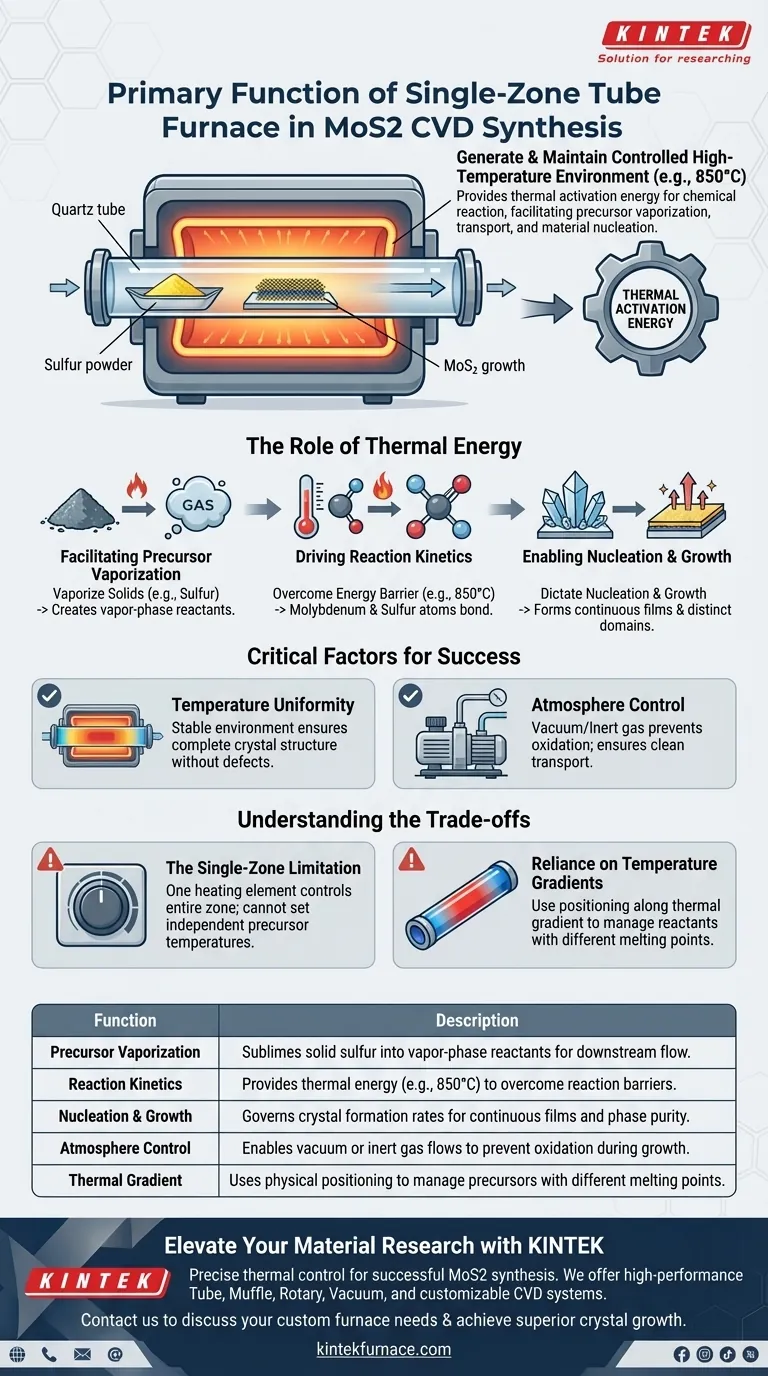
The primary function of a single-temperature zone tube furnace in this context is to generate and maintain a precisely controlled high-temperature environment required to drive the chemical reaction.
Specifically, the furnace heats the central reaction zone—often to temperatures such as 850°C—to simultaneously facilitate the vaporization of sulfur powder, transport precursor molecules via carrier gas, and provide the necessary kinetic energy for molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) to nucleate and grow on the target substrate.
Core Takeaway While the furnace acts as the physical vessel for the experiment, its operational purpose is to provide the thermal activation energy needed for the reaction. It converts solid precursors into vapor and governs the kinetics of crystallization, ensuring the final material achieves the correct phase purity and structural integrity.
