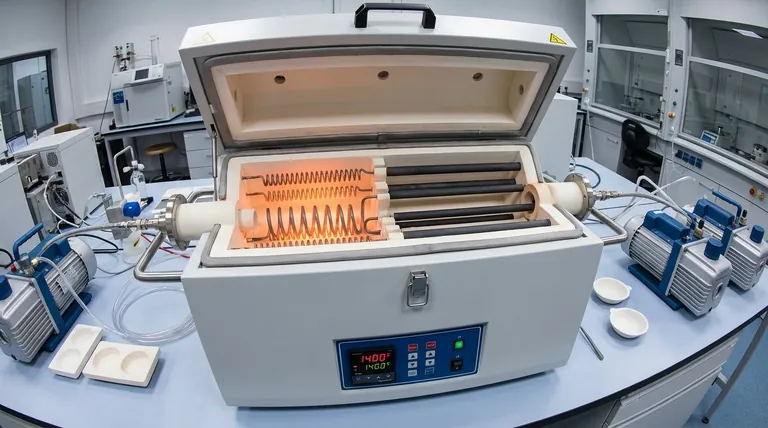
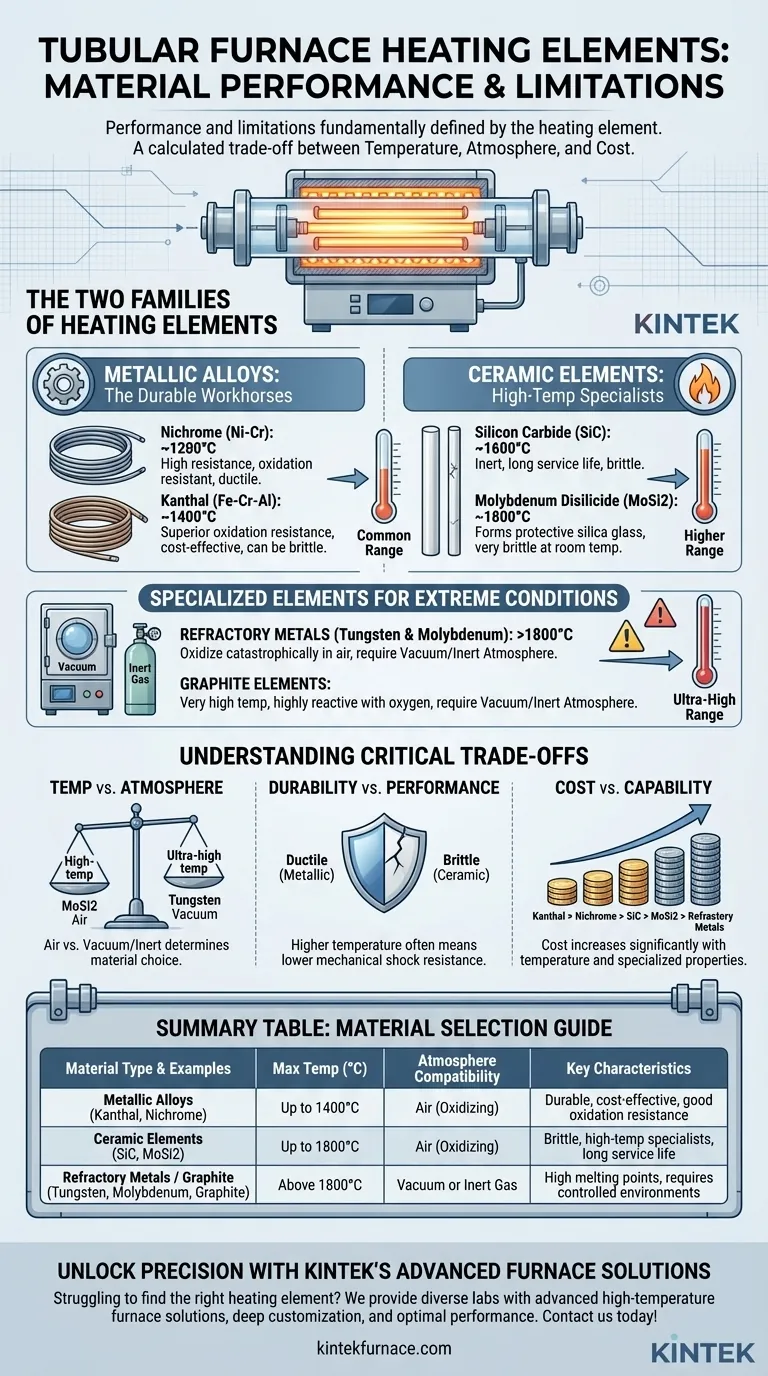
The performance and limitations of a tubular furnace are fundamentally defined by its heating element. While many materials can generate heat, only a select few possess the properties required for reliable, high-temperature operation. The most common materials are metallic alloys like Kanthal (Fe-Cr-Al) and Nichrome (Ni-Cr), and non-metallic ceramics such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
The choice of a heating element is a critical engineering decision that dictates the furnace's capabilities. It's a calculated trade-off between three key factors: the maximum operating temperature, the required processing atmosphere, and overall cost.

