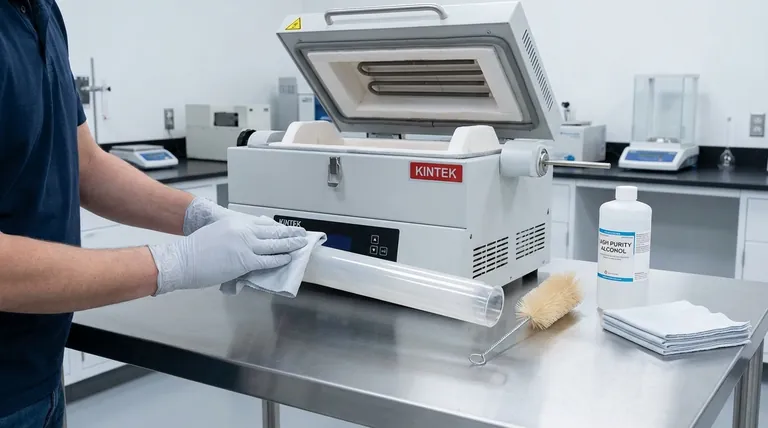
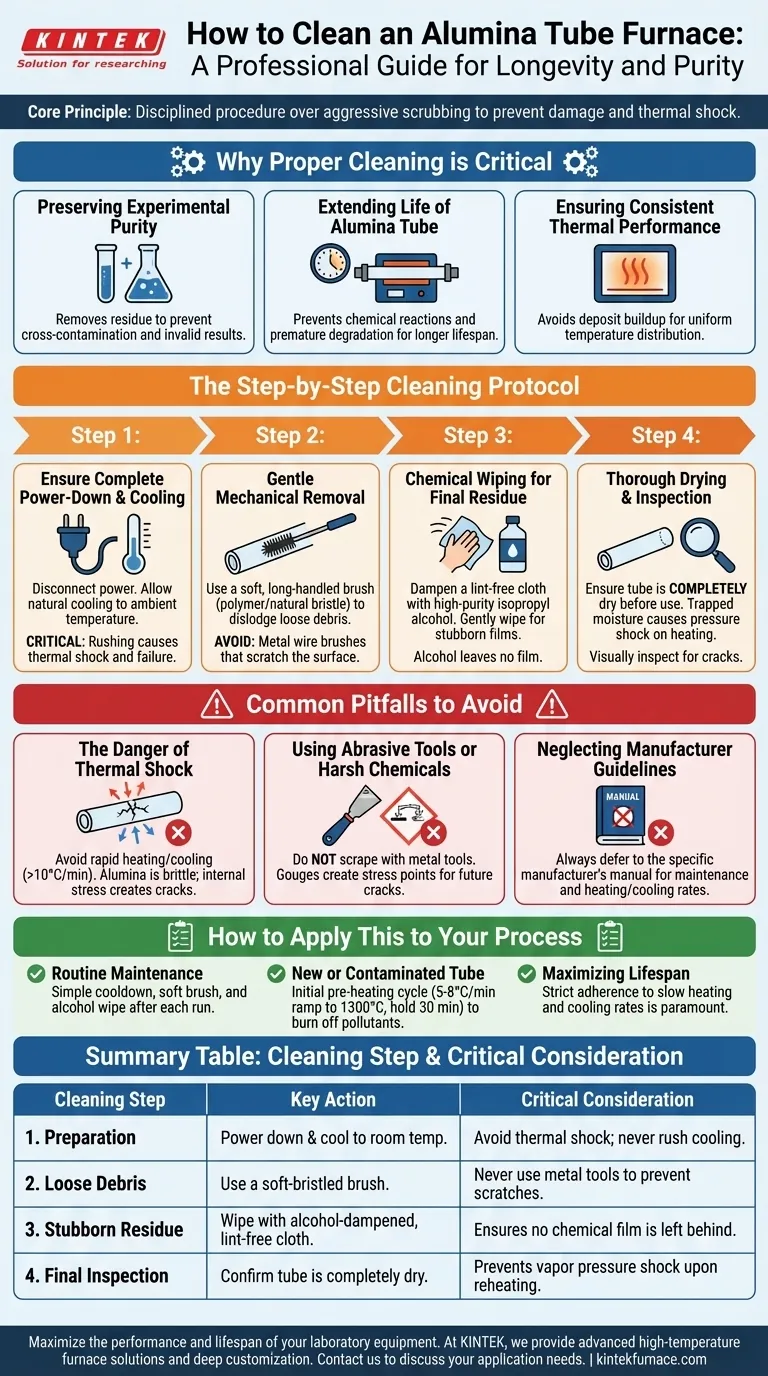
To properly clean an alumina tube furnace, you must first ensure the furnace is turned off, disconnected from power, and has cooled completely to room temperature. Once cool, use a soft-bristled brush to gently dislodge loose debris and deposits from the inner walls. For any remaining residue, wipe the tube with a soft, lint-free cloth lightly dampened with alcohol, and allow it to dry completely before its next use.
