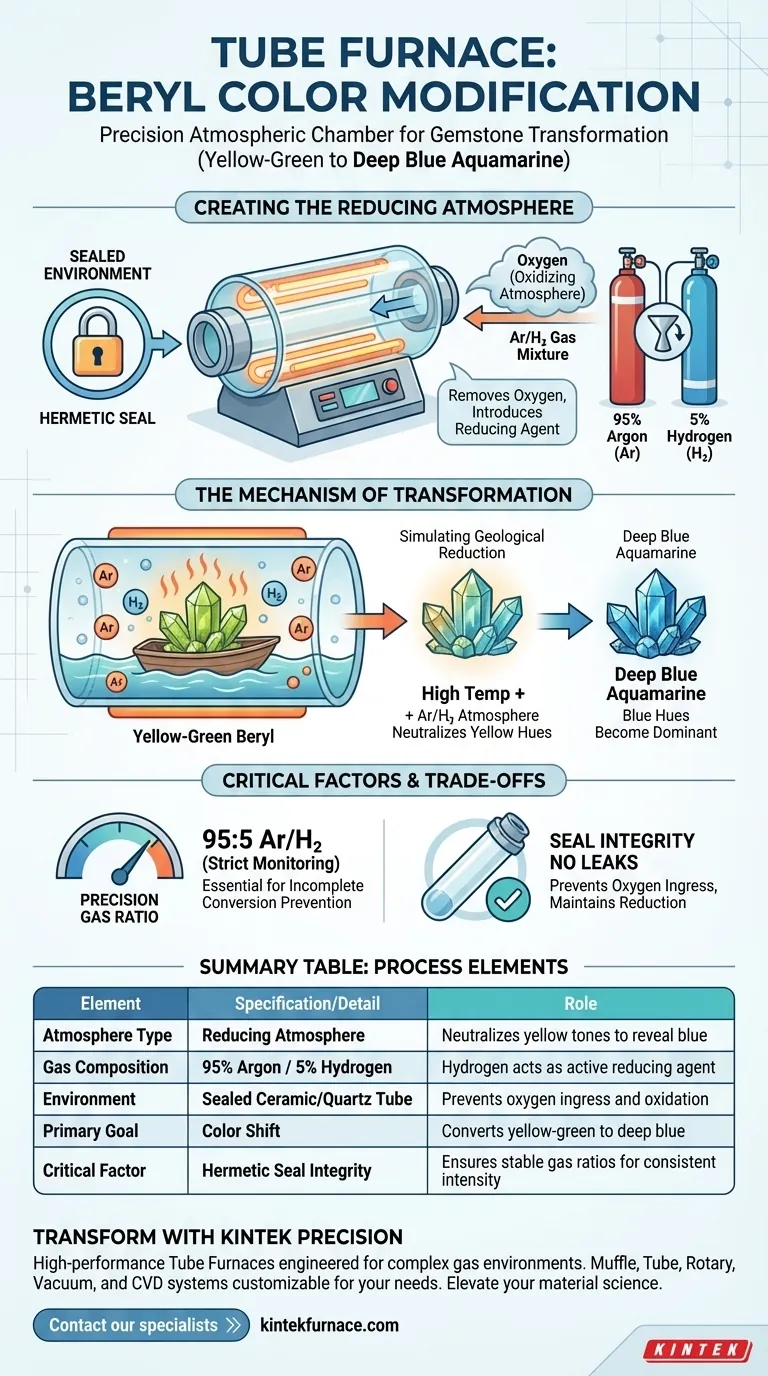
A Tube Furnace functions as a precision atmospheric chamber designed to alter the fundamental appearance of gemstones through controlled heat and gas exposure. Specifically for beryl, it is utilized to create a reducing atmosphere by sealing the material within a tube and introducing a specific gas mixture—typically 95% Argon and 5% Hydrogen—to convert yellow-green tones into deep blue aquamarine.
The Tube Furnace provides more than just high temperatures; it offers total atmospheric isolation. Its primary utility in beryl modification is its ability to simulate precise reduction conditions, allowing for the stable introduction of hydrogen-based gas mixtures that are necessary to strip away unwanted yellow hues.

