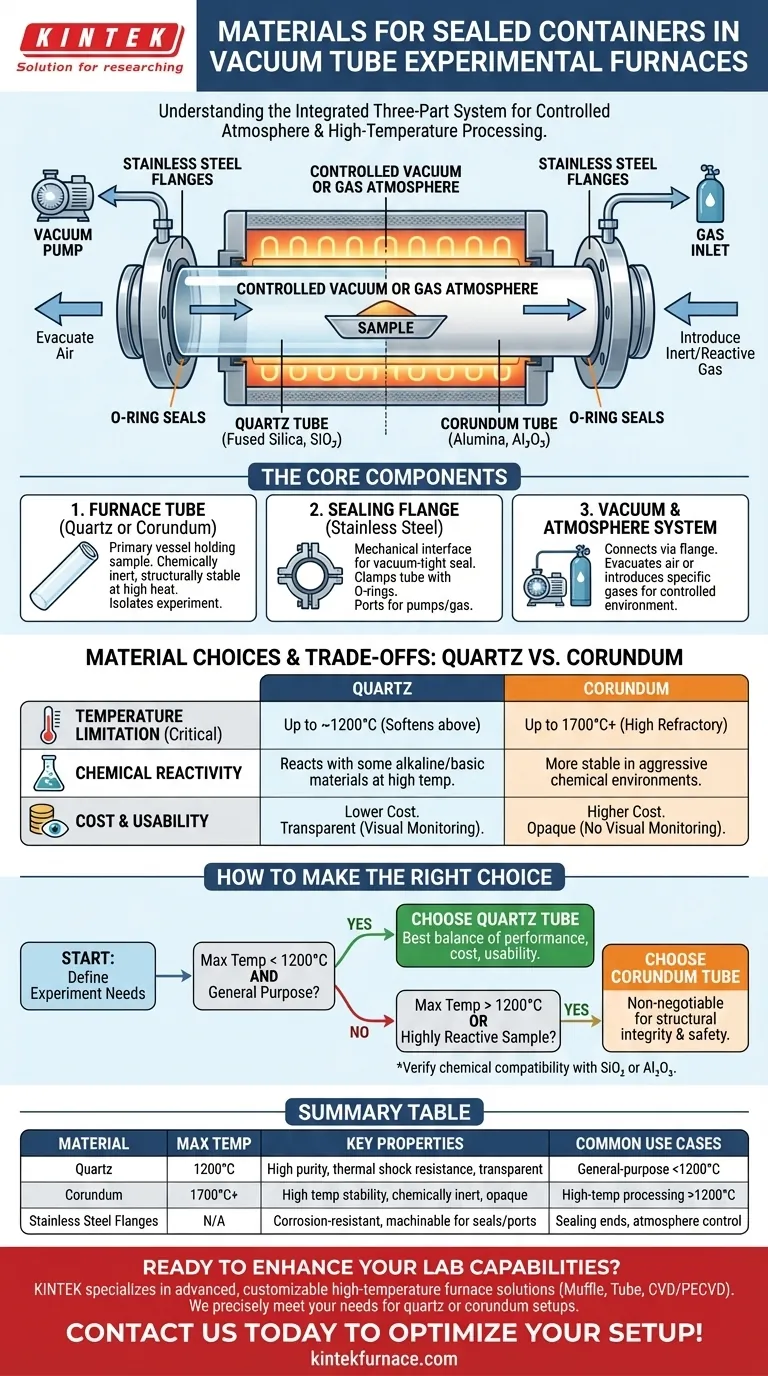
In a vacuum tube experimental furnace, the sealed container is a high-purity ceramic tube, most commonly made of either quartz or corundum. This tube is sealed at its ends using stainless steel flanges equipped with O-rings. This three-part system allows for the creation of a controlled vacuum or a specific gas atmosphere around the experimental material during high-temperature processing.
The choice between a quartz and a corundum tube is the single most critical decision in setting up your experiment. It is not an interchangeable selection but a deliberate choice based on your required maximum temperature, chemical environment, and budget.
