In short, production processes that benefit most from a tube furnace are those involving small batches of thermally sensitive materials where precise, uniform heating is non-negotiable. This includes critical applications such as annealing metal components, sintering advanced ceramics, purifying inorganic compounds, and calibrating temperature sensors, all of which depend on an exceptionally stable and consistent thermal environment.
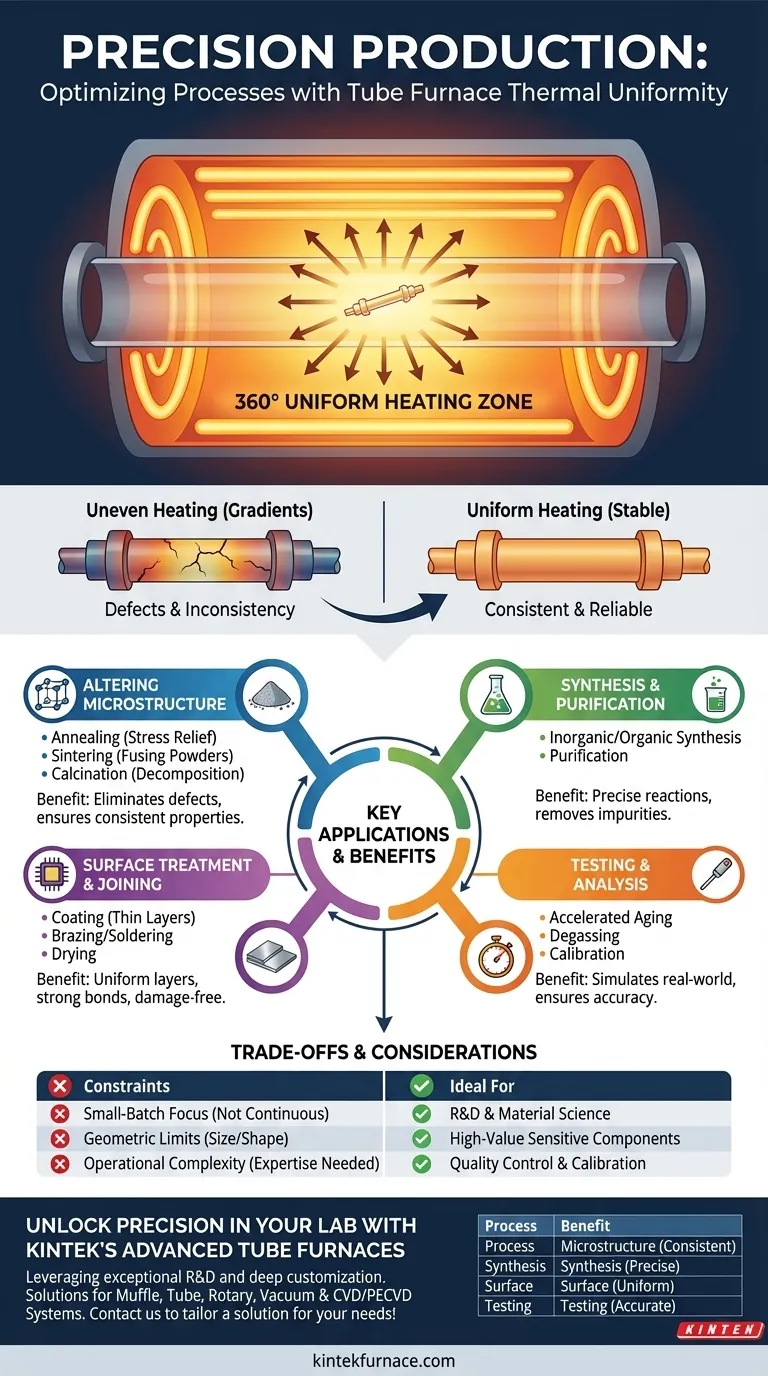
The core value of a tube furnace is not simply reaching high temperatures, but achieving near-perfect thermal uniformity. Its cylindrical heating chamber eliminates temperature variations, ensuring that every surface of a component is processed identically, which is essential for applications where even minor deviations could lead to material failure or inconsistent results.

The Core Principle: Why Uniformity is Critical
The defining feature of a tube furnace is its ability to create an exceptionally uniform thermal zone. This capability is not just an incremental improvement; it is a fundamental enabler for a class of highly sensitive thermal processes.
The 360° Heating Advantage
A tube furnace uses cylindrical heating elements that encircle the processing tube. This design ensures that heat radiates evenly from all directions toward the center.
This 360° heat distribution guarantees that the entire sample, regardless of its position within the central hot zone, experiences a consistent temperature, often exceeding 1000°C.
