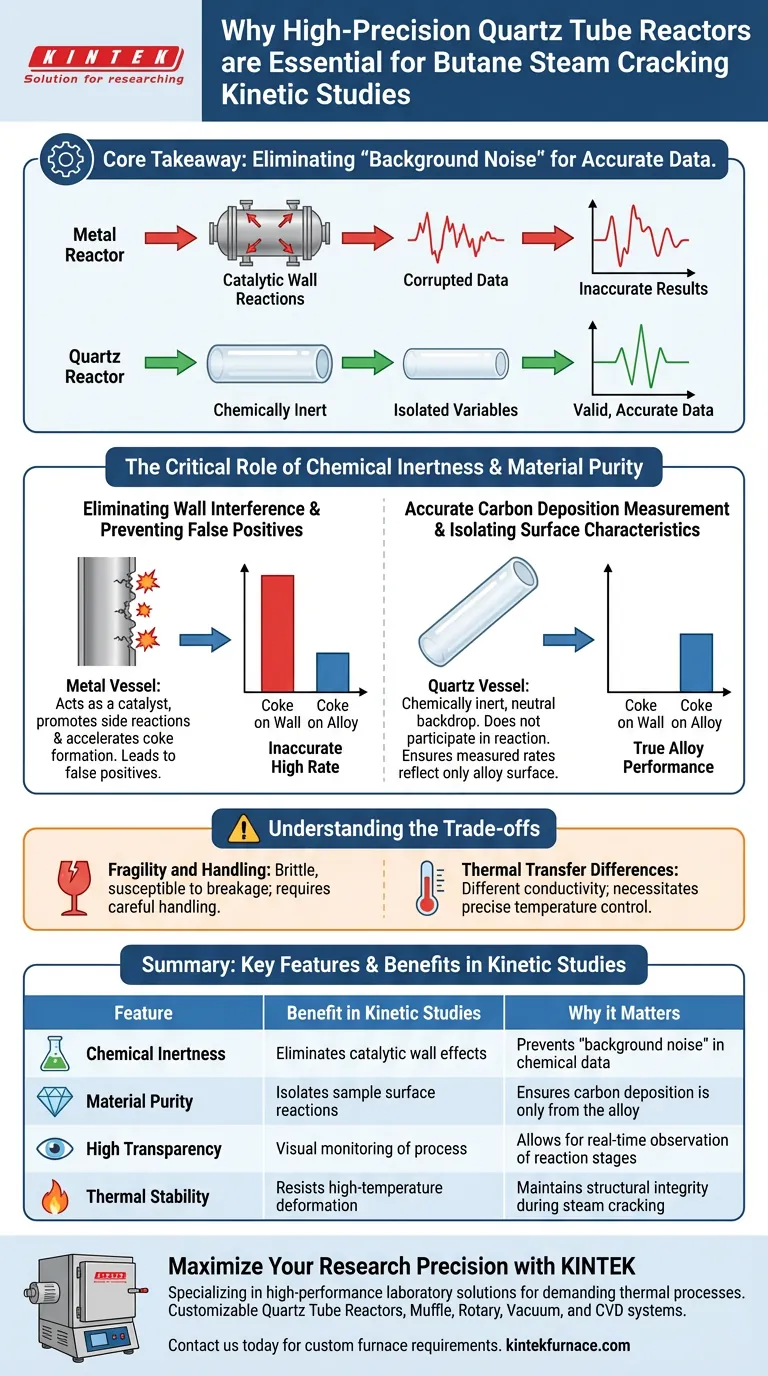
High-precision industrial quartz tube reactors are indispensable for butane steam cracking kinetic studies primarily due to their exceptional chemical inertness at elevated temperatures. Unlike metallic vessels, quartz prevents the reactor walls from acting as a catalyst during the reaction. This ensures that the data collected regarding carbon formation is accurate and uncorrupted by the vessel material itself.
Core Takeaway In kinetic studies, the validity of your data depends on isolating the variables. Quartz reactors eliminate "background noise" caused by wall reactions, ensuring that measured carbon deposition rates are solely a result of the alloy samples being tested, not the equipment holding them.