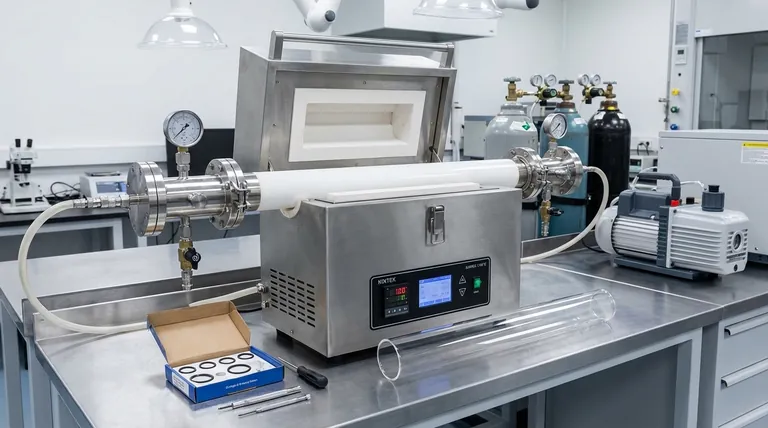

The Core Components of the Sealing System
To understand the material choices, it's essential to see the container not as a single piece, but as an integrated system designed for containment, access, and atmospheric control.
The Furnace Tube (Quartz or Corundum)
This is the primary vessel that holds your sample and endures the extreme heat. Its job is to remain chemically inert and structurally stable at high temperatures, isolating the experiment from the outside world and the furnace's heating elements.
The Sealing Flange (Stainless Steel)
The flange is the mechanical interface that makes a vacuum-tight seal. It clamps onto the end of the ceramic tube, compressing an O-ring to prevent leaks. Crucially, it also includes ports for connecting vacuum pumps and introducing specific gases.
The Vacuum and Atmosphere System
Connected via the flange, a vacuum pump is used to evacuate air from the tube, preventing oxidation of sensitive materials. Alternatively, the ports on the flange can be used to introduce a pure, inert atmosphere (like argon) or a reactive gas as required by the experiment.
Why These Specific Materials Are Used
The selection of quartz, corundum, and stainless steel is based on a precise balance of thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties. Each material serves a distinct and vital function.
Quartz Tubes: The Versatile Workhorse
Quartz (fused silica, SiO₂) is the most common choice for many vacuum furnace applications. It offers an excellent combination of properties, including high purity, good resistance to thermal shock (cracking from rapid temperature changes), and optical transparency, which allows you to visually monitor the experiment.
Corundum Tubes: For Extreme Temperatures
Corundum (high-purity alumina, Al₂O₃) is chosen when experimental temperatures exceed the operational limits of quartz. It is a highly refractory ceramic that maintains its strength and stability at much higher temperatures.
Stainless Steel Flanges: The Reliable Interface
Stainless steel is the ideal material for the flanges. It is strong enough to create a secure clamp, highly resistant to corrosion, and easy to machine into the complex shapes needed for vacuum ports. It forms a reliable, repeatable seal against the ceramic tube.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quartz vs. Corundum
Your choice of tube material directly impacts your experiment's capabilities and cost. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is a common source of experimental failure.
Temperature Limitation
This is the most critical distinction. Quartz tubes are generally reliable for experiments up to approximately 1200°C. Above this, they begin to soften. Corundum tubes are required for higher temperatures, often capable of operating up to 1700°C or more.
Chemical Reactivity
While both are relatively inert, they are not universally so. At very high temperatures, quartz (SiO₂) can react with certain alkaline or basic materials. Corundum (Al₂O₃) is often more stable in these aggressive chemical environments.
Cost and Usability
Quartz tubes are significantly less expensive than corundum tubes. Their transparency is also a major practical advantage for process monitoring and troubleshooting, an advantage that is lost with opaque corundum tubes.
How to Make the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Selecting the correct tube is fundamental to achieving a controlled environment for processes like vacuum annealing (to remove stress from metals like titanium alloys) or vacuum sintering (to densify powdered materials).
- If your primary focus is general-purpose experiments below 1200°C: A quartz tube offers the best balance of performance, cost, and usability.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing above 1200°C: A corundum tube is non-negotiable for structural integrity and safety.
- If your primary focus is working with highly reactive samples: You must verify the chemical compatibility of your sample with both SiO₂ and Al₂O₃ at your target temperature before making a final decision.
By understanding the distinct roles and limitations of these materials, you can ensure your experimental setup is robust, safe, and perfectly suited to your goals.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Properties | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1200°C | High purity, thermal shock resistance, transparent | General-purpose experiments below 1200°C |
| Corundum | Up to 1700°C+ | High temperature stability, chemically inert | High-temperature processing above 1200°C |
| Stainless Steel Flanges | N/A | Corrosion-resistant, machinable for vacuum seals | Sealing ends with O-rings for atmosphere control |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with the right vacuum furnace setup? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether you're working with quartz or corundum tubes. Don't let material choices hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup for superior performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















