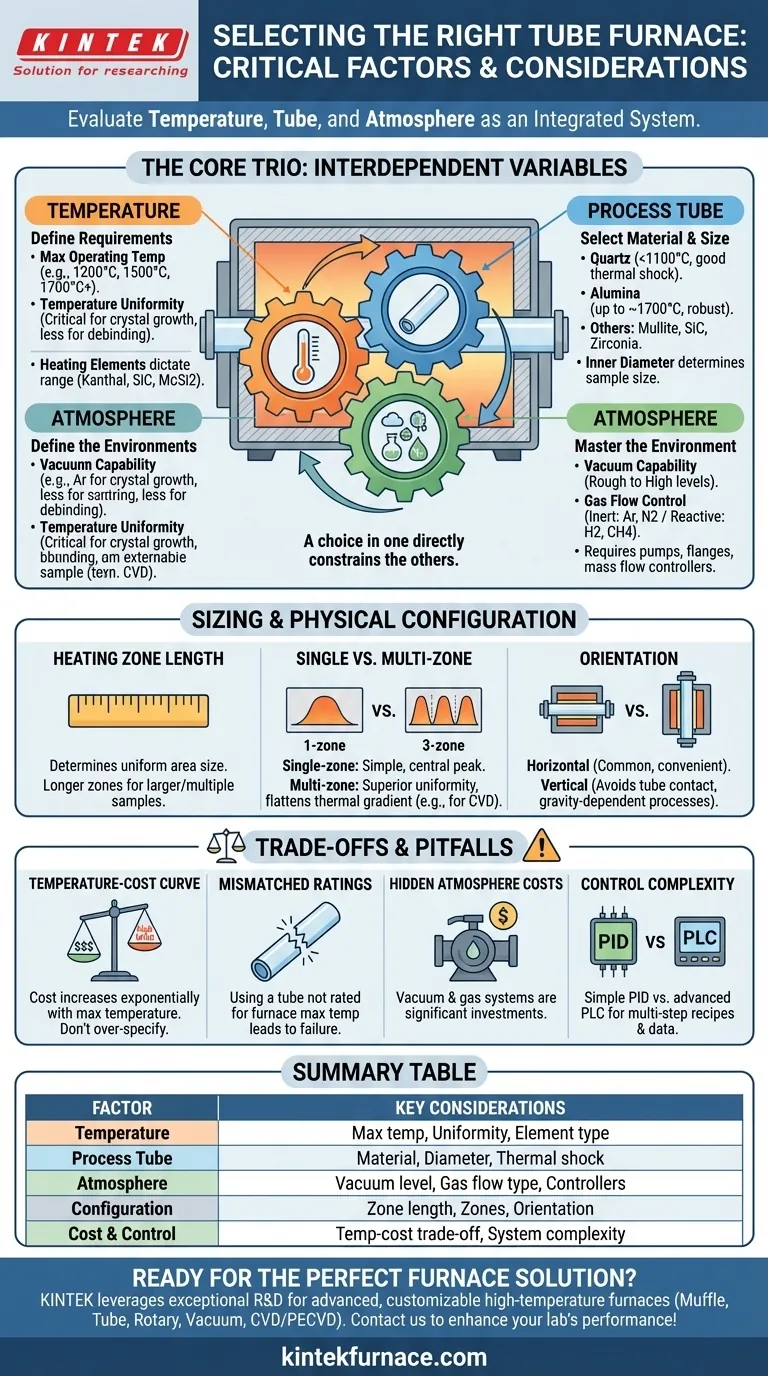
In selecting a tube furnace, the most critical factors to evaluate are your required temperature range, the material and diameter of the process tube, and the type of atmosphere control needed. These three interconnected elements form the core of your decision, as they directly dictate the furnace's capabilities, operational costs, and suitability for your specific application, whether it's for material synthesis, annealing, or chemical vapor deposition.
A tube furnace should be viewed not as a single instrument but as an integrated system where the heating elements, the process tube, and the gas/vacuum peripherals must work in harmony. The central challenge is to define your process requirements with precision first, as this will guide you to the only configuration that truly meets your needs without being over-engineered or insufficient.
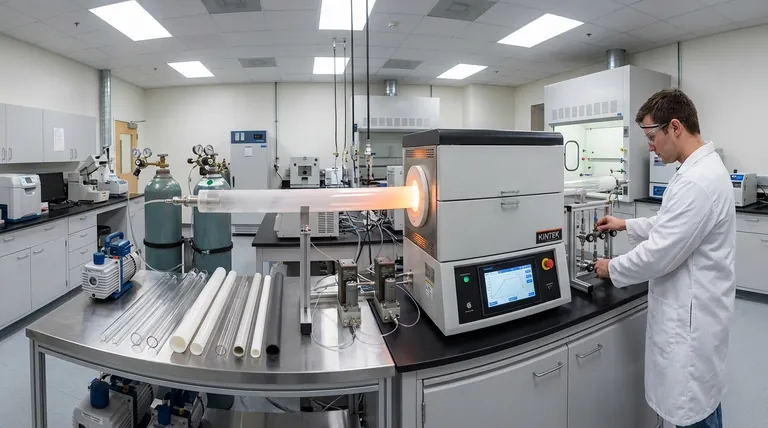

The Core Trio: Temperature, Tube, and Atmosphere
The decision-making process begins with understanding three fundamental, interdependent variables. A choice made in one area will directly constrain your options in the others.