The Critical Role of Chemical Inertness
Eliminating Wall Interference
In high-temperature processes like butane steam cracking, the reactor vessel is not just a container; it is a potential participant in the chemical reaction.
Many standard industrial materials can catalytically promote side reactions or accelerate coke formation.
Quartz is chosen specifically because it remains chemically inert, meaning it does not participate in the reaction even under extreme thermal stress.
Accurate Carbon Deposition Measurement
A primary goal of these kinetic studies is to measure the rate at which carbon (coke) deposits on specific alloy samples.
If the reactor walls contribute to this deposition, it becomes impossible to distinguish which carbon formed on the alloy and which formed due to the walls.
By using quartz, researchers minimize this interference, ensuring the measured rates reflect only the surface characteristics of the alloy samples.
Why Material Purity Matters in Kinetic Studies
Isolating Surface Characteristics
Kinetic studies are often conducted to evaluate how different alloy compositions resist or promote coking.
To fairly compare these alloys, the environment must be neutral.
Quartz provides this neutral backdrop, allowing the unique surface properties of the alloy to be the only variable influencing the carbon formation process.
Preventing False Positives
Using a reactive vessel material could lead to "false positives," where an alloy appears to coke heavily, but the reaction is actually being driven by the reactor wall.
Quartz ensures that the data integrity is maintained, providing a clear picture of the alloy's performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Fragility and Handling
While quartz provides superior chemical data, it lacks the mechanical robustness of steel.
These reactors are brittle and susceptible to breakage if handled mishandled or subjected to rapid thermal shock.
Thermal Transfer Differences
Quartz has different thermal conductivity properties compared to metals.
While this does not affect the chemical inertness, it requires precise temperature control mechanisms to ensure the heating profile within the reactor remains consistent with industrial simulations.
Ensuring Data Integrity in Your Research
If your primary focus is Material Characterization:
- Prioritize the use of quartz to ensure that observed catalytic behaviors are exclusively attributable to the alloy being tested.
If your primary focus is Process Simulation:
- While quartz is ideal for kinetics, remember that industrial scalups use metal; use quartz studies to establish a baseline for "pure" reaction kinetics before introducing industrial variables.
By removing the reactor vessel as a variable, quartz allows you to trust that your kinetic data tells the true story of your alloy's performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit in Kinetic Studies | Why it Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Eliminates catalytic wall effects | Prevents "background noise" in chemical data |
| Material Purity | Isolates sample surface reactions | Ensures carbon deposition is only from the alloy |
| High Transparency | Visual monitoring of process | Allows for real-time observation of reaction stages |
| Thermal Stability | Resists high-temperature deformation | Maintains structural integrity during steam cracking |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Don't let reactor wall interference compromise your kinetic data. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance laboratory solutions tailored for the most demanding thermal processes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Quartz Tube Reactors, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet your unique material characterization needs.
Whether you are studying butane steam cracking or developing next-generation alloys, our systems provide the neutral environment required for absolute accuracy. Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements and see how our expertise can elevate your laboratory results.
Visual Guide
References
- Hamed Mohamadzadeh Shirazi, Kevin M. Van Geem. Effect of Reactor Alloy Composition on Coke Formation during Butane and Ethane Steam Cracking. DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.3c03180
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a Vertical Fluidized Bed Furnace ensure reaction stability? Key Mechanisms for Sulfur Oxidation Experiments
- What are the space-saving benefits of a tube furnace? Maximize Lab Efficiency with Compact Design
- What is the primary function of a single-temperature zone tube furnace in MoS2 CVD? Master Your Synthesis Process
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What critical reaction conditions does a tube furnace provide during the synthesis of SFC5 materials?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the ammonolysis process? Master TiNx Nanoparticle Synthesis
- Why is a quartz tube fixed-bed reactor ideal for VOC/Hydrogen combustion? Unlock High-Temp Precision & Stability
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance



















