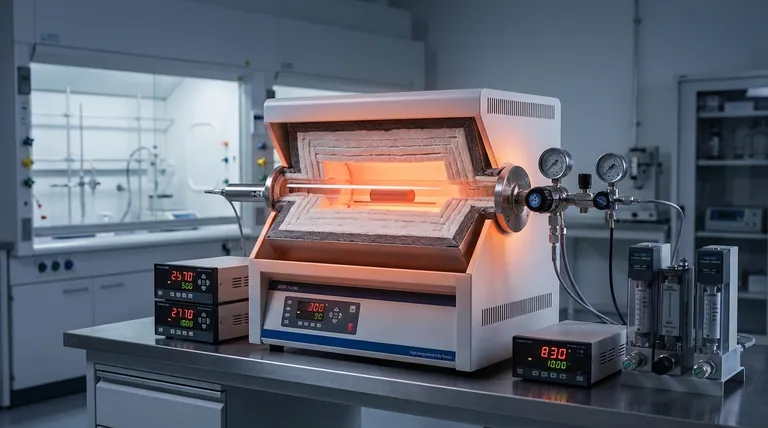
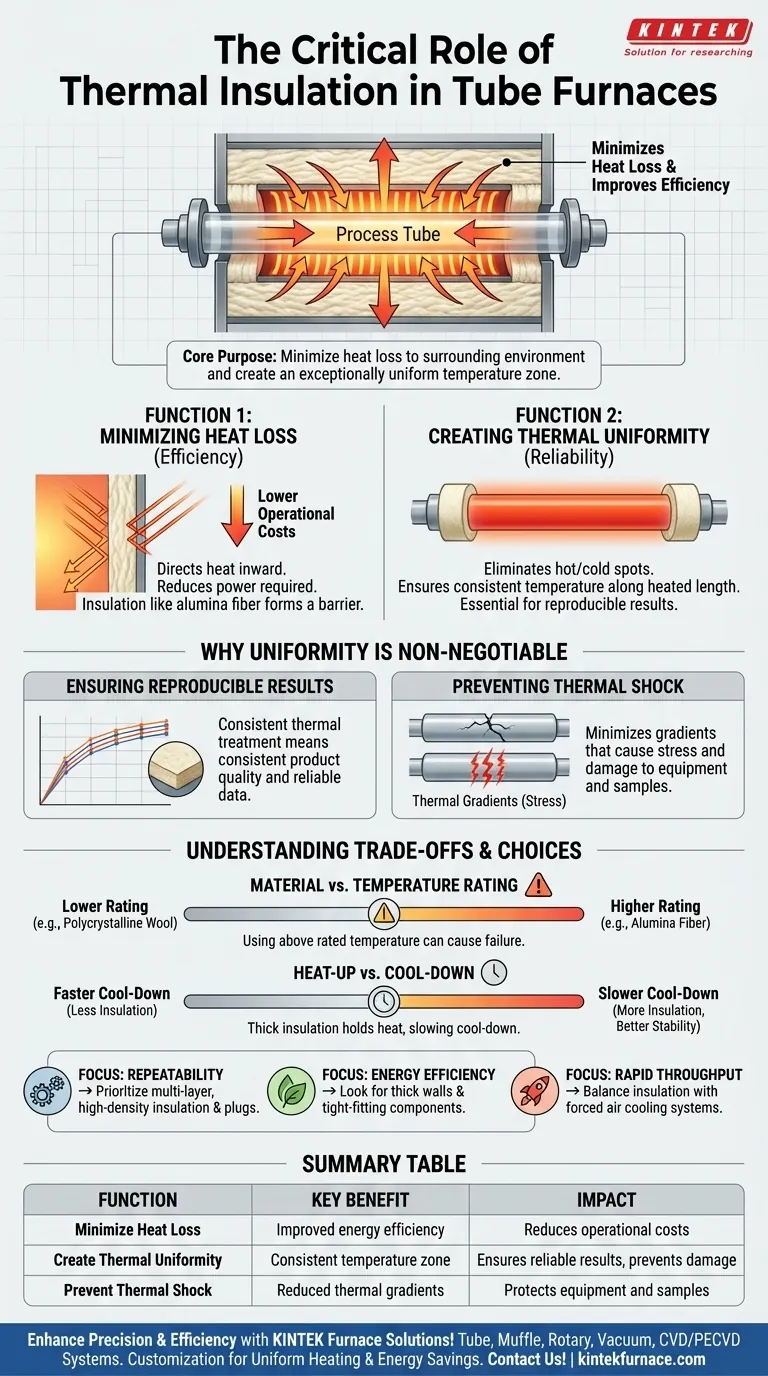
At its core, thermal insulation in a tube furnace serves two critical and interconnected functions. It is designed to minimize heat loss to the surrounding environment, which directly improves energy efficiency, and more importantly, to create an exceptionally uniform temperature zone within the process tube. This ensures the heat generated by the elements is concentrated precisely where it is needed.
