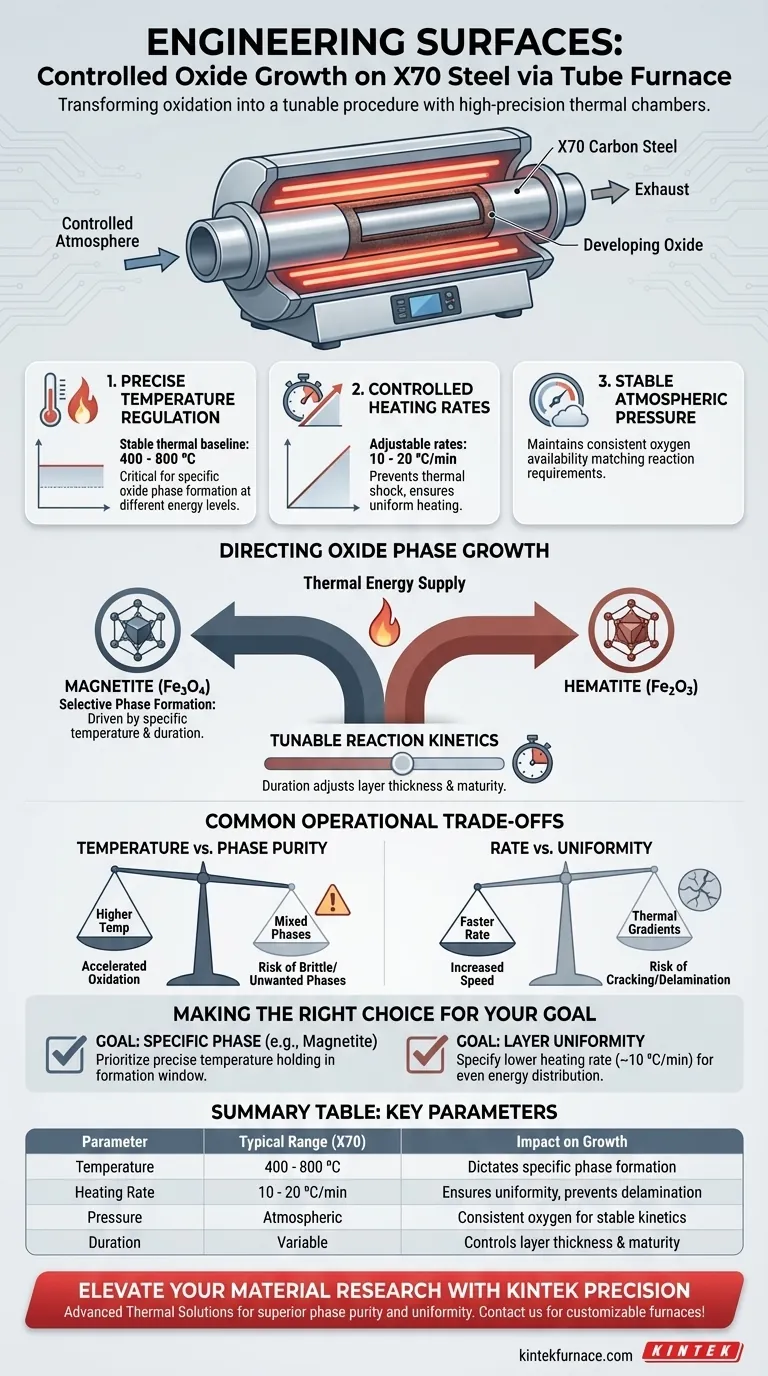
A tube furnace acts as a high-precision thermal chamber that facilitates controlled oxide growth by maintaining a stable environment at atmospheric pressure. By regulating critical variables—specifically temperature, heating rate, and duration—the furnace supplies the exact thermal energy required to induce specific oxidation reactions on the X70 carbon steel surface.
The tube furnace transforms the oxidation process from a random event into a tunable procedure. By precisely adjusting thermal parameters, you can dictate the kinetics of the reaction to selectively grow desired oxide phases, such as magnetite or hematite.

Creating the Ideal Reaction Environment
To grow a uniform and specific oxide layer, the heating environment must be strictly controlled. The tube furnace achieves this through three primary mechanisms.
Precise Temperature Regulation
The furnace provides a stable thermal baseline, typically operating between 400 and 800 ⁰C for X70 steel applications.
