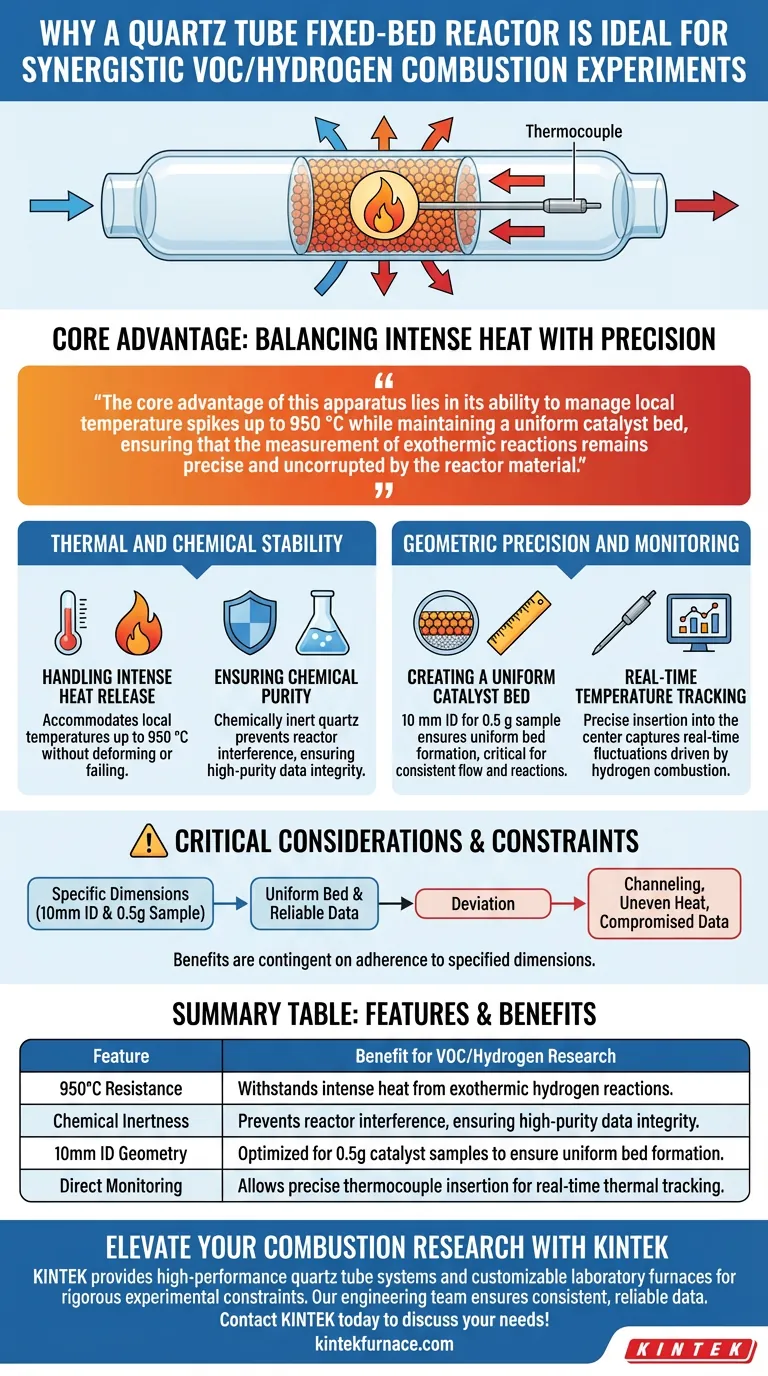
A quartz tube fixed-bed reactor is the optimal choice for these experiments because it combines exceptional high-temperature resistance with the specific geometry required for accurate thermal monitoring. It withstands the intense heat released during hydrogen combustion while providing a chemically inert environment that preserves data integrity.
