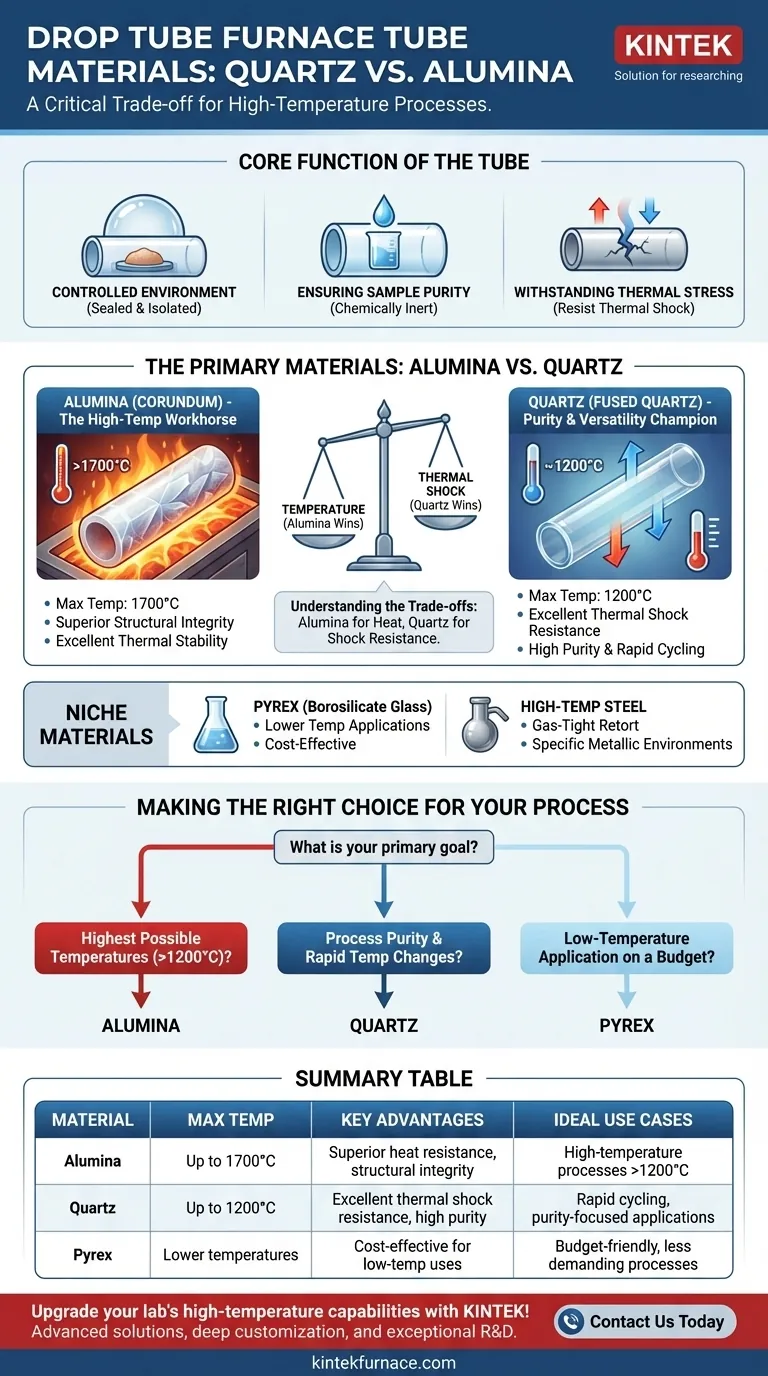
The choice of tube material in a drop tube furnace is critical, as it directly impacts the success and integrity of the high-temperature process. The tubes are almost always made from quartz or alumina (corundum). These materials are selected because they can withstand extreme temperatures and resist chemical reactions, ensuring the sample remains pure and uncontaminated by the tube itself.
The decision between quartz and alumina is not arbitrary; it's a critical trade-off. Alumina is chosen for its superior heat resistance at the highest temperatures, while quartz is favored for its exceptional ability to handle rapid temperature changes without cracking.
