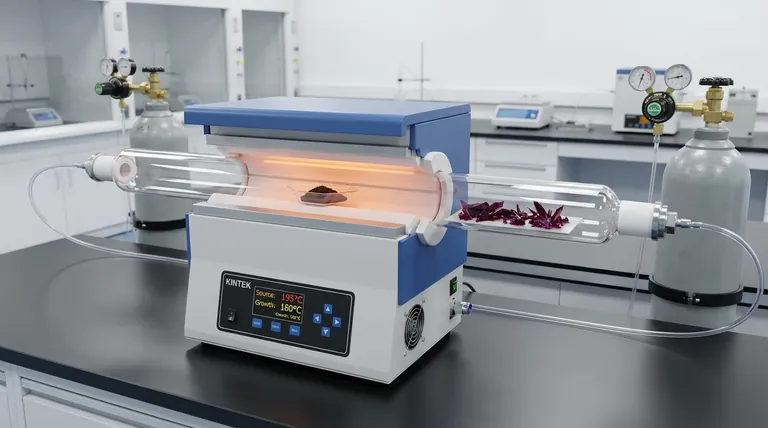
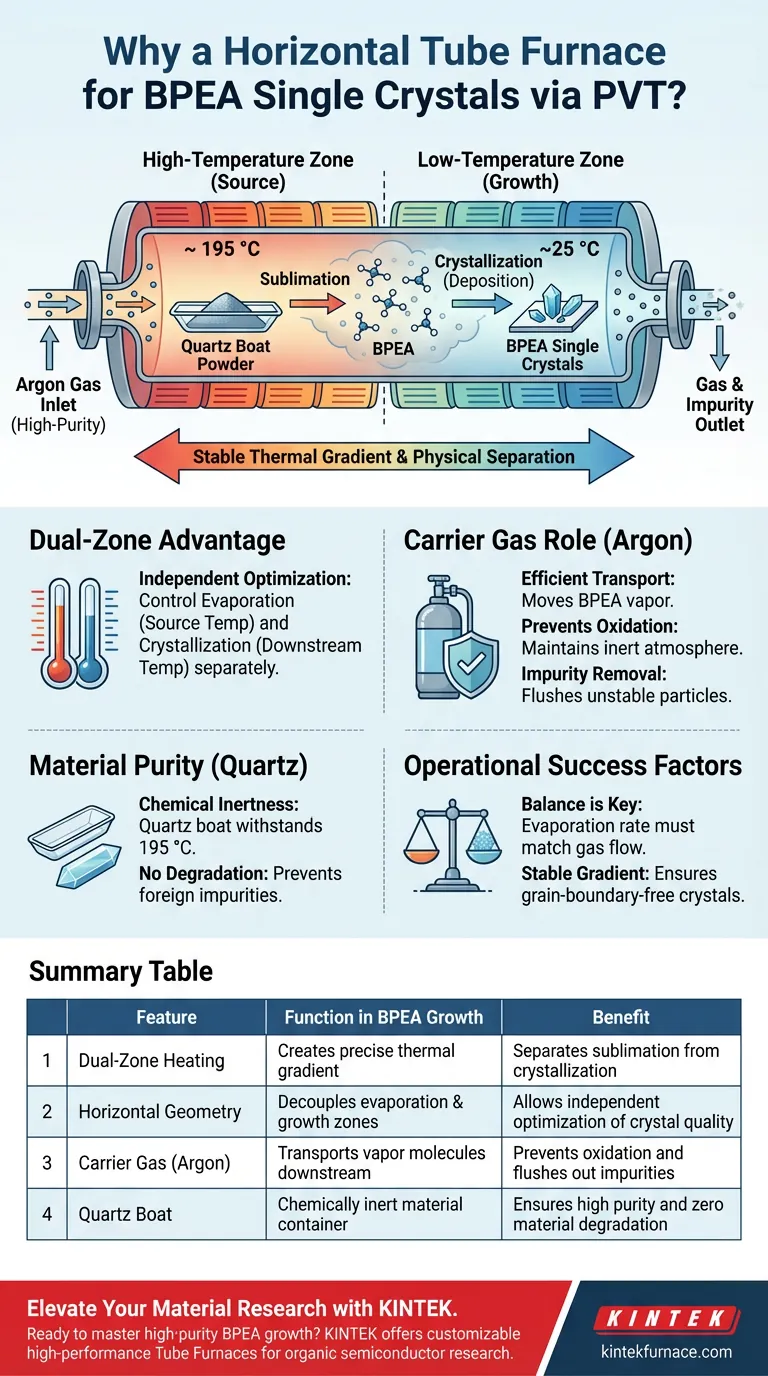
A horizontal tube furnace is utilized primarily to create a stable, strictly controlled temperature gradient. This specific geometry allows 9,10-bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene (BPEA) to sublime in a heated zone and travel to a cooler zone, physically separating the evaporation phase from the crystallization phase.