The Two Families of Heating Elements
Heating element materials are broadly divided into two categories: metallic alloys, which are the versatile workhorses, and ceramic elements, which are specialists for higher temperature ranges.
Metallic Alloys: The Durable Workhorses
Metallic alloys are prized for their ductility, resistance to thermal shock, and excellent performance in the most common temperature ranges.
Nichrome (Ni-Cr) is a widely used alloy of approximately 80% nickel and 20% chromium. It offers a great balance of high resistance, a high melting point (around 1400°C), and strong resistance to oxidation, making it a reliable choice for general-purpose applications up to about 1200°C.
Kanthal (Fe-Cr-Al) is an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy that can operate at higher temperatures than Nichrome, often up to 1400°C. It forms a very stable and protective layer of aluminum oxide on its surface, giving it superior oxidation resistance. While more cost-effective than Nichrome, it can become more brittle after prolonged use at high temperatures.
Ceramic Elements: The High-Temperature Specialists
When temperatures need to exceed the limits of common metallic alloys, ceramic elements are the solution. They are more brittle but offer superior performance at extreme heat.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are rigid, self-supporting ceramic rods known for their chemical inertness and long service life. They can operate continuously at temperatures up to 1600°C in air, making them ideal for high-temperature sintering and heat treatment.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is the top performer for high-temperature applications in an oxidizing atmosphere, capable of reaching 1800°C. At high temperatures, it forms a protective layer of silica glass that prevents further oxidation. These elements are, however, brittle at room temperature.
Specialized Elements for Extreme Conditions
For the most demanding applications, such as in vacuum furnaces or for ultra-high temperatures, even more specialized materials are required. These elements require tightly controlled environments to function.
Refractory Metals (Tungsten & Molybdenum)
Metals like Tungsten (W) and Molybdenum (Mo) have exceptionally high melting points and are used for processes exceeding 1800°C. Their critical limitation is that they oxidize catastrophically in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. Therefore, they must be used exclusively in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen).
Graphite Elements
Graphite is an excellent electrical conductor that can withstand very high temperatures. Like refractory metals, it is highly reactive with oxygen. It will rapidly burn away if heated in air, so its use is also restricted to vacuum or inert atmosphere environments.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting the right material is not just about picking the one with the highest temperature rating. It involves balancing competing factors.
Temperature vs. Atmosphere
This is the most crucial trade-off. MoSi2 offers the highest temperature capability in air. Tungsten can go even hotter, but only in a vacuum. Using a tungsten element in an air furnace will destroy it instantly upon heating.
Durability vs. Performance
Metallic alloys like Nichrome are ductile and resistant to mechanical shock. Ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi2 offer superior temperature performance but are inherently brittle and must be handled with care to avoid fracture from thermal or physical shock.
Cost vs. Capability
There is a clear cost hierarchy. Kanthal (Fe-Cr-Al) is often the most economical, followed by Nichrome (Ni-Cr). The price increases significantly for ceramic elements (SiC, MoSi2) and is highest for specialized refractory metals like Tungsten, Molybdenum, and Platinum.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by the specific requirements of your work. Consider the maximum temperature and the processing atmosphere as your primary decision points.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose use up to 1200°C in air: A Nichrome (Ni-Cr) or Kanthal (Fe-Cr-Al) element offers the best balance of cost and durability.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (1200°C to 1800°C) in air: A ceramic element like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is necessary.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature processing (above 1800°C): You must use a refractory metal (like Tungsten) or Graphite element within a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to select a furnace that aligns precisely with your scientific or industrial goals.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Max Temperature (°C) | Atmosphere Compatibility | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Kanthal (Fe-Cr-Al), Nichrome (Ni-Cr) | Up to 1400°C | Air (Oxidizing) | Durable, cost-effective, good oxidation resistance |
| Ceramic Elements | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1800°C | Air (Oxidizing) | Brittle, high-temperature specialists, long service life |
| Refractory Metals / Graphite | Tungsten, Molybdenum, Graphite | Above 1800°C | Vacuum or Inert Gas | High melting points, requires controlled environments |
Unlock Precision with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Struggling to find the right heating element for your tubular furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need durable metallic alloys or high-temperature ceramics, we ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let our experts help you select the perfect furnace for your application. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