Eliminating Destructive Thermal Gradients
For many advanced materials, uneven heating—or thermal gradients—can introduce stress, micro-fractures, or incomplete chemical reactions. A uniform thermal profile eliminates these hot and cold spots.
This stability is crucial when altering a material's microstructure, as in annealing, where the goal is to soften a material and improve its ductility without creating internal defects.
Enabling High-Fidelity Processes
Some processes require the furnace itself to be a benchmark of accuracy. For example, thermocouple calibration involves testing a sensor's accuracy against a known, stable temperature.
The outstanding uniformity of a tube furnace provides this reliable thermal standard, making it an indispensable tool in metrology and quality control labs.
Key Processes Enabled by Tube Furnace Technology
The unique combination of uniform heating, high temperatures (up to 1800°C), and precise atmospheric control makes tube furnaces ideal for a range of specialized tasks.
Altering Material Microstructure
Processes that fundamentally change a material's internal structure demand absolute temperature control.
- Annealing: Softening metals or glass to relieve internal stresses and improve workability.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials, such as ceramics or metals, into a solid mass just below their melting point.
- Calcination: Inducing thermal decomposition to create new compounds, often by heating materials to drive off volatile substances.
Advanced Synthesis and Purification
Creating or purifying high-value compounds often requires a pristine, controlled environment that a tube furnace provides.
This includes the synthesis of inorganic and organic compounds, where precise temperatures trigger specific chemical reactions, and purification, where temperature control separates desired materials from impurities.
Surface Treatment and Component Joining
Tube furnaces excel at modifying material surfaces or joining components with high reliability.
- Coating: Applying thin, uniform layers to a substrate, a process foundational to semiconductor manufacturing.
- Brazing and Soldering: Joining materials using a filler metal, where uniform heat ensures a strong, complete bond across the entire joint.
- Drying: Removing all moisture from a sample without causing thermal damage.
Material Testing and Analysis
The controlled environment is perfect for simulating conditions and analyzing material behavior.
- Accelerated Aging: Exposing components to high temperatures to simulate long-term use and predict their lifespan.
- Degassing: Heating materials under a vacuum to remove trapped or dissolved gases, a critical step in producing components for high-vacuum systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, tube furnaces are a specialized tool. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Optimized for Batches, Not Continuous Flow
Tube furnaces are inherently designed for small-batch production. Their configuration is not suited for high-volume, continuous manufacturing where materials flow constantly through a heating zone.
Geometric and Size Constraints
The cylindrical chamber limits the size and shape of the parts that can be processed. They are ideal for wafers, rods, powders, or small components but cannot accommodate large, flat, or irregularly shaped objects.
Operational Complexity
Features like multi-zone temperature control, vacuum systems, and gas mixing capabilities provide immense process control. However, they also demand a higher level of operator expertise to manage parameters and ensure repeatable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a tube furnace is the right tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is material science research and development: A tube furnace offers the unparalleled control over temperature and atmosphere needed to synthesize novel materials and study their fundamental properties.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing high-value, sensitive components: The furnace's uniformity ensures high yield and repeatability for processes like annealing medical implants or coating semiconductor wafers.
- If your primary focus is quality control and calibration: Its stable and uniform thermal zone makes it the definitive instrument for calibrating sensors or conducting reliable material aging tests.
Ultimately, a tube furnace excels wherever precise control over the thermal environment is more critical than processing high volumes.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Benefits of Uniform Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Altering Microstructure | Annealing, Sintering, Calcination | Eliminates defects, ensures consistent material properties |
| Synthesis and Purification | Inorganic/Organic Synthesis, Purification | Enables precise chemical reactions, removes impurities |
| Surface Treatment and Joining | Coating, Brazing, Drying | Provides uniform layers, strong bonds, damage-free drying |
| Testing and Analysis | Accelerated Aging, Degassing, Calibration | Simulates real-world conditions, ensures accurate results |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's Advanced Tube Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in material science research, manufacturing high-value components, or quality control, our tube furnaces deliver the thermal uniformity and control you need for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and boost your process efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in NaRu2O4 synthesis? Master Solid-State Reaction & Phase Purity
- What is the difference between a vacuum tube furnace and a standard tube furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the role of a horizontal tube furnace in the plastic waste pyrolysis process? Driving Polymer Decomposition
- What are the key features of three-zone tube furnaces? Unlock Precision for Advanced Materials Processing
- Why use sealed vacuum tubes for perovskite supports? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Thin-Film Synthesis
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in heavy metal adsorption research? Precision Thermal Simulation Guide
- How does a laboratory tube furnace facilitate the sulfidation of Co3O4@CNT? Advanced Synthesis Secrets
- What is the function of a tube furnace in the final synthesis stage of C–Ag@ZnO nanocomposites? Key Roles Explained



