Creating the Reducing Atmosphere
The Necessity of a Sealed Environment
To modify beryl effectively, you cannot simply heat the stone in open air. Open air contains oxygen, which creates an oxidizing atmosphere.
The Tube Furnace solves this by enclosing the beryl in a sealed tube. This isolation is the first step in preventing oxidation and preparing the stone for chemical reduction.
Introducing the Gas Mixture
Once the tube is sealed, the furnace allows for the introduction of a specific gas mixture. The standard requirement for this process is an Argon and Hydrogen (Ar/H2) ratio of 95:5.
This mixture replaces the natural atmosphere inside the tube. The presence of Hydrogen is the active agent that facilitates the chemical changes required for color modification.
The Mechanism of Color Transformation
Simulating Geological Conditions
The Tube Furnace is designed to replicate specific geological conditions that occur deep within the earth.
By maintaining the Ar/H2 atmosphere at high temperatures, the furnace accurately simulates the reduction conditions. This forces the chemical structure of the beryl to react as it would under natural reducing pressure.
Converting Yellow-Green to Blue
The ultimate goal of this setup is specific: converting yellow-green beryl into deep blue aquamarine.
The reducing atmosphere neutralizes the chemical components responsible for the yellow tones. Once the yellow is removed, the remaining blue hues become dominant, resulting in the desired deep aquamarine color.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precision vs. Complexity
Using a Tube Furnace is more complex than using a standard muffle furnace (box furnace).
Because you are managing gas flow and ratios, the setup requires strict monitoring. You must ensure the 95:5 ratio is maintained constantly; a deviation in gas composition can lead to incomplete color conversion.
The Criticality of the Seal
The effectiveness of the process relies entirely on the integrity of the tube's seal.
If the tube leaks, oxygen will enter the chamber. This disrupts the reducing atmosphere, rendering the Hydrogen ineffective and preventing the beryl from transforming into the desired blue shade.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a Tube Furnace in beryl treatment, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Color Intensity: Adhere strictly to the 95:5 Argon/Hydrogen ratio, as this specific balance is proven to facilitate the deep blue transformation.
- If your primary focus is Process Consistency: Ensure your furnace tube maintains a hermetic seal throughout the heating cycle to prevent oxygen contamination.
By controlling the atmosphere as precisely as the temperature, you turn the furnace from a simple heater into a tool for chemical transformation.
Summary Table:
| Process Element | Specification/Detail | Role in Beryl Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Type | Reducing Atmosphere | Neutralizes yellow tones to reveal blue |
| Gas Composition | 95% Argon / 5% Hydrogen | Hydrogen acts as the active chemical reducing agent |
| Environment | Sealed Ceramic/Quartz Tube | Prevents oxygen ingress and oxidation |
| Primary Goal | Color Shift | Converts yellow-green beryl to deep blue aquamarine |
| Critical Factor | Hermetic Seal Integrity | Ensures stable gas ratios for consistent color intensity |
Transform Your Gemstone Processing with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect aquamarine blue requires more than just heat—it requires absolute atmospheric control. KINTEK provides high-performance Tube Furnaces specifically engineered for complex gas environments.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique material needs. Whether you are simulating geological reduction or developing advanced material coatings, our systems ensure the stability and precision your lab demands.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect customizable furnace solution for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Bin Hao, Qingfeng Guo. The Effect of Heat Treatment on Yellow-Green Beryl Color and Its Enhancement Mechanism. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15080746
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How does a vacuum tube furnace serve as the core equipment in the consolidation of Ti-xCr-2Ge alloys?
- What are the key components of a tubular furnace? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace utilized for BPEA growth? Mastering Physical Vapor Transport for Single Crystals
- Why is calibration important for a horizontal electric furnace? Ensure Precise Temperature Control for Your Materials
- How does precise temperature control facilitate YIG crystallization activation energy calculations?
- What are the methods for treating exhaust gas using a tube furnace? Safely Neutralize Hazards in Your Lab
- Why use a tube furnace for TiO2–TiN/S heat treatment? Achieve Perfect Sulfur Infusion and Purity



















