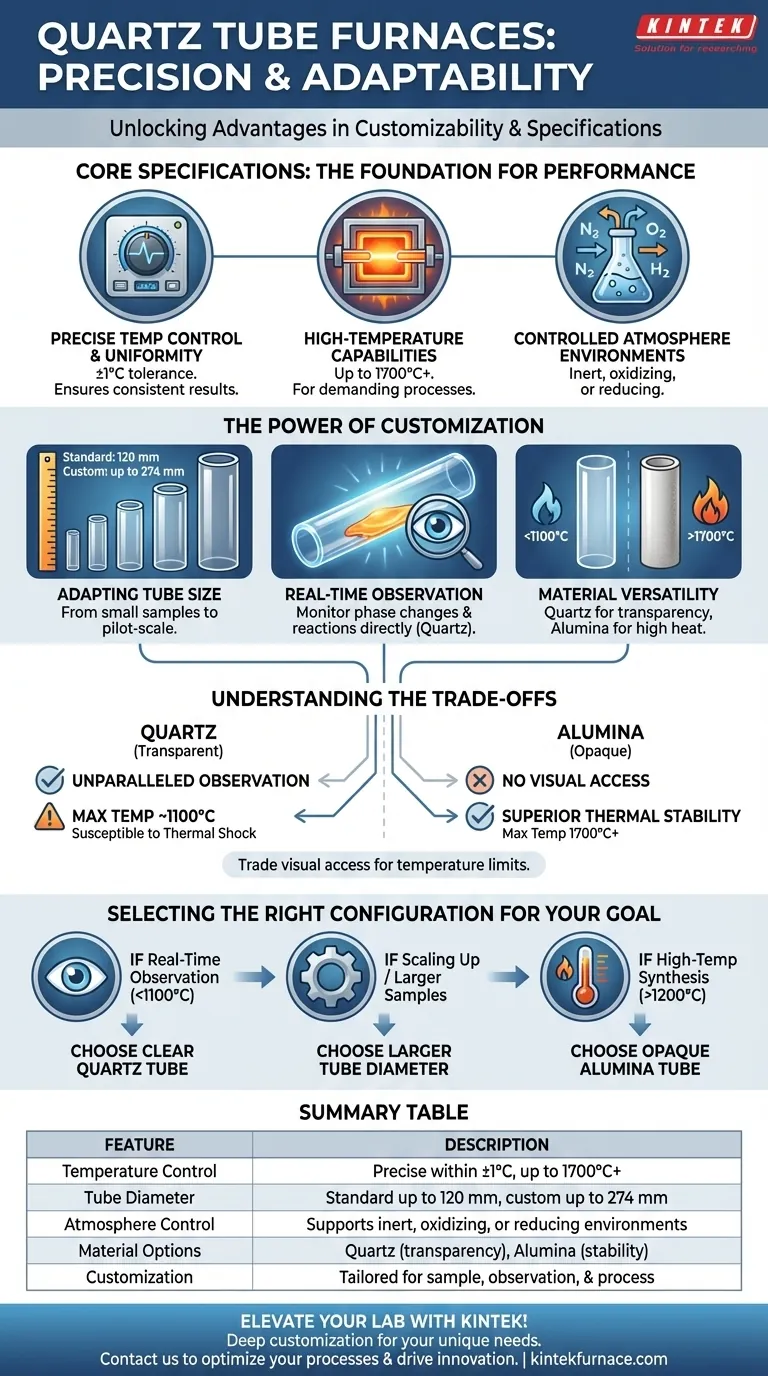
For applications demanding precision and adaptability, quartz tube furnaces provide a distinct advantage through extensive customization options and high-performance specifications. They can be tailored for a wide range of sample sizes, with standard models supporting tube diameters up to 120 mm and custom configurations extending to 274 mm. This flexibility is coupled with elite performance metrics, including precise temperature control within ±1°C and capabilities reaching 1700°C or more.
The true value of a quartz tube furnace lies not just in its specifications, but in its ability to be precisely configured for a specific scientific or industrial process, often while enabling direct, real-time visual monitoring of the material inside.

