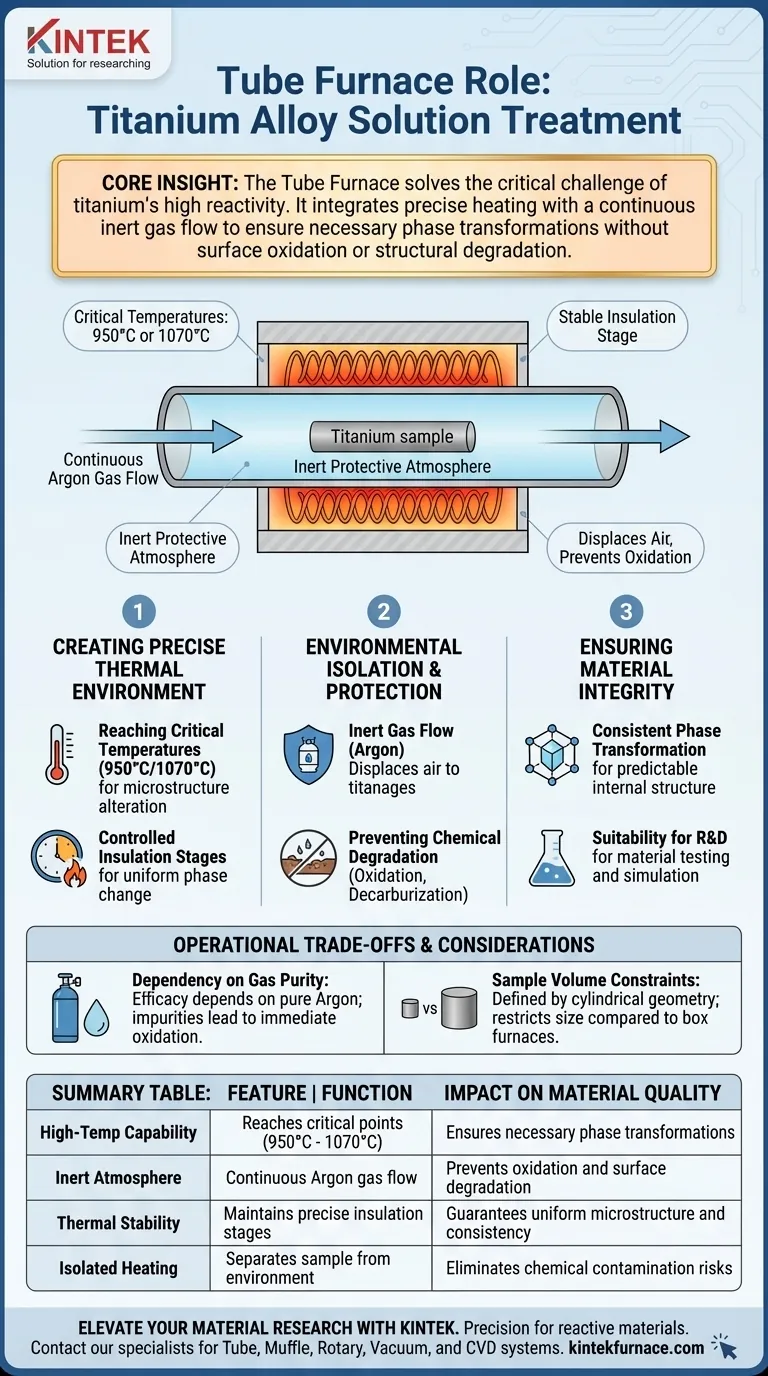
The Tube Furnace serves as the central heat treatment vessel for titanium alloys, facilitating solution treatment by maintaining a highly stable thermal environment. It allows samples to reach critical temperatures, such as 950°C or 1070°C, while simultaneously isolating the material from environmental contaminants through a controlled atmosphere.
Core Insight: The Tube Furnace solves the critical challenge of titanium’s high reactivity at elevated temperatures. By integrating precise heating with a continuous flow of inert gas, it ensures the alloy undergoes necessary phase transformations without suffering from surface oxidation or structural degradation.
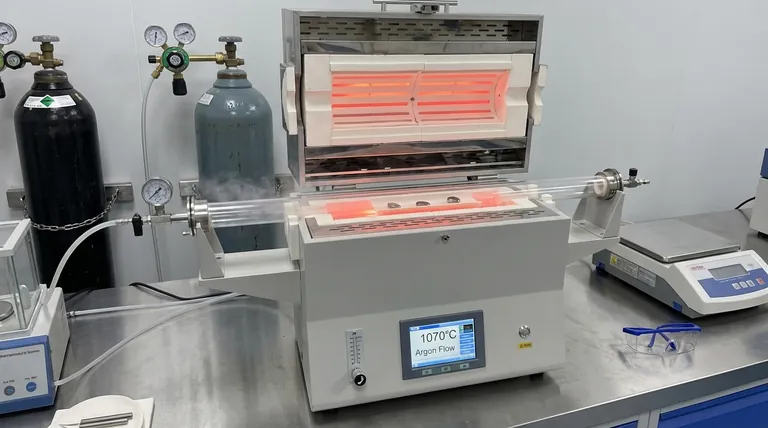

Creating a Precise Thermal Environment
Reaching Critical Solution Temperatures
To alter the microstructure of titanium alloys effectively, the material must be heated to specific solution treatment points.