The core principle of cleaning an alumina tube is not aggressive scrubbing but disciplined procedure. Your primary goal is to remove contaminants without introducing physical damage or, most importantly, thermal shock, which can crack the tube and ruin your equipment.

Why Proper Cleaning is Critical
Understanding the purpose behind the procedure helps ensure the longevity and accuracy of your furnace. Alumina is chosen for its high-temperature resilience and chemical inertness, but it is not indestructible.
Preserving Experimental Purity
Any residue left from a previous process can become a contaminant in your next experiment. Cross-contamination can invalidate results, especially in sensitive material science or chemical synthesis applications.
Extending the Life of Your Alumina Tube
Regular, gentle cleaning prevents the buildup of materials that could chemically react with the alumina at high temperatures over long periods. This proactive maintenance helps avoid premature degradation and extends the tube's operational lifespan.
Ensuring Consistent Thermal Performance
A thick layer of deposits can act as an insulator, creating uneven temperature distribution along the tube. This disrupts the uniform heating environment that is one of the key functions of a high-quality tube furnace.
The Step-by-Step Cleaning Protocol
Follow this sequence rigorously to ensure both safety and effectiveness. Always defer to your specific furnace manufacturer's guidelines if they differ.
Step 1: Ensure Complete Power-Down and Cooling
Before any physical contact, disconnect the furnace from its power source. Allow the tube to cool down naturally to ambient temperature. Rushing this step is the single most common cause of tube failure.
Step 2: Gentle Mechanical Removal
Use a soft, long-handled brush (like a polymer or natural bristle tube brush) to sweep out any loose powders or deposits. Never use a metal wire brush, as this will scratch and weaken the alumina surface.
Step 3: Chemical Wiping for Final Residue
For stubborn films or residue, dampen a lint-free cloth with a high-purity solvent like isopropyl alcohol. Wipe the interior surface gently. The alcohol acts as a solvent to lift contaminants without leaving a film of its own.
Step 4: Thorough Drying and Inspection
Ensure the tube is completely dry before reinstalling it or running the next heating cycle. Trapped moisture or solvent can vaporize rapidly upon heating, creating a pressure shock that can crack the tube. Visually inspect for any new cracks or damage.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes during operation or cleaning are more damaging than the process itself. Understanding these risks is essential.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
Alumina, while resistant to high heat, is a ceramic material that is brittle and highly susceptible to thermal shock. Rapid heating or cooling creates internal stress that leads to cracks.
As a rule, heating and cooling rates should not exceed 10°C per minute. A slow, controlled cooldown is just as important as a slow, controlled heat-up.
Using Abrasive Tools or Harsh Chemicals
Avoid the temptation to scrape baked-on deposits with metal tools. This will inevitably gouge the tube's surface, creating stress points where cracks will form during future thermal cycles. Stick to soft brushes or, for extreme cases, a piece of soft wood or plastic.
Neglecting Manufacturer Guidelines
The information provided here is a general guide. Your furnace manufacturer has performed extensive testing on their specific alumina composition and furnace design. Their manual is your ultimate source of truth for maintenance procedures and heating/cooling rates.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your cleaning and maintenance strategy should align with your specific use case.
- If your primary focus is routine maintenance: A simple cooldown, soft brush, and alcohol wipe after each run is the most effective and safe procedure.
- If your primary focus is preparing a new or contaminated tube: Perform an initial pre-heating cycle by ramping temperature at 5-8°C/min to 1300°C and holding for 30 minutes to burn off manufacturing pollutants or unknown residues.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan: Adhering strictly to slow heating and cooling rates is more critical than any other single factor.
Proper maintenance is the key to ensuring your furnace delivers safe, reliable, and repeatable results for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Cleaning Step | Key Action | Critical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Power down & cool to room temperature. | Avoid thermal shock; never rush cooling. |
| 2. Loose Debris | Use a soft-bristled brush. | Never use metal tools to prevent scratches. |
| 3. Stubborn Residue | Wipe with alcohol-dampened, lint-free cloth. | Ensures no chemical film is left behind. |
| 4. Final Inspection | Confirm tube is completely dry. | Prevents vapor pressure shock upon reheating. |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your laboratory equipment.
At KINTEK, we understand that precise and reliable results depend on well-maintained tools. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability allows us to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Let our expertise support your research. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application needs and discover how our robust furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















