At its core, a drop tube furnace is a specialized vertical furnace designed to study the effects of high temperatures on materials in a free-fall or rapid-transit state. Its primary applications include energy research, particularly coal and biomass combustion, pyrolysis for materials decomposition, the synthesis of advanced materials, and high-temperature performance testing for ceramics and alloys.
The defining feature of a drop tube furnace isn't just its high temperature, but its vertical orientation. This design allows researchers to simulate and study rapid, "in-flight" thermal processes on small particles, something that is impossible to achieve in a standard horizontal or box furnace.
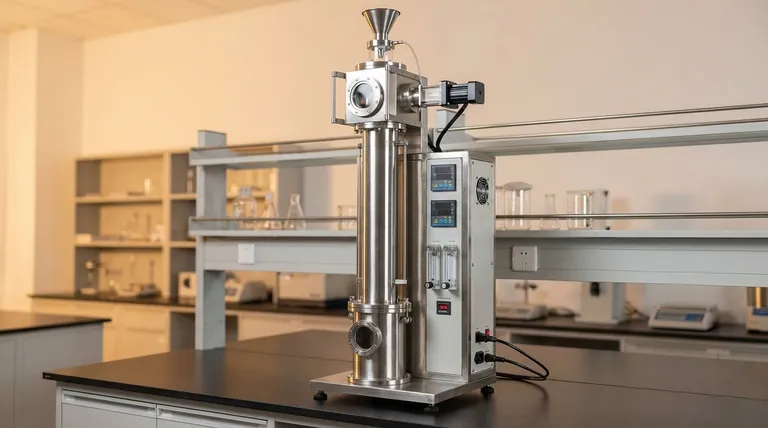

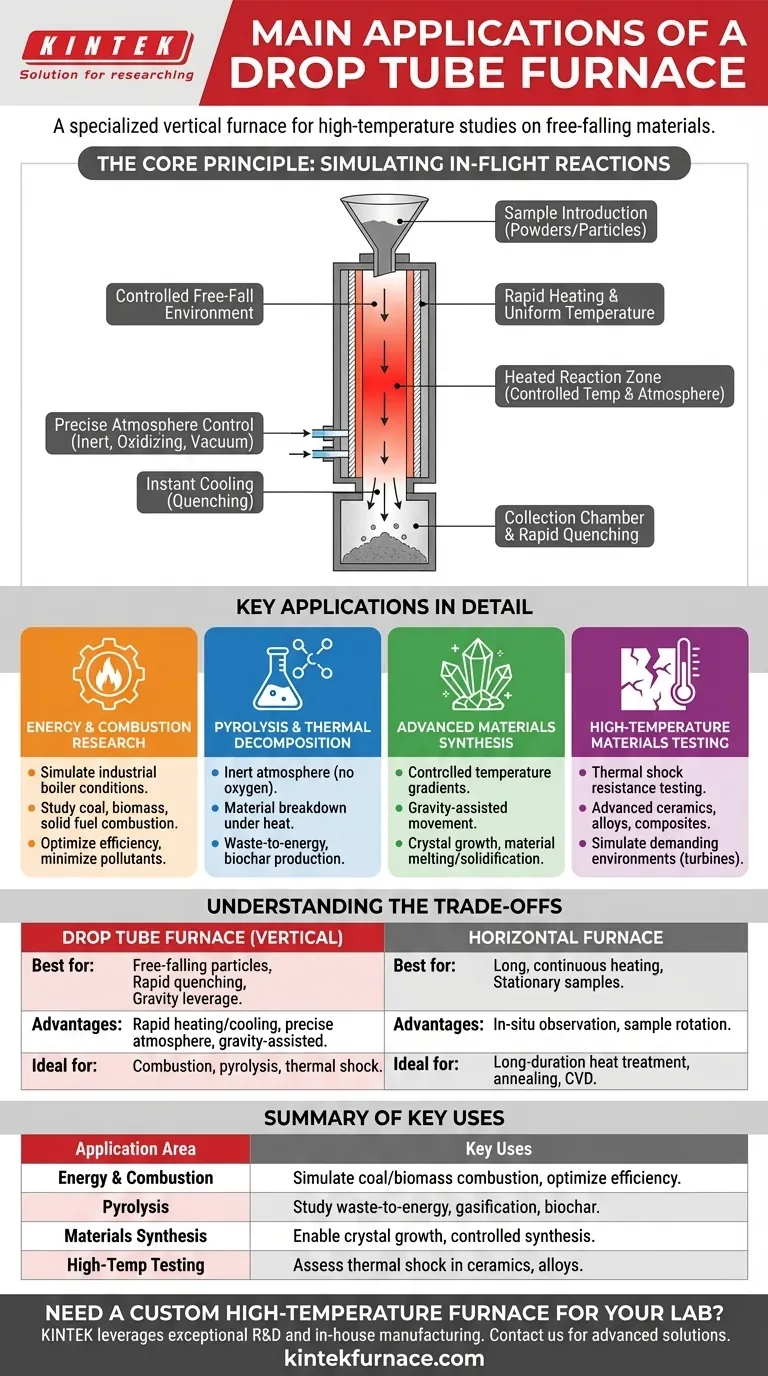
The Core Principle: Simulating In-Flight Reactions
A drop tube furnace operates on a simple yet powerful concept. It uses gravity to pass a sample through a precisely controlled, high-temperature reaction zone. This unique method is what unlocks its specific applications.
