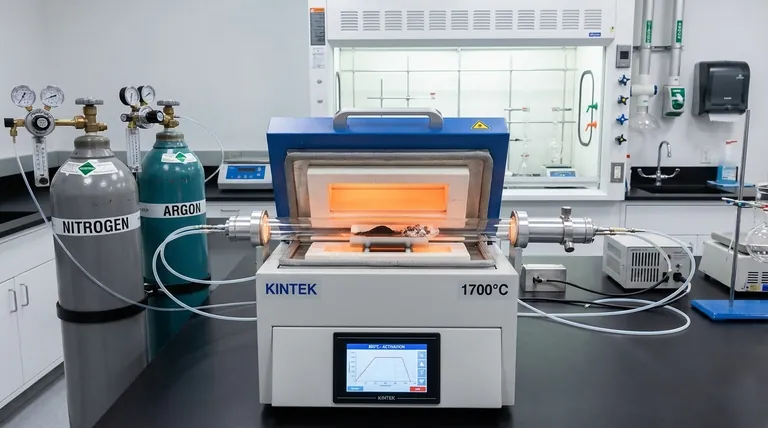
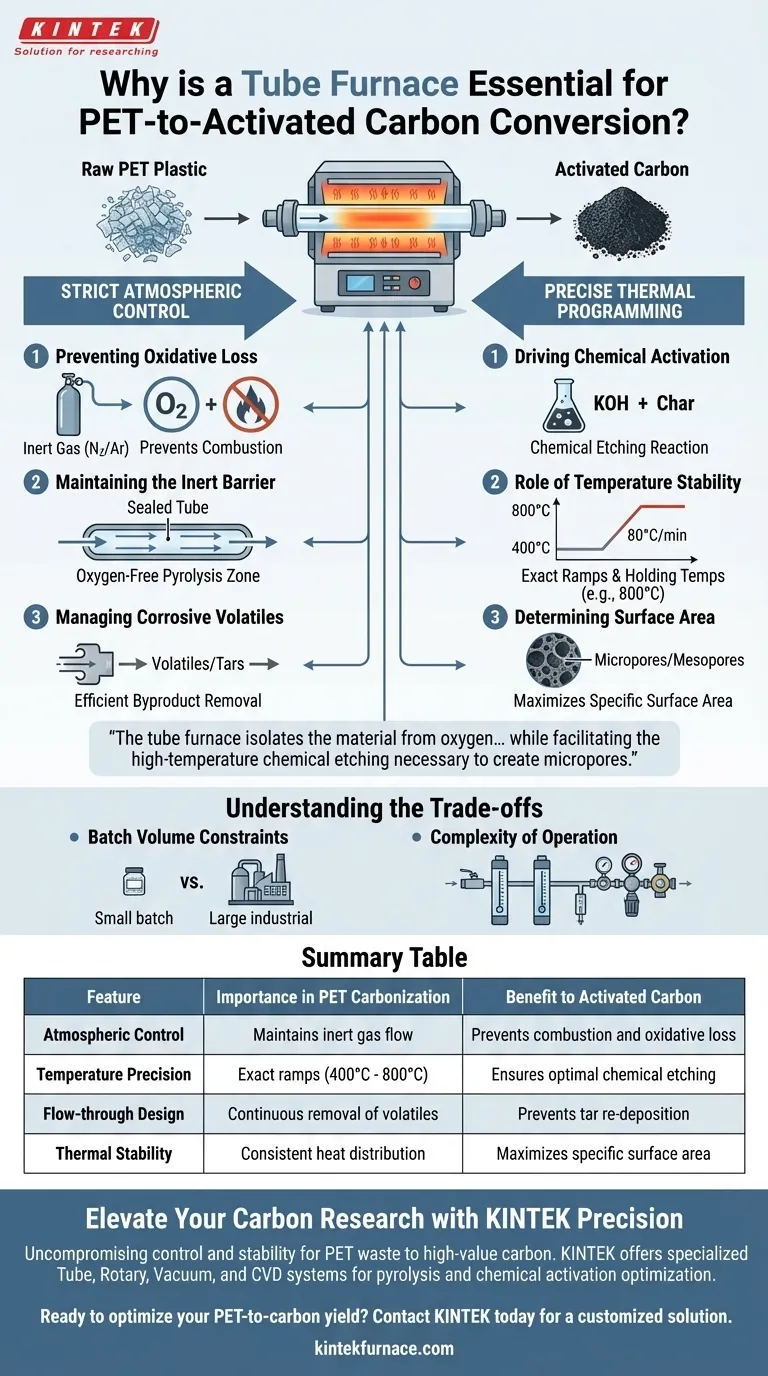
A tube furnace is the fundamental processing tool for this application because it provides the two non-negotiable conditions required to convert PET plastic into activated carbon: strict atmospheric control and precise thermal programming. Specifically, it enables the maintenance of a continuously flowing inert environment (usually nitrogen or argon) which prevents the carbon from burning away via oxidation, while simultaneously delivering the exact temperatures (between 400°C and 800°C) needed to drive the chemical kinetics of pyrolysis and pore formation.