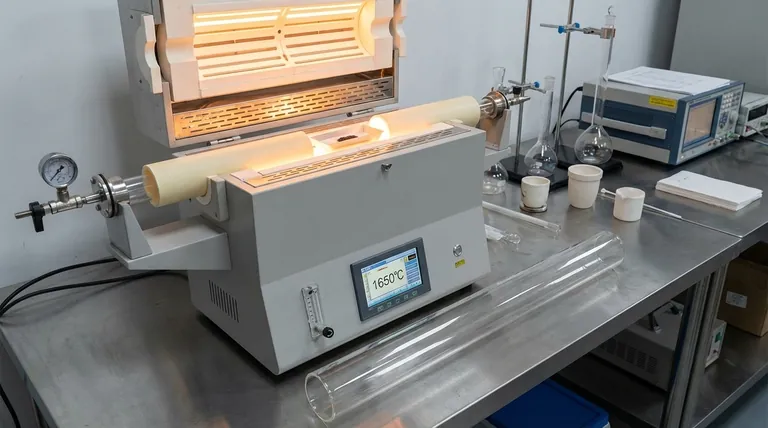

The Core Function of the Furnace Tube
Before comparing materials, it's essential to understand the tube's role. It is not merely a container; it is an engineered component that performs several critical functions.
Creating a Controlled Environment
The primary job of the tube is to create a sealed, isolated environment. It separates the sample from the furnace's heating elements and the outside atmosphere, allowing for precise control over the process conditions, such as working under a vacuum or in a specific gas.
Ensuring Sample Purity
The tube material must be chemically inert. At high temperatures, reactivity increases dramatically, and the wrong material could leach impurities into your sample, corrupting experimental results.
Withstanding Thermal Stress
The tube must maintain its structural integrity during rapid heating and cooling cycles. The ability to endure this thermal shock without fracturing is a key performance characteristic that varies significantly between materials.
Comparing the Primary Tube Materials
While other materials exist for specific applications, the choice for most drop tube furnaces comes down to a decision between alumina and quartz.
Alumina (Corundum): The High-Temperature Workhorse
Alumina is the go-to material when the absolute highest temperatures are required, often rated for continuous use up to 1700°C.
Its primary advantage is its excellent thermal stability and structural integrity at extreme temperatures where other materials would fail.
Quartz (Fused Quartz): The Purity & Versatility Champion
Quartz is an extremely versatile material known for its high purity and exceptional thermal shock resistance. It can be heated and cooled very quickly without the risk of cracking.
However, its temperature limit is lower than alumina's, typically around 1200°C for continuous use. It is the ideal choice for a wide range of processes that demand purity and rapid cycling below this temperature threshold.
Other Niche Materials
Pyrex is a type of borosilicate glass that can be used for lower-temperature applications, but it lacks the thermal resistance of quartz or alumina.
High-temperature resistant steel is sometimes used to construct a gas-tight "retort," particularly in furnaces where a metallic environment is acceptable or desired, but it is less common for standard, high-purity laboratory drop tube furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right material requires balancing competing priorities. An ideal material for one application may be entirely unsuitable for another.
Temperature vs. Thermal Shock
This is the most critical trade-off. Alumina can go to higher temperatures, but it is more susceptible to cracking if heated or cooled too quickly. Quartz cannot reach the same peak temperatures, but its low thermal expansion coefficient makes it incredibly resistant to thermal shock.
Chemical Compatibility
Both quartz and alumina are highly inert, but their compatibility with specific aggressive chemicals at high temperatures can differ. The exact chemical nature of your process should be cross-referenced with the material's chemical resistance charts.
Cost and Handling
Alumina tubes are often more robust and resistant to devitrification (crystallization) at high temperatures. Quartz, while incredibly strong against thermal shock, is a glass-ceramic that can be more fragile to mechanical impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific process parameters will dictate the correct material choice. To simplify the decision, consider your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (above 1200°C): Alumina (corundum) is the necessary choice for its unparalleled thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is process purity and rapid temperature changes: Quartz is the superior option, provided your operating temperature remains below approximately 1200°C.
- If your primary focus is a low-temperature application on a tight budget: Pyrex can be a viable alternative for less demanding processes.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to select the precise tube that ensures the safety, integrity, and success of your high-temperature experiments.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Up to 1700°C | Superior heat resistance, structural integrity at high temps | High-temperature processes above 1200°C |
| Quartz | Up to 1200°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance, high purity | Rapid temperature cycling, purity-focused applications |
| Pyrex | Lower temperatures | Cost-effective for low-temp uses | Budget-friendly, less demanding processes |
Upgrade your lab's high-temperature capabilities with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your process efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















