The primary advantages of a tubular furnace are its exceptional temperature uniformity, precise process control, and operational versatility. Their unique cylindrical design allows them to create a highly consistent thermal environment, while advanced controllers enable pinpoint accuracy for sensitive applications. This combination makes them suitable for everything from basic heat treatment to complex chemical vapor deposition.
A tubular furnace excels not just at heating, but at creating a highly controlled and repeatable micro-environment. It is an indispensable tool for advanced material science, research, and process development where precision is non-negotiable.

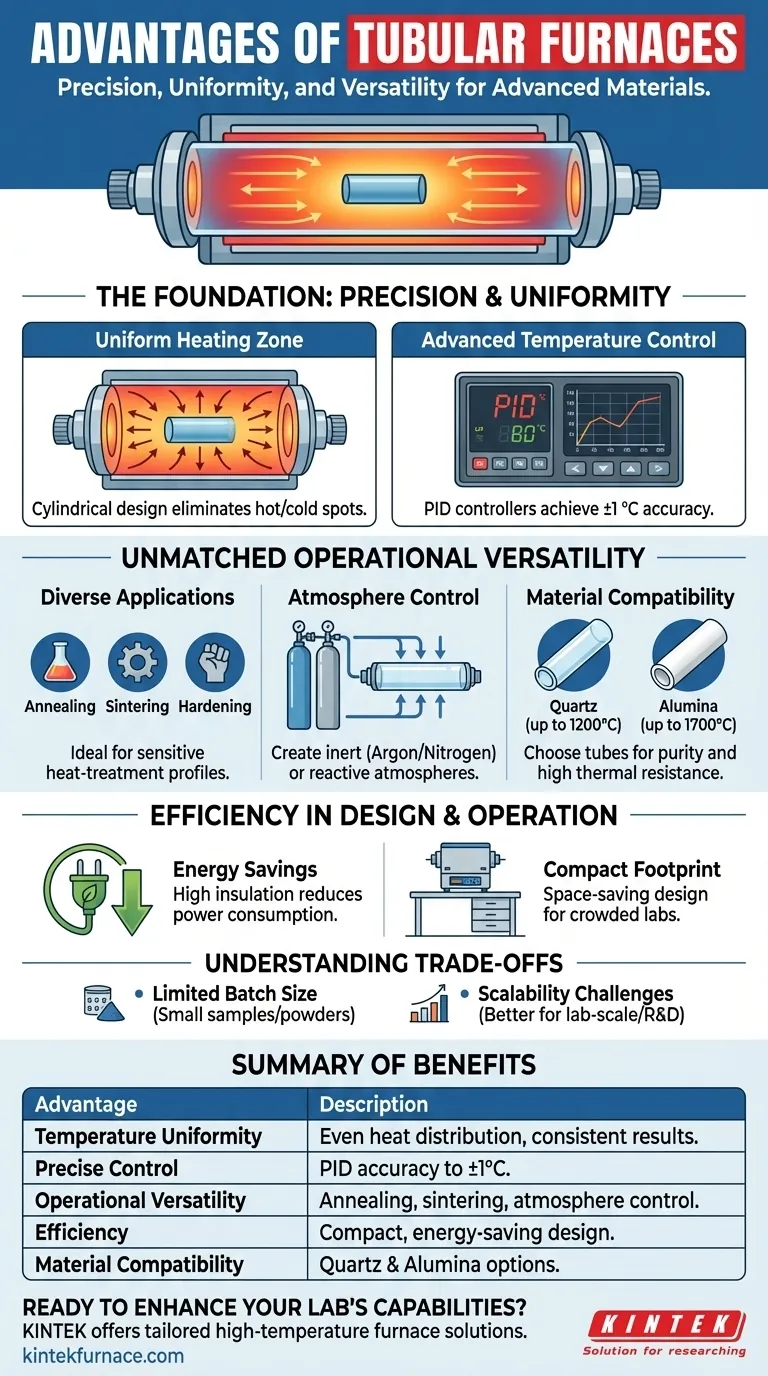
The Foundation: Precision and Uniformity
A tubular furnace's core strength lies in its ability to deliver heat exactly where and when it's needed. This precision is the foundation upon which all its other benefits are built.