The quality of PET-derived activated carbon—defined by its surface area and pore structure—is determined by how strictly you control the reaction environment. A tube furnace isolates the material from oxygen to prevent combustion while facilitating the high-temperature chemical etching necessary to create micropores.

The Criticality of Atmospheric Control
Preventing Oxidative Loss
The most immediate risk when heating carbon-rich materials like PET to high temperatures is oxidation. In the presence of oxygen, carbon at 800°C does not activate; it combusts, turning into carbon dioxide and ash.
Maintaining the Inert Barrier
A tube furnace solves this by sealing the sample within a tube (often quartz or alumina) and purging it with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This creates an oxygen-free zone where the material can undergo thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) rather than burning, preserving the carbon skeleton that serves as the base for the final product.
Managing Corrosive Volatiles
During the breakdown of PET and subsequent activation, volatile components and gases are released. The flow-through design of a tube furnace allows these byproducts to be efficiently swept away by the carrier gas. This prevents the re-deposition of tars onto the carbon surface and protects the heating elements from corrosive damage.
Precision Heating and Reaction Kinetics
Driving Chemical Activation
Creating activated carbon often involves chemical agents, such as potassium hydroxide (KOH), which are mixed with the PET-derived char. This is not a passive heating process; it is a chemical etching reaction.
The Role of Temperature Stability
The tube furnace allows for specific, programmed heating rates (e.g., 80°C/min) and holds precise temperatures (e.g., 800°C). This thermal precision drives the redox reactions between the activator and the carbon matrix. These reactions "eat" into the carbon structure, creating a vast network of micropores and mesopores.
Determining Surface Area
The ultimate specific surface area of the material is directly linked to this thermal profile. If the temperature fluctuates or is too low, the etching is incomplete. If it is too uncontrolled, the pore structure may collapse. The tube furnace ensures the chemical equilibrium required to maximize surface area.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Batch Volume Constraints
While tube furnaces offer superior control over atmosphere and temperature, they are typically limited in volume. They are ideal for high-precision batch processing but may act as a bottleneck for high-throughput industrial production compared to rotary kilns.
Complexity of Operation
Unlike simple muffle furnaces, a tube furnace requires a peripheral gas management system. You must manage gas cylinders, flow meters, and regulators to ensure a continuous, precise flow of nitrogen or argon. Failure in the gas delivery system immediately compromises the batch quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you are selecting the correct equipment configuration for your PET carbonization project, consider your specific end-goals:
- If your primary focus is maximizing surface area: Prioritize a tube furnace with high-precision PID temperature controllers to strictly regulate the activation temperature (e.g., 800°C) for optimal pore etching.
- If your primary focus is surface chemistry modification: Ensure your tube furnace supports variable gas atmospheres, allowing you to switch between inert gases (like Nitrogen) and potentially reactive gases to functionalize the carbon surface.
Precise control over heat and atmosphere is the only way to transform waste plastic into high-value functional materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Importance in PET Carbonization | Benefit to Activated Carbon |
|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Control | Maintains inert gas flow (N2/Argon) | Prevents combustion and oxidative loss |
| Temperature Precision | Exact ramps (400°C - 800°C) | Ensures optimal chemical etching and pore formation |
| Flow-through Design | Continuous removal of volatiles | Prevents tar re-deposition and maintains purity |
| Thermal Stability | Consistent heat distribution | Maximizes specific surface area and structural integrity |
Elevate Your Carbon Research with KINTEK Precision
Transforming PET waste into high-value activated carbon requires more than just heat—it requires the uncompromising atmospheric control and thermal stability only a KINTEK furnace can provide.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to optimize your pyrolysis and chemical activation processes. Whether you need to maximize surface area or functionalize carbon surfaces, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces are built to meet your unique research specifications.
Ready to optimize your PET-to-carbon yield? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Lai Thi Hoan, Duong Duc La. Sustainable Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Media by Activated Carbon Valorized from Polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) Plastic Waste. DOI: 10.3390/su17020548
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Tube Furnace utilized in the color modification process of beryl? Master Deep Blue Aquamarine Transformation
- What are the limitations of vertical tube furnaces? Key Trade-offs for Lab Efficiency
- What industries benefit from the use of tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in Semiconductor and Battery Tech
- What are the benefits of a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control and Versatility
- What are the heating zone options for Tube Furnaces? Choose Single or Multi-Zone for Optimal Thermal Control
- What is a tubular furnace? Precision Heating for Lab and Industrial Applications
- What are the key features of a Split Tube Furnace (Single Zone)? Unlock Easy Access and Uniform Heating
- How does a high vacuum tube furnace contribute to the carbonization process? Engineered Hard Carbon Synthesis



















