At its core, a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace is environmentally friendly due to its exceptional thermal efficiency and its role as a critical tool for developing green technologies. The unique fluidized bed design transfers heat far more effectively than conventional methods, drastically reducing energy waste and fuel consumption. Simultaneously, these furnaces are instrumental in research and production for carbon capture, renewable energy, and waste-to-energy applications.
The environmental benefit of this technology is twofold: it operates more efficiently and cleanly than traditional alternatives, and it is a key enabler for creating the next generation of sustainable materials and energy solutions.

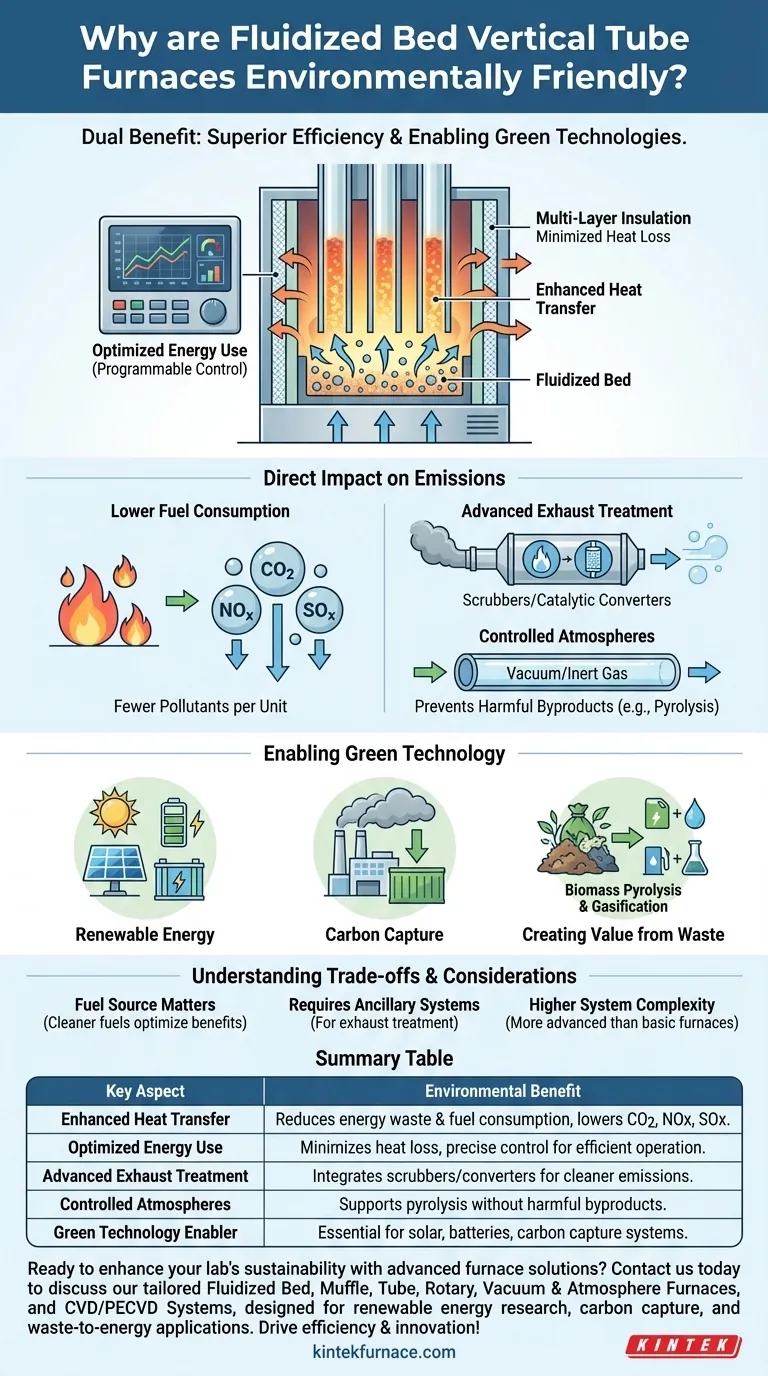
The Core Principle: Superior Efficiency and Control
The primary environmental advantage of a fluidized bed furnace stems from its fundamental design, which is engineered for maximum energy efficiency.
Enhanced Heat Transfer
A fluidized bed is created when a flow of gas is passed up through a bed of solid particles, such as sand or alumina. This causes the solid particles to behave like a liquid, suspending and circulating rapidly.
