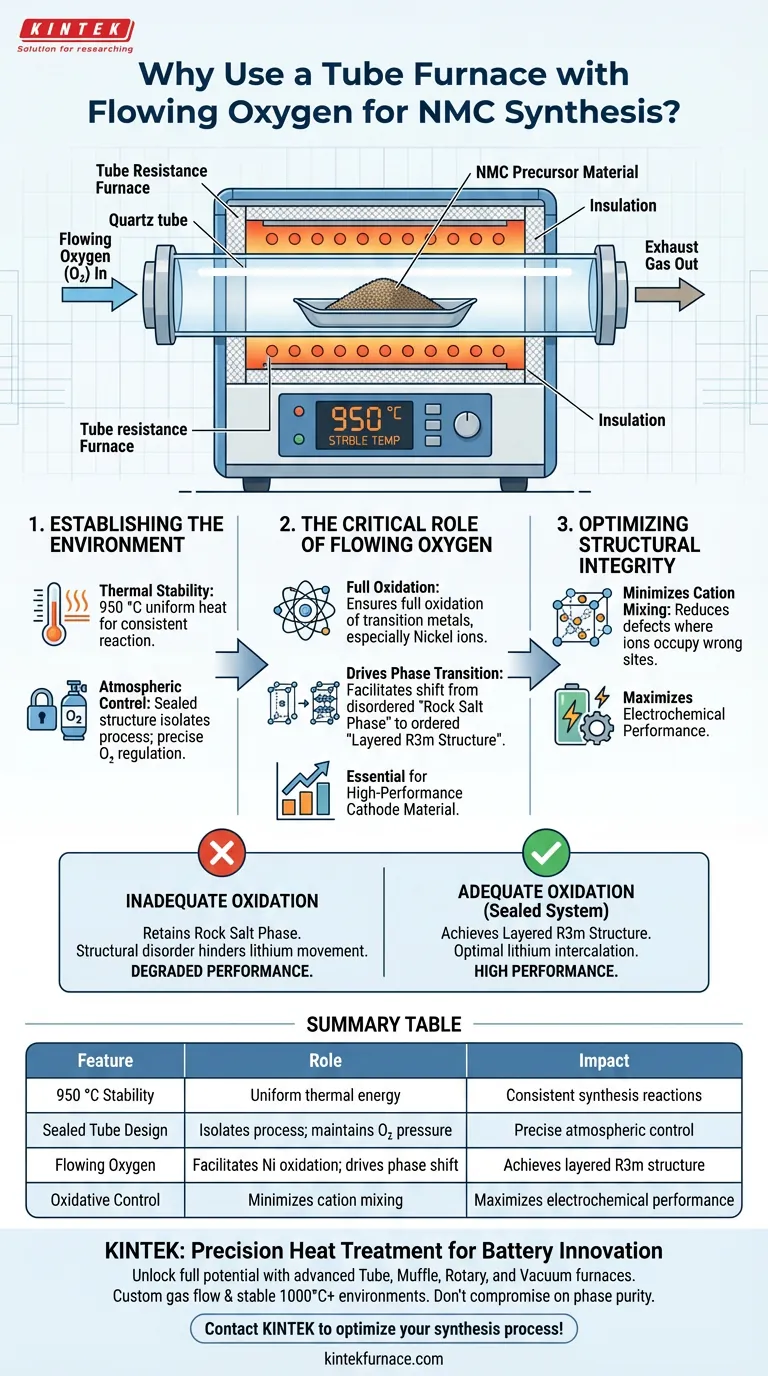
The primary purpose of using a tube resistance furnace with flowing oxygen is to create a controlled, oxidative environment that forces the Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) material to adopt the correct crystal structure. The furnace maintains a stable temperature of 950 °C, while the continuous flow of oxygen ensures the full oxidation of transition metals, specifically nickel, which is required to form a high-performance cathode material.
Core Takeaway: The combination of a sealed, high-temperature environment and flowing oxygen is the critical driver that transitions NMC material from a disordered rock salt phase to the ordered layered R3m structure by minimizing cation mixing.

Establishing the Reaction Environment
Thermal Stability
The tube resistance furnace is selected specifically for its ability to provide a stable high-temperature environment.