Core Specifications That Define Performance
The baseline performance of a tube furnace dictates its suitability for sensitive and demanding applications. These specifications are the foundation upon which customization is built.
Unmatched Temperature Control and Uniformity
A key advantage is the ability to maintain highly precise and uniform temperatures. Advanced digital controllers ensure a tight tolerance, often within ±1°C of the setpoint.
The cylindrical geometry of the heating chamber naturally promotes an even distribution of heat around the sample, which is critical for achieving consistent and repeatable results in material synthesis and heat treatment.
High-Temperature Capabilities
These furnaces are engineered to operate at elevated temperatures, with many models capable of reaching 1700°C or higher.
This high thermal range makes them suitable for a vast array of processes, including annealing, sintering, crystal growth, and chemical vapor deposition for advanced materials.
Controlled Atmosphere Environments
Tube furnaces are exceptionally well-suited for atmosphere control. Their sealed design allows for the easy introduction of specific gases to create inert, oxidizing, or reducing environments.
This capability is essential for experiments where interaction with oxygen or other ambient gases must be prevented or carefully managed.
The Power of Customization
Beyond baseline specifications, the ability to tailor the furnace to the exact needs of an experiment is a primary reason for its widespread adoption in research and development.
Adapting Tube Size to Your Sample
Furnaces can be configured to accommodate various tube diameters. Standard options typically go up to 120 mm, but custom builds can handle much larger tubes of 200 mm or even 274 mm.
This scalability allows researchers to move from processing small, experimental samples to handling larger batches for pilot-scale production within the same technology platform.
The Advantage of Real-Time Observation
The signature feature of a quartz tube furnace is its transparency. A clear quartz process tube serves as the heating chamber, allowing operators to directly monitor the sample during thermal processing.
This visual access is invaluable for observing phase changes, melting behavior, color shifts, and other physical or chemical reactions in real time, providing insights that are impossible to gain with opaque furnace chambers.
Material Versatility for Different Needs
While quartz is prized for its transparency, these furnaces also support alternative tube materials like alumina.
Alumina tubes are used when operating temperatures exceed the softening point of quartz (typically around 1100-1200°C) or when processing materials that are highly reactive with silica. This adds another layer of versatility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single solution is perfect for every application. Understanding the limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Quartz vs. Alumina Tubes
The primary trade-off is between visual access and maximum temperature. A clear quartz tube offers unparalleled observation but is generally limited to continuous use at temperatures around 1100°C.
For processes requiring temperatures up to 1700°C or higher, an opaque alumina tube is necessary. This provides superior thermal and chemical stability at the cost of losing real-time visual monitoring.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
Quartz, while robust, can be susceptible to thermal shock. Extremely rapid heating or cooling cycles can risk cracking the tube, requiring operators to follow programmed ramp rates. This is a managed risk but one to be aware of in operational protocols.
Selecting the Right Configuration for Your Goal
Your ideal furnace configuration depends directly on your experimental or production objectives.
- If your primary focus is real-time observation of processes below ~1100°C: A clear quartz tube is the definitive choice for its unmatched transparency.
- If your primary focus is processing larger samples or scaling up: Prioritize a custom furnace with a larger tube diameter to increase your batch capacity.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis above 1200°C: An opaque alumina tube is the necessary specification, trading visual access for enhanced thermal stability.
By matching the furnace's specifications and customization options to your core requirements, you can ensure your equipment is a powerful and precise tool for discovery.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Precise within ±1°C, up to 1700°C or higher |
| Tube Diameter | Standard up to 120 mm, custom up to 274 mm |
| Atmosphere Control | Supports inert, oxidizing, or reducing environments |
| Material Options | Quartz for transparency, alumina for high-temperature stability |
| Customization | Tailored for sample size, real-time observation, and specific processes |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with customizable quartz tube furnaces, muffle furnaces, vacuum systems, and more. Our deep customization ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, from real-time monitoring to high-temperature synthesis. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