This specific temperature range is critical because different oxide phases form at different energy levels.
Controlled Heating Rates
Rather than subjecting the steel to thermal shock, the furnace allows for adjustable heating rates, commonly set between 10 and 20 ⁰C/min.
This gradual ramp-up ensures the material reaches the target temperature uniformly, preventing uneven surface reactions.
Stable Atmospheric Pressure
The equipment operates effectively at atmospheric pressure, simplifying the oxidation process.
It maintains this pressure consistently throughout the treatment, ensuring the availability of oxygen matches the reaction requirements.
Directing Oxide Phase Growth
The ultimate goal of using a tube furnace is not just to heat the steel, but to engineer its surface properties.
Selective Phase Formation
The precise thermal energy supplied by the furnace dictates which iron oxide polymorphs will grow.
By manipulating the temperature and duration, you can drive the formation of specific phases like magnetite or hematite.
Tunable Reaction Kinetics
The furnace allows you to adjust the duration of the heat treatment to control the thickness and maturity of the oxide layer.
This "constant temperature duration" ensures the reaction proceeds to the desired extent without over-oxidizing the substrate.
Common Operational Trade-offs
While a tube furnace offers high precision, achieving the correct oxide layer requires balancing competing variables.
Temperature vs. Phase Purity
Higher temperatures generally accelerate oxidation, but they may lead to the formation of mixed oxide phases if not strictly monitored.
If the temperature drifts outside the 400-800 ⁰C window, you risk growing unwanted brittle phases rather than the protective layers intended.
Rate vs. Uniformity
A faster heating rate (e.g., exceeding 20 ⁰C/min) increases process speed but can result in thermal gradients across the X70 steel sample.
These gradients can cause the oxide layer to crack or delaminate during growth, compromising the surface integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To effectively use a tube furnace for X70 carbon steel oxidation, align your settings with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is growing a specific phase (e.g., Magnetite): Prioritize precise temperature holding within the specific formation window for that phase, ensuring no deviations occur during the dwell time.
- If your primary focus is layer uniformity: specific a lower heating rate (closer to 10 ⁰C/min) to ensure the thermal energy is distributed evenly across the steel surface before the peak temperature is reached.
Success in growing controlled oxide layers relies on viewing the tube furnace not as a heater, but as a precision instrument for chemical surface engineering.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range for X70 Steel | Impact on Oxide Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 400 - 800 ⁰C | Dictates specific phase formation (e.g., Magnetite vs. Hematite) |
| Heating Rate | 10 - 20 ⁰C/min | Ensures surface uniformity and prevents layer delamination |
| Pressure | Atmospheric | Maintains consistent oxygen availability for stable reaction kinetics |
| Duration | Variable | Controls the final thickness and maturity of the oxide layer |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your surface engineering projects with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Whether you are growing specialized oxide layers on X70 carbon steel or developing complex thin films, our high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems provide the industry-leading stability and control you require.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our furnaces are engineered for superior temperature uniformity and precision.
- Tailored Solutions: We offer fully customizable systems to meet your unique laboratory or industrial needs.
- Proven Performance: Trusted by researchers worldwide for high-temperature material processing.
Ready to achieve superior phase purity and layer uniformity? Contact us today to consult with our experts and find the perfect customizable furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
References
- Umi Zalilah, Mazli Mustapha. TAGUCHI OPTIMIZATION OF X70 CARBON STEEL HEAT TREATMENT: A STUDY ON HARDNESS, THICKNESS AND PHASE ANALYSIS. DOI: 10.11113/jurnalteknologi.v87.23474
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What accessories are typically included with a three-zone split tube furnace? Essential Tools for Safe Operation
- What is the specific role of a tube furnace in the synthesis and carbon-encapsulation of NiMo alloys? Explained
- How do you clean an alumina tube furnace? Ensure Peak Performance & Longevity
- What is the role of an industrial tubular furnace in the thermal treatment of municipal sludge? Expert Lab Insights
- What materials are used for the tubes in drop tube furnaces and why? Choose the Right Tube for High-Temp Success
- Why is a tube furnace required for PET carbonization? Achieve High-Surface Area Activated Carbon with Precise Control
- What industries commonly use horizontal furnaces? Unlock High-Temperature Processing for Your Sector
- What are the advantages of using a fixed-bed continuous flow tube reaction system? Unlock Precision CO2 Hydrogenation



















