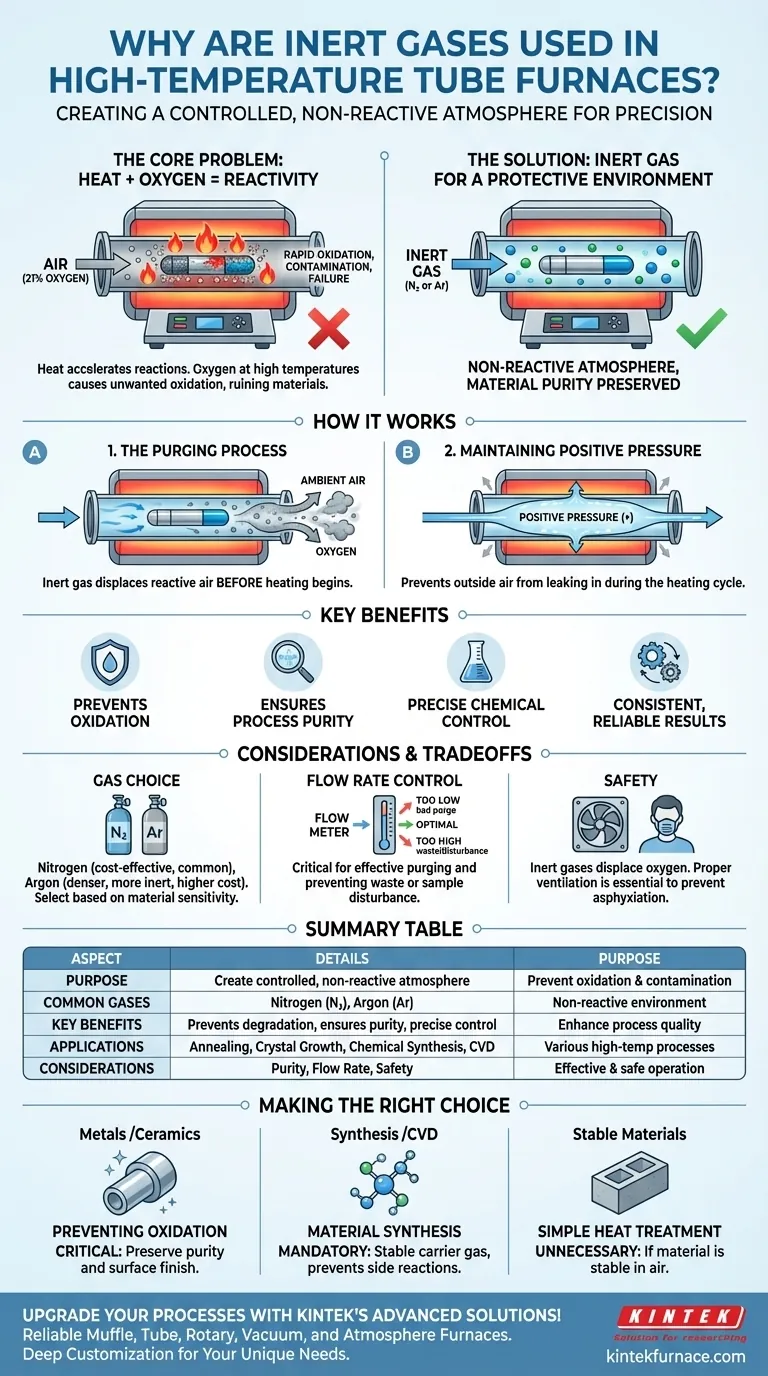
In short, inert gases are used in a high-temperature tube furnace to create a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere. This protective environment is essential because many materials, when heated, will aggressively react with the oxygen present in normal air, leading to unwanted oxidation, contamination, or complete failure of the process.
At its core, the use of an inert gas is about removing a single, highly reactive variable—oxygen—from a chemical process. High temperatures accelerate all reactions, and by replacing reactive air with a stable gas, you ensure that the only changes occurring are the ones you intend.

