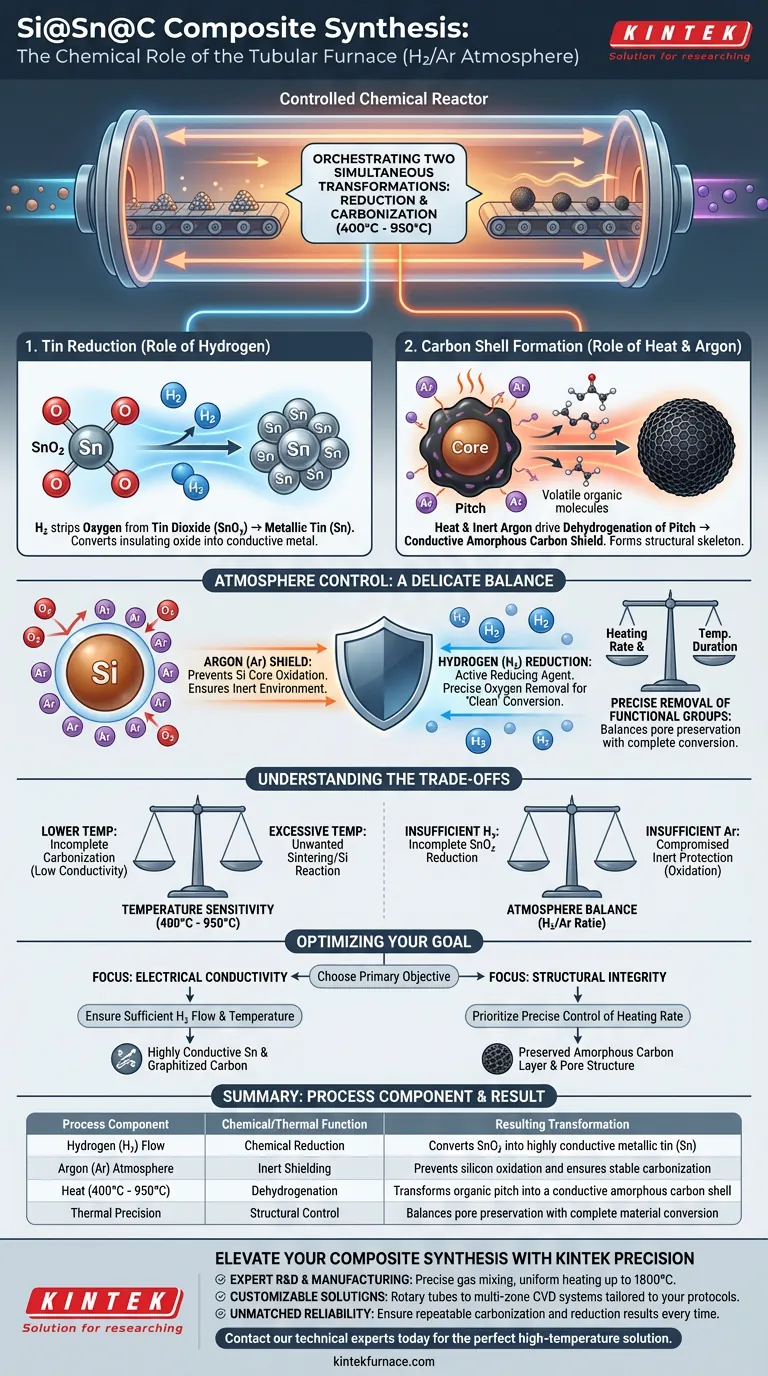
The tubular furnace functions as a controlled chemical reactor, orchestrating two simultaneous transformations: the reduction of metal oxides and the carbonization of organic precursors. By maintaining a specific hydrogen/argon atmosphere between 400 °C and 950 °C, the furnace enables the synthesis of a highly conductive Si@Sn@C ternary architecture.
Core Takeaway The furnace leverages the hydrogen component to chemically strip oxygen from tin oxide (SnO2) to form metallic tin, while the thermal environment under inert argon converts the pitch layer into a conductive amorphous carbon shield. This dual process creates a stable, conductive composite structure.
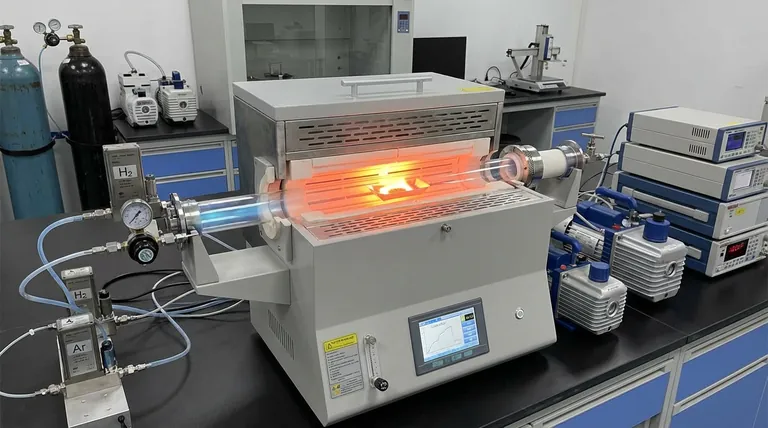

The Dual Chemical Mechanism
The tubular furnace is not merely a heating element; it provides the precise environment required for two distinct chemical reactions to occur in parallel.