While often seen simply as an efficiency feature, the true purpose of thermal insulation is to create a highly stable and uniform thermal environment. This uniformity is the single most critical factor for achieving reliable and reproducible results in high-temperature processing.

The Core Functions of Insulation
Thermal insulation is not merely a passive barrier; it is an active component in shaping the furnace's performance. Its design directly impacts both operational cost and, more critically, the quality of your results.
Function 1: Minimizing Heat Loss
A tube furnace's primary job is to generate and contain high levels of heat. Without effective insulation, a significant portion of that thermal energy would radiate away into the laboratory.
The heating elements are typically embedded within a matrix of insulating material, such as alumina fiber. This ensures that the vast majority of the heat they produce is directed inward toward the furnace chamber, not outward into the room. This concentration of energy dramatically reduces the power required to reach and maintain a target temperature, lowering operational costs.
Function 2: Creating Thermal Uniformity
The most crucial function of insulation is achieving thermal uniformity. This means ensuring the temperature is consistent along the entire heated length of the process tube.
By preventing heat from escaping, insulation forces the thermal energy to distribute evenly throughout the heating chamber. This eliminates hot and cold spots that would otherwise compromise the process. Specific components like insulation plugs are used at the ends of the process tube to block a major path of heat loss, further enhancing this uniformity.
Why Thermal Uniformity is Non-Negotiable
Inconsistent heating is the enemy of reliable material science and processing. The entire purpose of a laboratory furnace is to subject a sample to a known and repeatable thermal profile.
Ensuring Reproducible Results
For any scientific experiment or manufacturing process, the results must be reproducible. If a sample is heated unevenly, different parts of it will undergo different thermal treatments. This invalidates experimental data and leads to inconsistent product quality, making it impossible to draw reliable conclusions.
Preventing Thermal Shock and Damage
Poor insulation creates steep thermal gradients, which are sharp differences in temperature over a short distance. These gradients induce physical stress in materials as different sections expand or contract at different rates.
This stress can easily cause the expensive ceramic or quartz process tube to crack. It can also damage the sample itself, a phenomenon known as thermal shock. High-quality insulation minimizes these gradients, protecting both your equipment and your sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, the choice and implementation of insulation involve important design considerations that can impact furnace operation.
Insulation Material vs. Temperature Rating
Different insulating materials are rated for different maximum temperatures. Materials like alumina fiber and polycrystalline wool are common, but they have distinct thermal properties and cost. Using an insulation material above its rated temperature can lead to degradation, furnace failure, and potential process contamination.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Rates
A furnace with exceptionally effective, thick insulation is excellent at holding heat. While this is great for stability and efficiency, it also means the furnace will cool down very slowly once the power is turned off. For applications requiring rapid thermal cycling and high throughput, this slow cooldown can become a significant bottleneck.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal dictates which aspect of insulation performance is most important.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Prioritize furnaces with multi-layer, high-density insulation and dedicated insulation plugs to achieve the best possible thermal uniformity.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Look for designs with thick insulation walls and tight-fitting components that minimize all potential paths for heat loss.
- If your primary focus is rapid throughput: Be aware that excellent insulation will slow your cooldown times; you may need to balance insulation performance against systems that incorporate forced air cooling.
Ultimately, understanding the role of insulation moves you from simply operating a furnace to controlling a precise thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Minimize Heat Loss | Improved energy efficiency | Reduces operational costs and power consumption |
| Create Thermal Uniformity | Consistent temperature zone | Ensures reliable, reproducible results and prevents sample damage |
| Prevent Thermal Shock | Reduced thermal gradients | Protects equipment and samples from stress-induced failure |
Enhance your laboratory's precision and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored options like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for uniform heating and energy savings. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your thermal processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















