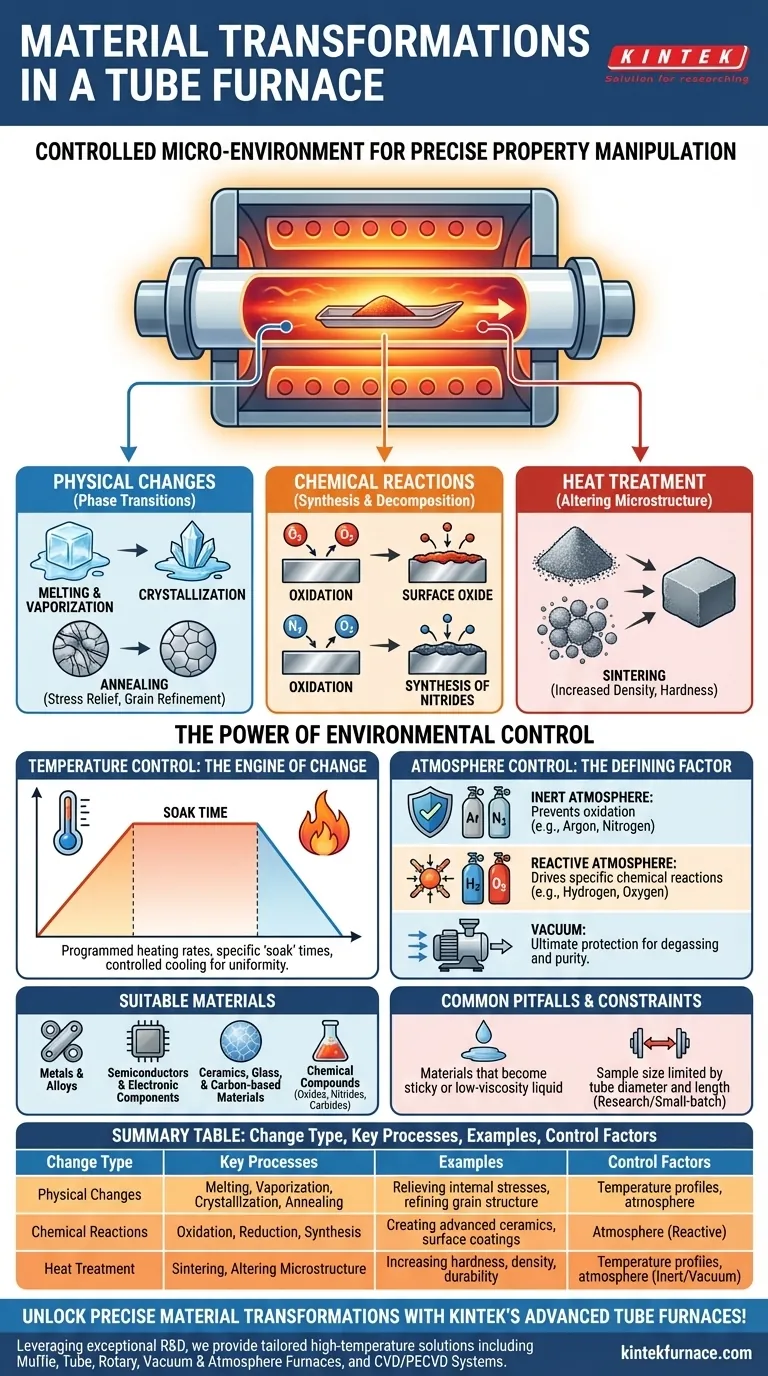
At its core, a tube furnace facilitates three primary types of material transformation: physical changes, chemical reactions, and heat treatments. These changes are not arbitrary; they are the direct result of subjecting a material to a precisely controlled temperature profile within a highly specific, isolated atmosphere. This level of control is what allows for the creation of materials with desired properties that would be impossible to achieve in open air.
A tube furnace should be understood not as a simple oven, but as a controlled micro-environment. Its true function is to manipulate a material's fundamental properties by precisely managing both heat and the surrounding atmosphere, enabling targeted physical and chemical transformations.

The Core Mechanisms of Transformation
The changes that occur within a tube furnace are intentional and can be broadly categorized. Understanding each mechanism allows you to select the right process for your material.