Achieving a Uniform Heating Zone
The cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace is its defining feature. This shape naturally promotes even heat distribution around the sample placed inside the tube.
This design ensures that the entire sample experiences the same temperature, eliminating hot or cold spots that could compromise process results. This is critical for achieving consistent material properties.
The Role of Advanced Temperature Control
Modern tubular furnaces use sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers to manage temperature with extreme accuracy.
This allows operators to maintain a setpoint with deviations as small as ±1°C. It also enables precise control over heating and cooling rates, which is essential for processes like annealing and tempering.
Unmatched Versatility in Material Processing
Beyond simple heating, a tubular furnace is a versatile platform for a wide range of sophisticated thermal processes. Its design allows for precise manipulation of the sample's environment.
From Annealing to Sintering
These furnaces are workhorses for numerous applications. They are routinely used for processes like annealing (to soften materials), hardening (to increase strength), and sintering (to compact powders into a solid mass).
Their precise control makes them ideal for developing and repeating these sensitive heat-treatment profiles.
Mastering the Atmosphere
Many advanced processes require the absence of oxygen or the presence of a specific reactive gas. Tubular furnaces excel at atmosphere control.
By sealing the ends of the process tube and flowing a gas like argon or nitrogen, users can create an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation. They can also introduce reactive gases for chemical synthesis.
Compatibility with Various Materials
The choice of process tube material further enhances versatility. Quartz tubes are excellent for processes up to ~1200°C where high purity and visual monitoring are needed.
For higher temperatures, up to and beyond 1700°C, high-purity alumina tubes are used, providing exceptional thermal and chemical resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single piece of equipment is perfect for every task. To make an informed decision, it's critical to understand the limitations of a tubular furnace.
Batch Size and Sample Geometry
The primary constraint of a tubular furnace is its limited processing volume. It is ideal for smaller samples, powders, and wafers that fit within the diameter of the process tube.
It is not designed for bulk heat treatment of large or irregularly shaped parts, for which a batch or chamber furnace would be more appropriate.
Process Scalability
While excellent for lab-scale research, development, and small-batch production, scaling a tubular furnace process to very high volumes can be challenging. Its inherent design favors precision over sheer throughput.
Efficiency in Design and Operation
Modern tubular furnaces are engineered for efficiency, not just in energy consumption but also in their use of valuable laboratory space.
Thermal Efficiency and Energy Savings
High-quality insulation and efficient heating elements ensure that energy is focused on the sample, not wasted heating the surrounding room. This results in lower power consumption and faster heating and cooling cycles.
Compact and Space-Saving Footprint
Compared to larger chamber furnaces, tubular furnaces have a significantly smaller, more compact design. This makes them an ideal choice for crowded research labs where bench space is at a premium.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis: The unparalleled atmosphere control and temperature uniformity of a tubular furnace are essential.
- If your primary focus is repeatable quality control testing: The precise temperature cycling and data logging capabilities ensure consistent and reliable results.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab research: The versatility to handle various materials, atmospheres, and processes makes it a highly valuable and flexible tool.
By understanding these core advantages and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if a tubular furnace is the right instrument for your specific goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Cylindrical design ensures even heat distribution, eliminating hot/cold spots for consistent results. |
| Precise Control | Advanced PID controllers maintain temperature accuracy within ±1°C, ideal for sensitive processes. |
| Operational Versatility | Suitable for annealing, sintering, and atmosphere control with inert or reactive gases. |
| Efficiency | Compact design saves space, with high thermal insulation for energy savings and faster cycles. |
| Material Compatibility | Works with quartz tubes (up to 1200°C) and alumina tubes (up to 1700°C) for various applications. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a precision tubular furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for material science, research, and process development. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