A Controlled Free-Fall Environment
Samples, typically powders or small particles, are introduced at the top of a long, vertical ceramic tube (often made of corundum or quartz). They then fall through the central heated section, experiencing rapid and uniform heating for a very specific duration, known as the residence time.
Precise Atmosphere and Temperature Control
The furnace chamber can be sealed to control the internal atmosphere. This allows for experiments under specific conditions, such as an inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) for pyrolysis, an oxidizing gas for combustion studies, or a vacuum for purification processes. Thermocouples and advanced controllers maintain a precise and stable temperature profile.
Rapid Heating and Quenching
The "drop" mechanism exposes the particles to extreme heat almost instantly. As the particles exit the heated zone and fall into a collection chamber, they cool down very quickly (a process called quenching). This ability to study rapid heating and cooling cycles is critical for many research areas.
Key Applications in Detail
The unique design of a drop tube furnace makes it the ideal tool for several specialized fields of research and development.
Energy and Combustion Research
This is arguably the most common application. Researchers use drop tube furnaces to simulate the conditions inside a large-scale industrial boiler. By studying how single particles of coal, biomass, or other solid fuels burn as they fall, they can optimize combustion efficiency and minimize pollutant formation.
Pyrolysis and Thermal Decomposition
By filling the furnace tube with an inert gas to eliminate oxygen, scientists can study pyrolysis. This is the process of a material breaking down under heat alone. It is fundamental to understanding waste-to-energy technologies, gasification, and producing materials like biochar.
Advanced Materials Synthesis
The controlled temperature gradient and gravity-assisted movement are ideal for certain synthesis processes. This includes crystal growth, where materials are melted and then slowly solidified in a controlled manner as they pass through different temperature zones in the tube.
High-Temperature Materials Testing
The furnace can be used to test how materials, especially advanced ceramics, alloys, and composites, respond to thermal shock. A sample can be rapidly introduced to and removed from the extreme temperature, simulating demanding real-world environments like those found in turbines or engines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A drop tube furnace is a specialized tool. Choosing it requires understanding when its unique vertical design is an advantage versus a limitation.
When to Choose a Drop Tube Furnace
This design excels when your process involves studying free-falling particles, requiring extremely rapid heating and cooling rates (quenching), or leveraging gravity. The top-loading design can also simplify the introduction of samples for certain high-throughput or repetitive tests.
When a Horizontal Furnace is a Better Fit
A horizontal tube furnace is superior for processes that require long, continuous heating times for a stationary sample. It is also the only choice for applications that need in-situ observation or rotation of the sample during processing, such as in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or certain annealing protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace type depends entirely on the physical process you need to execute or study.
- If your primary focus is simulating particle combustion or pyrolysis: The drop tube furnace is the standard instrument for this research.
- If your primary focus is long-duration heat treatment or annealing: A horizontal or standard box furnace is a more practical and suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is observing a sample during heating: You must use a horizontal furnace, often with a quartz tube for visibility.
- If your primary focus is gas quenching or studying thermal shock: The drop tube furnace's ability to rapidly move a sample through the hot zone is a key advantage.
Ultimately, understanding the core operational principle—the controlled free-fall through a thermal zone—is the key to determining if a drop tube furnace is the right tool for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Energy & Combustion Research | Simulate coal/biomass combustion, optimize efficiency, reduce pollutants |
| Pyrolysis & Thermal Decomposition | Study waste-to-energy, gasification, biochar production in inert atmospheres |
| Advanced Materials Synthesis | Enable crystal growth and controlled material synthesis via temperature gradients |
| High-Temperature Materials Testing | Assess thermal shock resistance in ceramics, alloys, and composites |
| General Advantages | Rapid heating/cooling, precise atmosphere control, gravity-assisted particle movement |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Drop Tube, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether for energy research, materials synthesis, or performance testing. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















