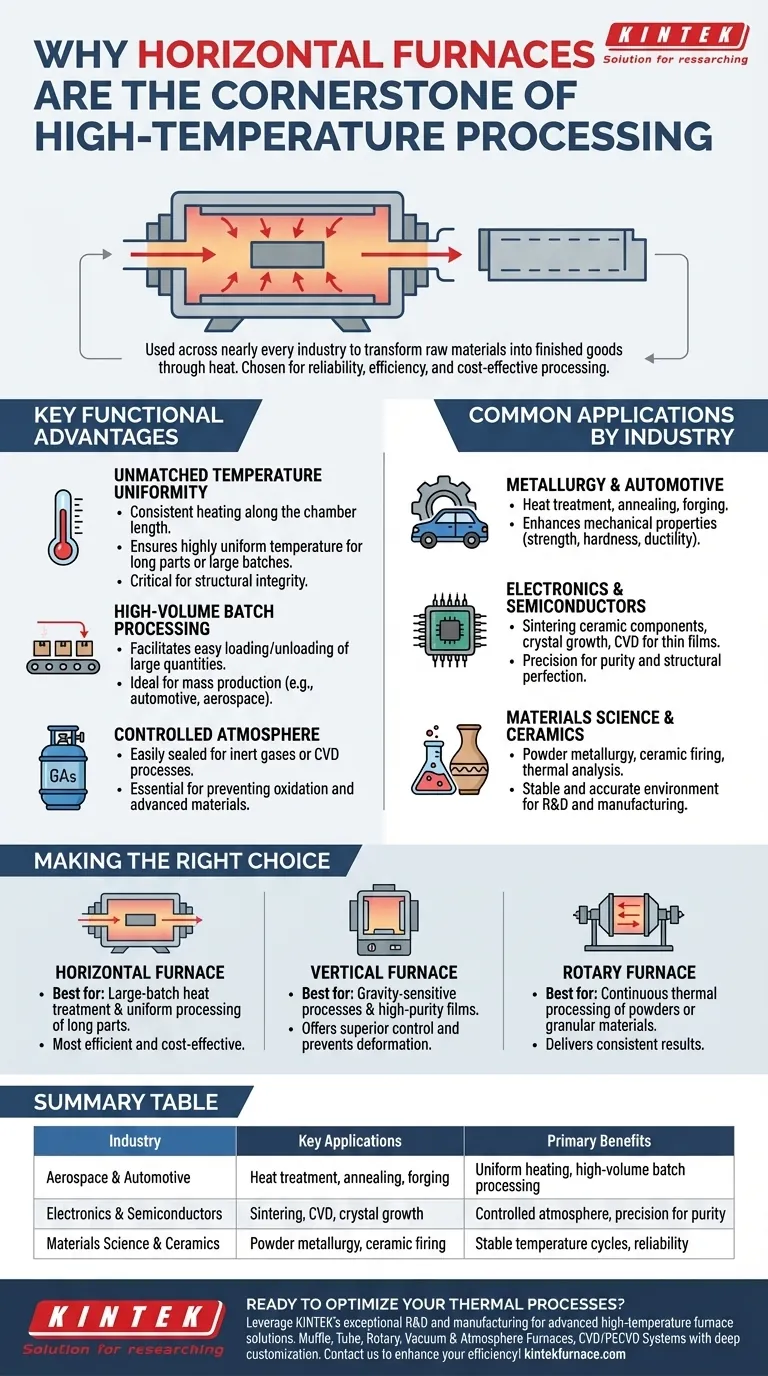
At a high level, horizontal furnaces are a cornerstone technology in nearly every industry that transforms raw materials into finished goods through heat. They are widely used in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, electronics manufacturing, materials science, metallurgy, and ceramics for their reliability and efficiency in high-temperature processing.
The specific industry is less important than the underlying process. Horizontal furnaces are chosen for their ability to deliver highly uniform heat across large batches or long parts, making them the default choice for cost-effective heat treatment, annealing, and sintering operations.

Why Horizontal Furnaces Are a Standard in Key Industries
The widespread adoption of horizontal furnaces is not accidental. It stems from a combination of functional design advantages that make them ideal for specific, high-volume industrial processes.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The horizontal configuration allows for consistent heating elements to be placed along the length of the chamber. This design ensures that parts, whether they are long shafts or trays of small components, experience a highly uniform temperature profile.
This uniformity is critical for processes like annealing and heat treating, where even small temperature deviations can compromise the structural integrity of the final product.
High-Volume and Batch Processing
Horizontal furnaces are exceptionally well-suited for batch processing. Their design facilitates easy loading and unloading of large quantities of materials, often on trays or conveyors.
This capability makes them highly cost-effective for mass production environments, such as those found in the automotive and aerospace industries, where thousands of identical parts must be treated consistently.
Controlled Atmosphere for Advanced Materials
Many modern applications require processing in a tightly controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation or introduce specific reactive gases. Horizontal tube furnaces excel at this.
They can be easily sealed and purged with inert gases like argon or nitrogen, or used for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which is fundamental in the semiconductor, optics, and advanced coatings industries.
Common Applications by Industry Sector
While the principles are universal, the specific applications highlight why horizontal furnaces are so prevalent.
Metallurgy and Automotive
In metallurgy, these furnaces are workhorses. They are used for forging, annealing, and heat treatment to enhance the mechanical properties of metals, improving their strength, hardness, and ductility. The automotive industry relies on this for everything from engine components to structural frames.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The electronics sector depends on the precision of horizontal furnaces. They are used for sintering ceramic components, growing crystals, and depositing thin films via CVD to create semiconductors and other electronic components where purity and structural perfection are paramount.
Materials Science and Ceramics
For researchers and manufacturers in materials science, horizontal furnaces provide the stable and accurate environment needed for developing new materials. Processes like powder metallurgy, ceramic firing, and thermal analysis rely on the furnace's ability to execute precise temperature cycles repeatedly.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Horizontal vs. Other Furnace Types
Choosing a furnace is about matching the tool to the task. While horizontal furnaces are versatile, other configurations exist for specialized needs.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Workhorse for Batches
Their primary advantage is uniform heating for large or long items in a batch configuration. Their simple, robust design often leads to lower maintenance and high reliability for general-purpose heat treatment.
Vertical Furnaces: Precision for Gravity-Sensitive Processes
Vertical furnaces are preferred when gravity can aid the process, such as in certain crystal growth applications or when trying to minimize part distortion at high temperatures. They are common in nanotechnology and some chemical processing where precise temperature gradients are required from top to bottom.
Rotary Furnaces: Continuous Processing for Powders
When the material is a powder or granular substance that needs to be tumbled for uniform exposure, a rotary furnace is the ideal choice. These are used for continuous processes like calcination and oxidation in metallurgy and chemical manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be driven entirely by the requirements of your thermal process, not by industry convention alone.
- If your primary focus is large-batch heat treatment or uniform processing of long parts: A horizontal furnace is almost always the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity films or processing gravity-sensitive materials: A vertical furnace may offer superior control and prevent unwanted material deformation.
- If your primary focus is continuous thermal processing of powders or granular materials: A rotary furnace is specifically designed for this task and will deliver the most consistent results.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is about understanding the physics of your application and choosing the design that best controls the flow of heat for your specific material and desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Automotive | Heat treatment, annealing, forging | Uniform heating, high-volume batch processing |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Sintering, CVD, crystal growth | Controlled atmosphere, precision for purity |
| Materials Science & Ceramics | Powder metallurgy, ceramic firing | Stable temperature cycles, reliability |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, electronics, or materials science, contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results! Contact us now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