The Fundamental Problem: Heat and Reactivity
A tube furnace is a tool for precision, offering exact control over temperature. However, heat alone is only half of the equation; the chemical environment is just as critical.
Why High Temperature Is a Challenge
Heat is a catalyst. As you increase the temperature inside the furnace tube, you dramatically increase the rate of potential chemical reactions.
Many materials that are stable at room temperature become highly reactive when subjected to intense heat. This energy allows atomic bonds to break and reform in new, often undesirable, ways.
The Role of Atmospheric Oxygen
The air around us is approximately 21% oxygen. While essential for life, oxygen is a highly reactive element, especially at elevated temperatures.
Introducing heat into an oxygen-rich environment promotes oxidation. For metals, this can mean rapid rusting or scaling. For other sensitive chemicals, it can lead to burning or the formation of unwanted oxide compounds that contaminate your final product.
The Goal: A Controlled Chemical Environment
The purpose of a high-temperature process is rarely just to heat something up. It is typically to induce a specific physical or chemical change, such as annealing a metal, growing a crystal, or synthesizing a new compound.
Without controlling the atmosphere, you are allowing a chaotic and destructive side-reaction (oxidation) to compete with your primary goal. Using an inert gas eliminates this competition.
How Inert Gas Solves the Problem
Inert gases provide a simple but highly effective solution by physically displacing the reactive air within the furnace tube.
Defining "Inert" Gas
Gases like nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar) are called "inert" because they are chemically stable and non-reactive under most conditions. Their electron shells are full, giving them no incentive to react with other materials, even at high temperatures.
The Purging Process
Before the heating process begins, the inert gas is flowed through the furnace tube. This flow purges the system, physically pushing the ambient air and its oxygen out of the tube.
This step ensures that by the time the temperature begins to rise, the sample is surrounded only by the non-reactive gas.
Maintaining a Positive Pressure
During the heating cycle, a slow, continuous flow of the inert gas is often maintained. This creates a slight positive pressure inside the tube.
This positive pressure is a safeguard, ensuring that if any microscopic leaks exist in the system, the inert gas will flow out, preventing any outside air from leaking in and compromising the atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While essential, implementing an inert atmosphere requires careful management.
Gas Choice, Purity, and Cost
Nitrogen is the most common and cost-effective choice for many applications. However, at very high temperatures, it can react with certain materials (like lithium or titanium) to form nitrides.
Argon is denser and more chemically inert than nitrogen, making it the superior choice for extremely sensitive processes, but it comes at a higher cost. The required purity level of the gas will also impact cost.
Flow Rate Control
Controlling the gas flow rate is critical. Too low a flow may not fully purge the oxygen, while too high a flow can waste expensive gas and, in the case of fine powders, may disturb the sample within the tube.
Safety and Asphyxiation Risk
Inert gases are not toxic, but they are asphyxiants. They displace oxygen, and a significant leak into a poorly ventilated lab space can create a serious breathing hazard. Proper ventilation and gas monitoring are essential safety precautions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding whether to use an inert atmosphere depends entirely on your material and your goal.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of metals or ceramics: Using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is absolutely critical to preserve the material's purity and surface finish.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis (e.g., Chemical Vapor Deposition): An inert gas is mandatory to act as a stable carrier for precursor chemicals and prevent unwanted side reactions with oxygen.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of a stable material: An inert atmosphere may be unnecessary if the material is not reactive with air or if a resulting surface oxide layer is acceptable.
By intentionally controlling the atmosphere, you gain precise control over your material's final chemistry and properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Create a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) |
| Key Benefits | Prevents material degradation, ensures process purity, and allows precise chemical control. |
| Applications | Annealing, crystal growth, chemical synthesis, and material processing. |
| Considerations | Gas purity, flow rate control, and safety measures for asphyxiation risks. |
Upgrade your laboratory processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