1. The Reduction of Tin (The Role of Hydrogen)
The primary chemical role of the furnace atmosphere is reduction.
The precursor material contains Tin Dioxide (SnO2). The furnace introduces hydrogen gas (H2) which reacts with the oxygen in the SnO2.
This reaction strips away the oxygen, converting the semi-conductive or insulating oxide into metallic tin (Sn). This conversion is critical for ensuring the final composite has the metallic properties necessary for high conductivity.
2. The Formation of the Carbon Shell (The Role of Heat and Argon)
Simultaneously, the furnace manages the carbonization of the outer coating.
The "pitch" layer surrounding the material is an organic precursor. Under the protection of inert argon gas, the high temperatures (400 °C – 950 °C) drive a process called dehydrogenation.
This removes non-carbon elements from the pitch, transforming it into a highly conductive amorphous carbon layer. This layer acts as a structural skeleton for the final composite.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
The success of this synthesis relies on the strict separation of chemical functions provided by the gas mixture.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
The argon component acts as a protective shield.
While hydrogen performs the reduction work on the tin, the argon ensures an inert environment for the rest of the material. This prevents the silicon core from oxidizing, which would degrade the material's performance.
Precise Removal of Functional Groups
The furnace environment allows for the directional removal of oxygen-containing groups.
By controlling the heating rate and temperature duration, the furnace ensures that volatile components leave the material without destroying the underlying pore structure. This results in a "clean" conversion from precursor to active material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tubular furnace enables this complex synthesis, the process requires a delicate balance.
Temperature Sensitivity The range of 400 °C to 950 °C is wide, but the specific temperature chosen dictates the final properties. Lower temperatures may result in incomplete carbonization (lower conductivity), while excessive temperatures could lead to unwanted sintering or reaction of the silicon core.
Atmosphere Balance The ratio of Hydrogen to Argon is critical. Insufficient hydrogen leads to incomplete reduction of SnO2 (leaving behind resistive oxides). Conversely, a lack of sufficient argon flow could compromise the inert protection, allowing oxygen ingress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When optimizing the carbonization stage for Si@Sn@C composites, consider your primary objective:
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Ensure the hydrogen flow and temperature are sufficient to fully reduce SnO2 to metallic Sn and completely graphitize the pitch layer.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize the precise control of the heating rate to prevent rapid outgassing, which preserves the amorphous carbon layer and the material's pore structure.
The tubular furnace is the critical tool that synchronizes the chemical reduction of tin with the structural formation of carbon, defining the final quality of your composite.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Chemical/Thermal Function | Resulting Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H2) Flow | Chemical Reduction | Converts SnO2 into highly conductive metallic tin (Sn) |
| Argon (Ar) Atmosphere | Inert Shielding | Prevents silicon oxidation and ensures stable carbonization |
| Heat (400°C - 950°C) | Dehydrogenation | Transforms organic pitch into a conductive amorphous carbon shell |
| Thermal Precision | Structural Control | Balances pore preservation with complete material conversion |
Elevate Your Composite Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect Si@Sn@C ternary structure requires absolute control over atmosphere and thermal gradients. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of advanced battery material research.
Why choose KINTEK for your lab?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our furnaces are engineered for precise gas mixing (H2/Ar) and uniform heating up to 1800°C.
- Customizable Solutions: From rotary tubes for uniform powder treatment to multi-zone CVD systems, we tailor equipment to your unique synthesis protocols.
- Unmatched Reliability: Ensure repeatable carbonization and reduction results every time.
Ready to optimize your material performance? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Jinhuan Li, Haiyong He. Simple and Safe Synthesis of Yolk-Shell-Structured Silicon/Carbon Composites with Enhanced Electrochemical Properties. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29061301
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a tube sintering furnace during the activation of carbon materials? Expert Guide to CO2 Activation
- What optional accessories are available for three-zone split tube furnaces? Enhance Control and Efficiency for Your Lab
- What role does a tubular furnace play in the preparation of biochar? Master Precise Biochar Pyrolysis
- Why is heat treatment in a tube furnace or muffle furnace required after synthesizing magnesium hydroxide nano-precursors via electrochemical methods? Unlock the Full Potential of Your MgO Nanomaterials
- How is a laboratory tube furnace utilized in the thermal shock reduction process to produce RGO?
- What role does a Vertical Tube Furnace play in ferronickel reduction smelting? Expert Process Simulation
- Why are high-precision industrial quartz tube reactors necessary for butane steam cracking kinetic studies? Ensure Accuracy
- What role does a Horizontal Tube Furnace play in MoP single crystal preparation? Master Thermal Kinetic Control



