During the secondary heating stage, the material is subjected to temperatures around 950 °C. Uniform heat distribution is essential to ensure the synthesis reaction occurs consistently throughout the entire batch of material.
Atmospheric Control
The physical design of the tube furnace features a sealed structure.
This sealing is vital because it isolates the synthesis process from ambient air. It allows for the precise introduction and regulation of specific gases—in this case, pure oxygen—without contamination or fluctuation in partial pressure.
The Critical Role of Flowing Oxygen
Ensuring Full Oxidation
The most distinct chemical requirement of this stage is the full oxidation of transition metal ions.
The primary reference highlights nickel ions as the critical component requiring oxidation. Without a continuous supply of flowing oxygen, the nickel may not reach the valence state necessary for the final material's stability.
Driving Phase Transition
The presence of oxygen dictates the physical arrangement of atoms within the crystal lattice.
The oxidative environment facilitates a specific phase transition. It drives the material from an intermediate "rock salt phase" into the desired layered R3m structure. This layered structure is the fundamental architecture required for lithium-ion intercalation in battery applications.
Optimizing Structural Integrity
Minimizing Cation Mixing
A common defect in NMC synthesis is cation mixing, where metal ions occupy the wrong sites within the crystal lattice.
By ensuring full oxidation and maintaining the correct phase transition conditions, the flowing oxygen minimizes this phenomenon. Reducing cation mixing is essential for maximizing the electrochemical performance of the final cathode material.
Understanding the Process Criticality
The Consequence of Inadequate Oxidation
If the oxidative environment is insufficient, the material fails to transition completely to the layered R3m structure.
Instead, the material may retain characteristics of the rock salt phase. This structural disorder creates barriers to lithium movement, ultimately degrading the potential performance of the NMC material.
The Necessity of the Sealed System
Relying on an open-air furnace rather than a sealed tube furnace introduces variables that compromise quality.
The sealed tube ensures that the oxygen concentration remains high and constant. This precision prevents the incomplete oxidation of nickel ions that would occur in a less controlled atmosphere.
Ensuring Material Success
To achieve high-quality NMC dry synthesis, align your process parameters with your specific structural goals:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure a continuous, regulated flow of oxygen to drive the transition from rock salt to the layered R3m structure.
- If your primary focus is Defect Reduction: maintain a stable 950 °C environment to fully oxidize nickel ions and minimize cation mixing.
The rigorous control of heat and oxygen is not merely a procedural step; it is the architect of the material's atomic structure.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in NMC Synthesis | Impact on Final Material |
|---|---|---|
| 950 °C Stability | Provides uniform thermal energy | Ensures consistent synthesis reactions |
| Sealed Tube Design | Isolates process from ambient air | Maintains precise oxygen partial pressure |
| Flowing Oxygen | Facilitates transition metal oxidation | Drives phase shift from rock salt to R3m |
| Oxidative Control | Minimizes cation mixing | Maximizes electrochemical performance |
Precision Heat Treatment for Battery Innovation
Unlock the full potential of your cathode materials with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces, specifically designed to handle the rigorous oxidative environments required for NMC and other battery material synthesis.
Whether you need custom gas flow controls or stable 1000°C+ environments, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique lab requirements. Don't compromise on phase purity.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your synthesis process!
Visual Guide
References
- Svena Yu, J. R. Dahn. In‐Situ Heating X‐Ray Diffraction of LiNi<sub>0.6</sub>Mn<sub>0.3</sub>Co<sub>0.1</sub>O<sub>2</sub> and LiNi<sub>0.7</sub>Mn<sub>0.3</sub>O<sub>2</sub> Made Using the All‐Dry Synthesis Process. DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202500632
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of a laboratory vacuum tube furnace? Master High-Performance Material Synthesis
- What chemical role does a tubular furnace play during the carbonization of Si@Sn@C? Unlock Advanced Material Synthesis
- What role does a Tube Furnace play in the CVD growth of carbon nanotubes? Achieve High-Purity CNT Synthesis
- What is the purpose of thermal insulation in a tube furnace? Ensure Uniform Heating and Energy Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in materials science and engineering? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What makes fluidized bed vertical tube furnaces environmentally friendly? Discover Efficient Green Tech Solutions
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- What are the main applications of a drop tube furnace? Unlock Insights in Energy and Materials Research



