When this "fluid" of hot particles surrounds the vertical tubes in the furnace, it provides exceptionally high and uniform heat transfer. This direct, constant contact ensures that energy is delivered to the material inside the tubes quickly and evenly, minimizing the amount of heat—and therefore fuel—that is wasted.
Minimized Inherent Heat Loss
Modern furnace designs incorporate high-quality, multi-layer ceramic fiber insulation. This significantly reduces the amount of heat that escapes from the furnace body into the surrounding environment, keeping the energy focused where it is needed.
Optimized Energy Use
These furnaces are typically managed by programmable controllers. This allows for precise optimization of heating cycles, ramps, and dwell times, ensuring the system only uses the exact amount of energy required for a given process, which eliminates the waste associated with less sophisticated controls.
A Direct Impact on Emissions
Higher efficiency directly translates to a smaller environmental footprint during operation. Fewer wasted resources mean less pollution.
Lower Fuel Consumption
Because the furnace transfers heat so efficiently, it requires less fuel to reach and maintain a target temperature compared to less efficient designs. This directly reduces the output of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other combustion-related pollutants like NOx and SOx per unit of production.
Enabling Advanced Exhaust Treatment
The exhaust gases produced during combustion can be channeled into secondary treatment systems, such as scrubbers or catalytic converters. The controlled nature of the furnace's operation makes it easier to integrate these systems to capture pollutants and ensure emissions comply with strict environmental standards.
Controlled Atmospheres for Cleaner Processes
Many of these furnaces can be equipped with vacuum systems or operate with a flow of inert gas. This creates a protected, oxygen-free atmosphere inside the tubes. This capability is critical for processes like pyrolysis, which thermally decomposes materials without combustion, preventing the creation of many harmful byproducts.
The Broader Role: Enabling Green Technology
Perhaps the most significant environmental impact of these furnaces is not just how they run, but what they are used to create. They are a foundational tool in many green-tech sectors.
Advancing Renewable Energy
Researchers and manufacturers use these furnaces to prepare and test high-performance materials essential for solar cells, next-generation batteries, and fuel cells. The precise temperature and atmospheric control is vital for achieving the material properties required by the new energy industry.
Research in Carbon Capture
Fluidized beds are a key area of research for carbon capture and storage (CCS). These furnaces are used in laboratory and pilot-scale settings to test new sorbents and processes designed to capture CO2 from industrial flue gas.
Creating Value from Waste
These furnaces are ideal for biomass pyrolysis and gasification, processes that convert organic waste, such as agricultural residue, into renewable fuels and chemicals. They are also used for the high-temperature incineration of hazardous waste, enabling its harmless disposal and resource utilization.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, it's important to view this technology with a clear understanding of its context and limitations.
"Cleanliness" Depends on the Fuel
A furnace's environmental credentials are tied to its fuel source. A fluidized bed furnace burning coal is more efficient than a conventional coal furnace, but it is still a fossil-fuel-burning device. The greatest benefits are realized when it is used with cleaner fuels or for processes like waste pyrolysis that actively solve an environmental problem.
Ancillary Systems are Key
The furnace itself provides the efficient heat. However, features like exhaust gas treatment rely on additional, ancillary systems. Achieving low emissions requires a complete system design, not just the furnace alone.
Higher System Complexity
The technology behind a fluidized bed is more complex than a simple heating chamber. This can translate to a higher initial investment and may require more sophisticated operational knowledge and maintenance protocols compared to more basic furnace types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this technology fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is improving industrial process efficiency: The key benefit is lower fuel cost and reduced emissions per unit of production due to superior heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is research of advanced materials: The furnace's precise control over temperature and atmosphere is essential for creating the next generation of battery, solar, and catalyst components.
- If your primary focus is waste management or clean energy: The furnace's ability to perform pyrolysis and gasification makes it a vital tool for converting biomass or industrial waste into valuable resources.
Ultimately, a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace is an advanced tool whose positive environmental impact is defined by both its efficient design and its powerful application in solving critical sustainability challenges.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Heat Transfer | Reduces energy waste and fuel consumption, lowering CO2, NOx, and SOx emissions |
| Optimized Energy Use | Minimizes heat loss and enables precise control for efficient operation |
| Advanced Exhaust Treatment | Facilitates integration with scrubbers or catalytic converters for cleaner emissions |
| Controlled Atmospheres | Supports pyrolysis and other processes without harmful byproducts |
| Green Technology Enabler | Essential for developing solar cells, batteries, fuel cells, and carbon capture systems |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with advanced furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Fluidized Bed, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for renewable energy research, carbon capture, or waste-to-energy applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive efficiency and innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