Defining Your Temperature Requirements
Your target temperature is the single most influential factor. It dictates the furnace's construction, materials, and cost.
The maximum operating temperature is the first specification to define. Furnaces are typically categorized by their upper limits, such as 1200°C, 1500°C, or 1700°C and higher. This rating determines the type of heating elements used, from Kanthal (up to ~1200°C) to Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) for higher ranges.
Temperature uniformity is equally critical. This refers to the consistency of temperature across the central "hot zone" where your sample is located. A process like crystal growth requires high uniformity, while simple debinding may be more forgiving.
Selecting the Right Process Tube
The process tube is not an accessory; it is the heart of the furnace, containing your sample and your atmosphere. Its material must be chosen based on your maximum temperature and chemical environment.
Quartz tubes are common and cost-effective but are generally limited to applications below 1100°C. They offer excellent thermal shock resistance and are ideal for processes requiring rapid heating and cooling.
Alumina tubes are used for higher temperatures (up to ~1700°C). They are more robust in high-heat applications but are more susceptible to thermal shock than quartz.
Other materials like mullite, silicon carbide (SiC), or zirconia offer specific benefits for extremely high temperatures or resistance to particular chemical reactions. The tube's inner diameter also dictates your maximum sample size.
Mastering the Process Atmosphere
Atmosphere control determines the chemical environment your sample is exposed to. This can range from ambient air to high vacuum or a precisely controlled flow of gas.
Vacuum capability is essential for preventing oxidation and removing contaminants. You must define the required vacuum level, from a rough vacuum for simple purging to a high vacuum for purity-sensitive applications. This choice determines the type of pumps and flanges required.
Gas flow control is needed for processes that require a specific environment, such as an inert gas (Argon, Nitrogen) to prevent reactions or a reactive gas (Hydrogen, Methane) that is part of the process itself, like in chemical vapor deposition (CVD). This requires mass flow controllers for precise regulation.
Sizing and Physical Configuration
Once the core trio is established, you must consider the furnace's physical layout to ensure it fits your sample, process, and lab space.
The Importance of Heating Zone Length
The length of the heated zone determines the size of the uniform temperature area. For processing larger samples or multiple small samples at once, a longer heating zone is necessary to ensure they all experience the same thermal conditions.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Furnaces
A single-zone furnace has one set of heating elements and one controller, creating a hot zone that peaks in the center. They are simpler and more common for basic heating applications.
Multi-zone furnaces, most often with three zones, offer superior temperature uniformity over a longer length. By independently controlling the temperature of the end zones relative to the center, they can flatten the thermal gradient, which is critical for sensitive processes like CVD or crystal growth.
Orientation: Horizontal vs. Vertical
Most tube furnaces are horizontal, which is convenient for loading and observing samples. However, vertical furnaces are preferred for certain applications, such as avoiding sample contact with the tube wall or for processes involving molten materials where gravity is a factor.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Selecting a furnace involves balancing performance with cost. Being aware of common pitfalls can prevent expensive mistakes.
The Temperature-Cost Curve
The cost of a tube furnace increases exponentially with its maximum temperature. A 1700°C furnace is significantly more expensive than a 1200°C model due to the high cost of MoSi2 heating elements, advanced insulation, and required power systems. Do not over-specify your temperature needs.
Mismatched Tube and Furnace Ratings
A common and costly mistake is using a process tube that is not rated for the furnace's maximum temperature. For example, placing a quartz tube in a 1500°C furnace and running it at high heat will cause the tube to fail, potentially destroying your sample and damaging the furnace.
The Hidden Costs of Atmosphere Control
Achieving high vacuum or precise gas control is not trivial. The cost of turbo pumps, mass flow controllers, vacuum-tight flanges, and gas safety systems can be a significant portion of the total investment.
Control System Complexity
A basic PID controller is sufficient for simple temperature ramps and soaks. However, complex multi-step recipes or the need for data logging requires a more advanced PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) system. Choose a control system that matches your process complexity without being overly difficult to program.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your primary application.
- If your primary focus is High-Temperature Material Synthesis: Prioritize the maximum temperature rating and a compatible high-purity tube material like dense alumina or zirconia.
- If your primary focus is Precise Thin-Film Deposition (CVD): A multi-zone furnace is essential for thermal uniformity, combined with high-precision mass flow controllers and a capable vacuum system.
- If your primary focus is General Lab Annealing or Calibration: A versatile single-zone horizontal furnace with a 1200°C rating and interchangeable quartz or alumina tubes offers the best balance of capability and cost.
- If your primary focus is Working with Air-Sensitive Materials: Your first priority is the quality of the vacuum system, including the flanges, seals, and pumping package, to ensure a pure inert atmosphere.
By methodically evaluating your process against these core factors, you can select a tube furnace that is not only capable but also a reliable and cost-effective tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Max operating temperature, uniformity, heating elements (e.g., Kanthal, SiC, MoSi2) |
| Process Tube | Material (e.g., quartz, alumina), diameter, thermal shock resistance |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum levels, gas flow (inert/reactive), mass flow controllers |
| Configuration | Heating zone length, single-zone vs. multi-zone, horizontal vs. vertical orientation |
| Cost and Control | Trade-offs in temperature-cost, control system complexity (PID vs. PLC) |
Ready to find the perfect tube furnace for your application? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