The core advantage of this apparatus lies in its ability to manage local temperature spikes up to 950 °C while maintaining a uniform catalyst bed, ensuring that the measurement of exothermic reactions remains precise and uncorrupted by the reactor material.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
Handling Intense Heat Release
The synergistic combustion of aromatic VOCs with hydrogen is a highly exothermic process. This reaction generates significant localized heat that can damage standard laboratory equipment. The quartz tube is essential here, as it accommodates local temperatures up to 950 °C without deforming or failing.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
To determine the true efficiency of a catalyst, the reactor vessel must not participate in the reaction. Quartz is chemically inert, ensuring that it does not react with the aromatic VOCs or the hydrogen. This guarantees that all observed chemical changes are the result of the catalyst and the reactants alone.
Geometric Precision and Monitoring
Creating a Uniform Catalyst Bed
The physical dimensions of the reactor are not arbitrary; they are calibrated for specific sample sizes. A reactor with a 10 mm inner diameter is specifically designed to house a 0.5 g catalyst sample. This ratio ensures the formation of a uniform bed, which is critical for consistent flow and reaction rates.
Real-Time Temperature Tracking
Accurate data collection requires monitoring the center of the reaction, where the heat is most intense. The fixed-bed design allows for the precise insertion of a thermocouple directly into the center of the catalyst bed. This enables researchers to capture real-time temperature fluctuations driven by the rapid heat release of hydrogen combustion.
Critical Considerations and Constraints
Dependency on Specific Dimensions
The "ideal" nature of this setup relies heavily on the adherence to specific specifications. The benefits of bed uniformity are contingent on matching the 0.5 g sample size to the 10 mm inner diameter. Deviating from these dimensions can lead to channeling or uneven heat distribution, compromising the validity of the thermal data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your combustion experiments, ensure your setup aligns with your specific analytical needs:
- If your primary focus is thermal safety: Ensure your reaction parameters do not exceed the quartz local limit of 950 °C to prevent structural failure.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy: Strictly adhere to the 10 mm diameter and 0.5 g sample ratio to maintain bed uniformity and reliable thermocouple readings.
Success in synergistic combustion experiments depends on balancing thermal resilience with precise geometric configuration.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for VOC/Hydrogen Research |
|---|---|
| 950°C Resistance | Withstands intense heat release from exothermic hydrogen reactions. |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reactor interference, ensuring high-purity data integrity. |
| 10mm ID Geometry | Optimized for 0.5g catalyst samples to ensure uniform bed formation. |
| Direct Monitoring | Allows precise thermocouple insertion for real-time thermal tracking. |
Elevate Your Combustion Research with KINTEK
Precision is paramount when managing high-temperature VOC and hydrogen reactions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance quartz tube systems and customizable laboratory furnaces designed to meet your most rigorous experimental constraints. Whether you need standard dimensions or a bespoke thermal solution, our engineering team ensures your equipment delivers consistent, reliable data every time.
Ready to optimize your lab's performance? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace and reactor needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Lutf Ullah, Weizhen Li. Hydrogen Co-Combustion of Aromatic Volatile Organic Compounds over Pd/Al2O3 Catalyst. DOI: 10.3390/catal14090563
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of secondary calcination in a tube furnace? Enhance Cu@Zn-NC Adsorbent Longevity
- What are the advantages of using tubular furnaces? Achieve Precision and Versatility in Thermal Processing
- Why are a split furnace and a PID temperature controller core in supercritical water gasification? Essential Guide
- What conditions do tube furnaces provide for Au-Seeded TiO2 nanowires? Master Precision Thermal Synthesis
- What are the technical requirements for a Tube Furnace in nitrogen-doping? Essential Specs for Metal Oxide Processing
- What is a split tube furnace? Unlock Easy Access for Complex Lab Experiments
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in heavy metal adsorption research? Precision Thermal Simulation Guide
- What role does a Tube Furnace play in the solution treatment of titanium alloys? Master Material Integrity.



