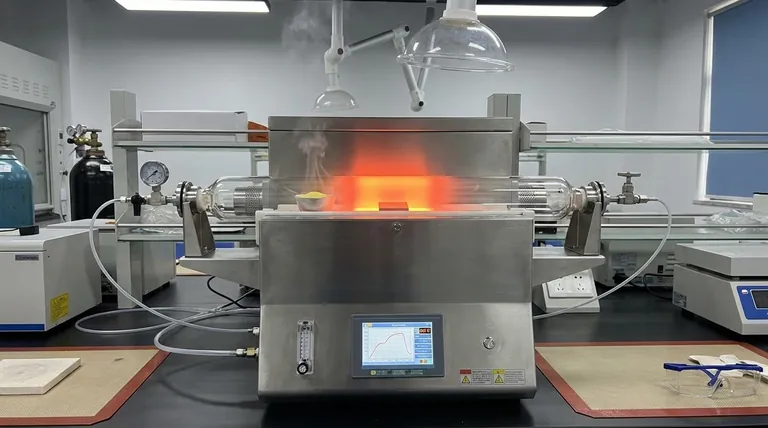

The Role of Thermal Energy in MoS2 Synthesis
Facilitating Precursor Vaporization
The synthesis of MoS2 typically begins with solid precursors, such as sulfur powder.
The tube furnace provides the thermal energy required to sublime or vaporize these solids. This creates the vapor-phase reactants necessary to flow downstream toward the substrate.
Driving Reaction Kinetics
Once the precursors are in the vapor phase, they must react chemically to form MoS2.
The furnace maintains the central reaction zone at a specific high temperature (e.g., 850°C). This high heat is critical for overcoming the energy barrier of the reaction, allowing the molybdenum and sulfur atoms to bond effectively.
Enabling Nucleation and Growth
Beyond simple bonding, the material must organize into a crystal structure.
The thermal energy provided by the furnace dictates the rate of nucleation (where crystals start) and growth (how they expand). Controlled heat ensures the formation of continuous films or distinct domains on the substrate.
Critical Factors for Success
Temperature Uniformity
In solid-state synthesis, the quality of the final product is heavily dependent on the stability of the environment.
A high-quality tube furnace ensures a high degree of temperature uniformity across the reaction zone. This uniformity is essential for ensuring the synthesized MoS2 has a complete crystal structure without significant defects.
Atmosphere Control
The furnace does not operate in isolation; it works in tandem with the internal atmosphere.
It allows for the maintenance of adjustable atmospheres, such as vacuum or inert gas flows. This prevents unwanted oxidation and ensures the transport of precursor molecules occurs in a clean, controlled environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Single-Zone Limitation
Using a single-temperature zone furnace presents a specific challenge regarding precursor management.
Because there is only one heating element controlling the entire zone, you cannot independently set different temperatures for the sulfur source and the substrate.
Reliance on Temperature Gradients
To manage reactants with different melting points in a single-zone setup, researchers must rely on positioning.
The sulfur precursor is often placed upstream, just outside the hottest central zone. This utilizes the natural temperature gradient of the tube (where it is cooler at the ends) to prevent the sulfur from vaporizing too quickly before the substrate reaches the optimal reaction temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a single-temperature zone furnace for MoS2 CVD, consider your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the substrate is positioned exactly in the center of the heating zone to maximize temperature uniformity and crystal structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Timing: Carefully calibrate the physical position of your sulfur precursor upstream to control its vaporization rate, as you cannot control its temperature electronically independent of the main zone.
Success in this process relies not just on reaching 850°C, but on understanding how that heat is distributed to control the state of your reactants.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Precursor Vaporization | Sublimes solid sulfur into vapor-phase reactants for downstream flow. |
| Reaction Kinetics | Provides thermal energy (e.g., 850°C) to overcome reaction barriers. |
| Nucleation & Growth | Governs crystal formation rates for continuous films and phase purity. |
| Atmosphere Control | Enables vacuum or inert gas flows to prevent oxidation during growth. |
| Thermal Gradient | Uses physical positioning to manage precursors with different melting points. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the backbone of successful MoS2 synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory research.
Whether you need a standard single-zone setup or a fully customizable high-temperature furnace for unique CVD requirements, our technical team is ready to assist. Achieve superior crystal growth and phase purity today—contact us now to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Feng Liao, Zewen Zuo. Optimizing the Morphology and Optical Properties of MoS2 Using Different Substrate Placement: Numerical Simulation and Experimental Verification. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15010059
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of temperature zoning for 1D ZnSe nanowires? Master Thermal Gradients for VLS Growth
- How do tube furnaces and isolation valves simulate TCOP experiments? Expert Setup for Thermochemical Oxygen Pumps
- What is the purpose of flushing a tube furnace with high-purity argon for hours? Ensure Pure Silicon Steel Results
- What is the primary role of a vacuum vertical tube furnace in the process of producing magnesium via carbothermal reduction? Enabling Efficient, High-Purity Metal Production
- What is the role of a dual-temperature zone tube furnace in MoS2 CVD growth? Mastering Precision 2D Synthesis
- What is the specific function of a high-temperature tube furnace for MXene-NiCo2Se4? Master the Selenization Process
- What are the technical advantages of using a tube furnace for carbon nitride? Master Advanced Defect Engineering
- Why is it necessary to precisely control the oxygen flow rate in a tube furnace? Optimize Li-Deficient Composites



