The horizontal configuration enables independent control over the evaporation rate and the crystallization environment, a fundamental requirement for growing high-purity, grain-boundary-free BPEA single crystals.

The Mechanism of Physical Vapor Transport
To understand why this specific furnace type is chosen, you must look at how it physically separates the stages of crystal growth.
The Dual-Zone Advantage
The horizontal tube furnace creates two distinct thermal environments within a single system.
In the high-temperature zone, BPEA powder contained in a quartz boat is heated to approximately 195 °C to initiate sublimation.
In the low-temperature zone, the vapor cools and deposits onto a substrate, transitioning back into a solid state to form crystals.
Independent Optimization
The primary benefit of this spatial separation is control.
You can adjust the temperature of the source zone to control the evaporation rate without directly altering the conditions where the crystal is growing.
Simultaneously, you can tune the downstream temperature to perfect the crystallization environment, ensuring the formation of high-quality single crystals.
The Role of Carrier Gas and Atmosphere
The horizontal geometry works in tandem with a flowing gas system to manage the movement and purity of the organic molecules.
Efficient Vapor Transport
High-purity Argon acts as an inert carrier gas within the tube.
This gas physically transports the sublimated BPEA molecules from the hot source zone to the cooler substrate zone.
Prevention of Oxidation
The continuous flow of Argon maintains a positive pressure and an inert atmosphere inside the furnace.
This prevents the oxidation of organic molecules, which is critical for maintaining the semiconductor's electrical performance.
Impurity Removal
The flow of carrier gas serves a secondary cleaning function.
It assists in flushing out unstable impurities, ensuring that only the desired BPEA molecules participate in the stable crystal growth process.
Material Compatibility and Stability
Successful PVT requires materials that can withstand the process without introducing contaminants.
Chemical Inertness
The quartz boat holds the BPEA powder and is selected for its exceptional chemical stability.
At the sublimation temperature of 195 °C, quartz does not react with the raw BPEA material.
Preventing Degradation
This inertness ensures the high purity of the organic semiconductor is maintained throughout the gas-phase transport.
It prevents performance degradation that would otherwise be caused by the introduction of foreign impurities from the container.
Critical Operational Considerations
While the horizontal tube furnace is the standard for BPEA growth, success relies on the precise management of specific variables.
The Necessity of Balance
The "independent optimization" mentioned earlier is not automatic; it requires operator intervention.
If the evaporation rate (source temp) is too high for the carrier gas flow rate, the crystallization zone may become oversaturated, leading to poor crystal morphology.
Grain Boundary Management
The ultimate goal of this setup is to produce grain-boundary-free crystals.
Achieving this requires a stable thermal gradient; fluctuations in furnace temperature or gas flow can induce defects that ruin the single-crystal structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your horizontal tube furnace for BPEA preparation, prioritize your parameters based on your specific end-goal.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Structural Quality: Focus strictly on the thermal gradient to ensure the crystallization zone allows for slow, grain-boundary-free growth.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize the integrity of the Argon flow and the cleanliness of the quartz boat to prevent oxidation and contamination.
By decoupling the evaporation source from the growth zone, the horizontal tube furnace provides the requisite control to turn raw BPEA powder into high-performance organic semiconductors.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in BPEA Growth | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dual-Zone Heating | Creates a precise thermal gradient | Separates sublimation from crystallization |
| Horizontal Geometry | Decouples evaporation and growth zones | Allows independent optimization of crystal quality |
| Carrier Gas (Argon) | Transports vapor molecules downstream | Prevents oxidation and flushes out impurities |
| Quartz Boat | Chemically inert material container | Ensures high purity and zero material degradation |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Ready to master the growth of high-purity BPEA single crystals?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our laboratory furnaces are fully customizable to meet the unique needs of organic semiconductor research, providing the thermal stability and atmospheric control essential for grain-boundary-free results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Yanan Sun, Lang Jiang. Low Contact Resistance Organic Single‐Crystal Transistors with Band‐Like Transport Based on 2,6‐Bis‐Phenylethynyl‐Anthracene. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202400112
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for Ti3AuC2 annealing? Achieve Perfect Atomic Exchange
- What is the purpose of pre-treating quartz tube reactors? Achieve High-Purity CVT Crystal Growth with Precision
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace for REBCO tapes? Find Critical 175°C Thresholds
- What maintenance does a horizontal tube furnace require? Ensure Peak Performance and Safety
- Why are near alpha-titanium alloy ingots often sealed in quartz tubes? Unlock Superior Purity and Microstructure
- What materials are commonly used for the heating element in tubular furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the function of a tube furnace for bond-coated substrates? Ensure TBC Durability with Controlled Pre-Oxidation
- What is a horizontal electric furnace designed for? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing in Controlled Environments



