Physical Changes (Phase Transitions)
This is the most fundamental change, where the material alters its physical state or crystal structure without changing its chemical composition.
Common examples include melting, vaporization, or crystallization. It also includes annealing, a process where heat relieves internal stresses and refines a material's grain structure to make it less brittle.
Chemical Reactions (Synthesis and Decomposition)
Here, the goal is to alter the material's chemical makeup, either by combining it with other elements or by breaking it down.
This is where atmospheric control is paramount. By introducing a reactive gas like oxygen, you can induce oxidation. By using nitrogen or ammonia, you can create nitrides. This is the foundation of synthesizing new compounds like advanced ceramics or surface coatings.
Heat Treatment (Altering Microstructure)
Heat treatment modifies a material's microscopic structure to achieve desirable macroscopic properties, such as increased hardness, durability, or density.
A key example is sintering, where fine powders (like ceramics or metals) are heated below their melting point. The particles fuse, reducing porosity and forming a solid, dense object. The chemical identity of the material remains, but its physical form and properties are radically changed.
The Power of Environmental Control
The unique value of a tube furnace comes from its two primary control variables. The transformation a material undergoes is entirely dependent on how you manipulate its temperature and its surrounding atmosphere.
Temperature Control: The Engine of Change
Precise temperature is the primary driver of any reaction or phase change. A tube furnace allows for programmed heating rates, specific "soak" times at a target temperature, and controlled cooling.
This precision ensures that processes happen uniformly and completely, whether you are slowly annealing a delicate crystal or rapidly firing a ceramic.
Atmosphere Control: The Defining Factor
The atmosphere inside the tube dictates which chemical pathways are possible. Without this control, most high-temperature processes would simply result in unwanted oxidation from the air.
-
Inert Atmosphere: Using gases like Argon or Nitrogen displaces oxygen, creating a neutral environment. This is critical for preventing oxidation when melting metals or annealing sensitive materials.
-
Reactive Atmosphere: Intentionally introducing gases like hydrogen (for reduction) or oxygen (for oxidation) allows you to actively drive specific chemical reactions on the material's surface or throughout its bulk.
-
Vacuum: Pumping the air out of the tube creates a vacuum, which is the ultimate protective atmosphere. It is essential for processes like degassing materials, preventing any contamination, and enabling high-purity applications in electronics and aerospace.
Understanding Applications and Limitations
While versatile, a tube furnace is a specialized tool with clear use cases and constraints. Knowing these helps determine if it's the right instrument for a given task.
Suitable Materials
Tube furnaces excel at processing a wide range of materials in granular, powder, or solid forms. This includes:
- Metals and alloys
- Semiconductors and electronic components
- Ceramics, glass, and carbon-based materials
- Chemical compounds like oxides, nitrides, and carbides
Common Pitfalls and Constraints
The primary limitation is physical form. Materials that become very sticky or melt into a low-viscosity liquid at high temperatures can be difficult to manage and are often unsuitable for certain setups, especially rotary tubes.
Furthermore, the sample size is inherently limited by the diameter and length of the furnace tube. This makes it a tool for research, development, and small-batch production rather than mass manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, match the furnace's capabilities directly to your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is material purification or property refinement: Use a vacuum or an inert atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation during annealing or degassing.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing a new compound: Introduce a specific reactive gas (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen) to drive a targeted chemical reaction on your base material.
- If your primary focus is creating a dense, solid part from powder: Use sintering, which requires precise temperature control just below the melting point, typically under a protective vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Ultimately, a tube furnace empowers you to engineer a material's properties with precision by mastering its environment.
Summary Table:
| Change Type | Key Processes | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Changes | Melting, vaporization, crystallization, annealing | Relieving internal stresses, refining grain structure |
| Chemical Reactions | Oxidation, reduction, synthesis of nitrides/carbides | Creating advanced ceramics, surface coatings |
| Heat Treatment | Sintering, altering microstructure | Increasing hardness, density, durability |
| Control Factors | Temperature profiles, atmosphere (inert/reactive/vacuum) | Preventing oxidation, driving specific reactions |
Unlock precise material transformations with KINTEK's advanced tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental requirements are met for superior results in material synthesis and processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