The Tube Furnace is engineered to reliably reach and maintain these high temperatures, specifically standard benchmarks like 950°C or 1070°C.
Controlled Insulation Stages
Beyond simply reaching a peak temperature, the furnace maintains a stable "insulation stage."
This ensures the alloy is soaked at the target temperature for the exact duration required to initiate phase changes, ensuring uniformity throughout the sample.
Environmental Isolation and Protection
The Role of Inert Gas Flow
Heat alone is destructive to titanium due to its reactivity with oxygen.
The Tube Furnace counters this by maintaining a continuous flow of argon gas throughout the process. This displaces air and creates an inert protective atmosphere around the sample.
Preventing Chemical Degradation
Without this protective atmosphere, high temperatures would ruin the alloy's surface properties.
The furnace prevents surface oxidation and decarburization, two common defects that compromise the mechanical strength and fatigue resistance of titanium components.
Ensuring Material Integrity
Consistent Phase Transformation
The ultimate goal of solution treatment is to achieve a specific internal structure.
By controlling both heat and atmosphere, the Tube Furnace ensures that the phase transformation structures remain consistent and predictable after the treatment is complete.
Suitability for Research and Development
As noted in broader material science contexts, these furnaces are essential for periodic operations in laboratory settings.
They are the standard tool for element analysis and material testing, allowing researchers to simulate industrial hardening processes on a smaller, controlled scale.
Operational Trade-offs and Considerations
Dependency on Gas Purity
The efficacy of the Tube Furnace is entirely dependent on the quality of the inert atmosphere.
If the argon flow is interrupted or the gas is impure, the protective barrier fails, leading to immediate oxidation regardless of temperature accuracy.
Sample Volume Constraints
Tube furnaces are defined by their geometry—a cylindrical heating zone.
While excellent for samples, rods, and smaller components used in material testing, they may restrict the size and shape of the titanium parts you can treat compared to larger box furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a Tube Furnace in your titanium workflow, consider your specific objective:
- If your primary focus is surface integrity: Prioritize the calibration of the argon gas flow system to ensure zero oxygen ingress during the heating and cooling phases.
- If your primary focus is microstructural research: Leverage the furnace's precise temperature controls to test specific phase transformation points (e.g., exactly 950°C vs. 1070°C).
Success in treating titanium alloys relies not just on the heat applied, but on the rigorous protection of the material surface during the thermal cycle.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Titanium Solution Treatment | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Capability | Reaches critical points (950°C - 1070°C) | Ensures necessary phase transformations |
| Inert Atmosphere | Continuous Argon gas flow | Prevents oxidation and surface degradation |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains precise insulation stages | Guarantees uniform microstructure and consistency |
| Isolated Heating | Separates sample from environment | Eliminates chemical contamination risks |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when treating reactive materials like titanium. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the most demanding laboratory environments. Our furnaces offer the precise thermal control and atmospheric isolation required to prevent oxidation and ensure consistent phase transformations.
Whether you need a standard setup or a customizable system for unique research needs, KINTEK delivers the reliability your lab deserves. Consult with our specialists today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your workflow.
Visual Guide
References
- Ahmed H. Awad, Shimaa El‐Hadad. Studying the Behavior of Cast and Thermally Treated α + β -Titanium Alloys Using the Abbott Firestone Technique. DOI: 10.1007/s40962-024-01528-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What functions does a support frame provide in tube furnace modernization? Gain Stability and Experimental Flexibility
- What is the importance of segmented temperature control in a tube furnace for Cu/Zn-SAN? Master Atomic Dispersion
- What critical function does a high-temperature tube furnace perform for FCNCuM@CNT? Achieve FCC Phase Precision
- What are the advantages of Quartz Tube Furnaces in terms of customizability and specifications? Unlock Precision and Flexibility for Your Lab
- Why are inert gases used in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Process Precision
- How does a tube furnace facilitate the growth of controlled oxide layers on X70 carbon steel? Engineering Precision
- Why use a tube furnace for TiO2–TiN/S heat treatment? Achieve Perfect Sulfur Infusion and Purity
- What is the primary function of introducing high-purity argon into the tube furnace? Expert Pyrolysis Solutions



















