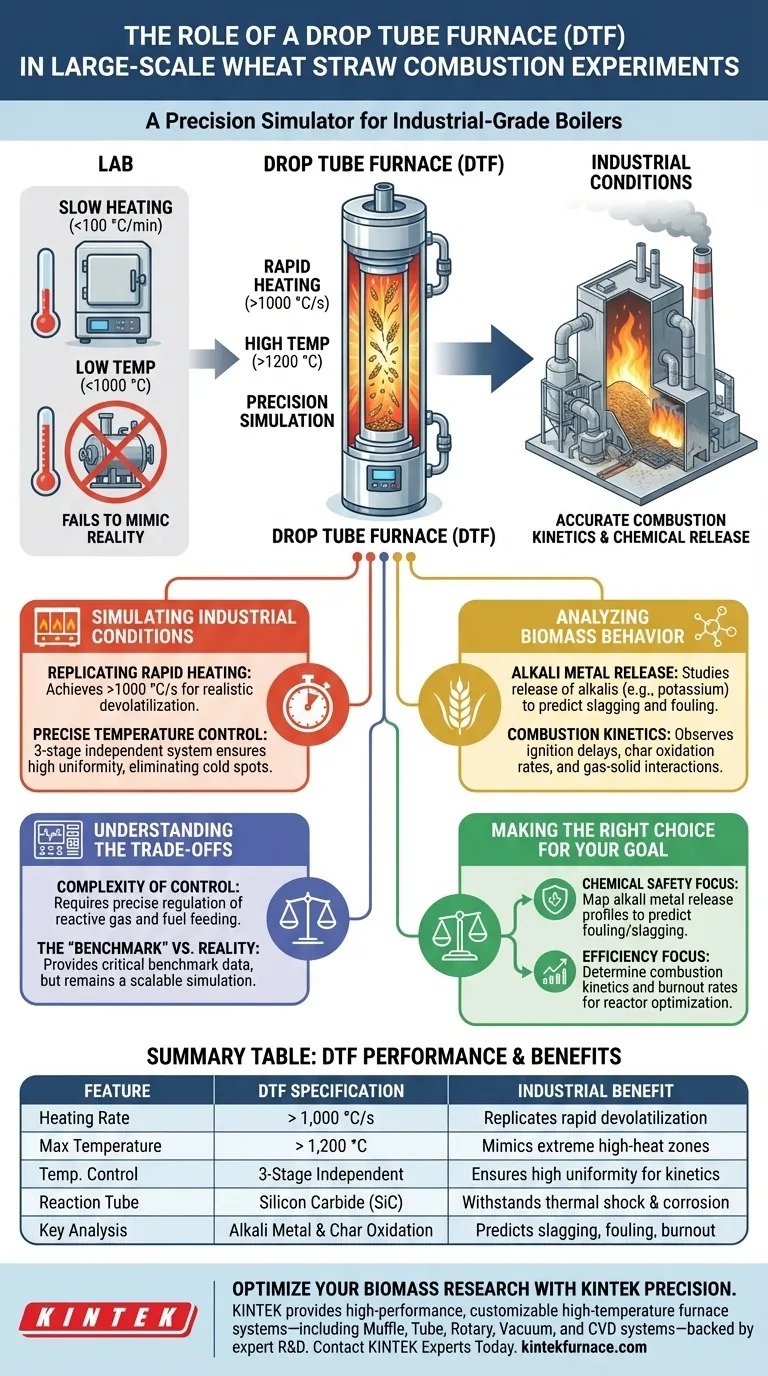
A Drop Tube Furnace (DTF) serves as a precision simulator designed to replicate the extreme environments of industrial-grade boilers within a laboratory setting. In the context of large-scale wheat straw experiments, its primary role is to subject biomass particles to high temperatures (exceeding 1200 °C) and rapid heating rates (over 1000 °C/s) to accurately model combustion kinetics and chemical release.
Core Takeaway Standard laboratory heating methods often fail to mimic the aggressive conditions of a real power plant. The Drop Tube Furnace bridges this gap by providing a controlled, high-temperature environment with rapid heating, making it the definitive tool for understanding how wheat straw will actually ignite, burn, and release alkali metals in industrial energy production.

Simulating Industrial Conditions
To understand how wheat straw performs as a fuel source, researchers must move beyond standard slow-heating tests. The DTF creates an environment that closely mirrors the physics of a pulverized coal or biomass boiler.
Replicating Rapid Heating
Industrial boilers heat fuel almost instantly. The DTF is capable of achieving heating rates exceeding 1000 °C/s (with some configurations reaching significantly higher magnitudes).
This rapid heating is critical for observing realistic devolatilization—the phase where volatile gases are released from the straw.
Precise Temperature Control
The equipment features a three-stage independent temperature control system. This allows researchers to fine-tune the thermal profile across the reactor.
This system ensures high temperature uniformity within the combustion zone, eliminating cold spots that could skew data regarding particle burnout.
Analyzing Biomass Behavior
Wheat straw presents unique challenges compared to traditional fossil fuels. The DTF provides the specific data points needed to address these challenges.
Alkali Metal Release
A critical function of the DTF in wheat straw experiments is studying alkali metal release characteristics.
Wheat straw is rich in alkalis (like potassium), which can cause slagging and fouling in boilers. The DTF allows scientists to quantify exactly when and how these chemicals are released under high heat.
Combustion Kinetics
The device serves as a high-temperature reaction platform to study combustion kinetics.
It allows for the observation of ignition delays, char oxidation rates, and the interaction between solid particles and gases in a short residence time.
Reaction Environment
The core of the furnace often utilizes a silicon carbide tube. This material withstands the extreme thermal shock required for these experiments.
This setup ensures that the gas-solid contact conditions mimic the flight path of a particle in a large-scale combustor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the DTF is a powerful simulation tool, it is important to recognize the complexities involved in its operation.
Complexity of Control
Achieving accurate results requires precise regulation of multiple variables, including reactive gas flow and fuel feeding rates. Small deviations in these inputs can significantly alter the residence time and thermal history of the particles.
The "Benchmark" vs. Reality
The DTF produces char and data that serve as a critical benchmark for validating other metrics (such as thermogravimetric indices). However, it remains a simulation; while it is scalable and representative, it isolates specific variables that may interact more chaotically in a full-scale commercial furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When planning wheat straw combustion experiments, the DTF offers specific advantages depending on your research focus.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Safety: Use the DTF to map alkali metal release profiles to predict potential fouling or slagging issues in industrial boilers.
- If your primary focus is Efficiency: Rely on the DTF to determine combustion kinetics and burnout rates to optimize the residence time required for your full-scale reactor design.
The Drop Tube Furnace effectively translates the theoretical potential of wheat straw into actionable, industrial-grade data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | DTF Performance Specification | Industrial Simulation Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | Over 1,000 °C/s | Replicates rapid devolatilization in boilers |
| Max Temperature | Exceeds 1,200 °C | Mimics extreme high-heat reaction zones |
| Temp. Control | 3-stage independent zones | Ensures high uniformity for accurate kinetics |
| Reaction Tube | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Withstands extreme thermal shock and corrosion |
| Key Analysis | Alkali metal & Char oxidation | Predicts slagging, fouling, and burnout efficiency |
Optimize Your Biomass Research with KINTEK Precision
Transitioning from lab-scale testing to industrial reality requires reliable data. KINTEK provides high-performance, customizable high-temperature furnace systems—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing. Whether you are studying alkali metal release in wheat straw or optimizing combustion kinetics, our lab furnaces are designed to meet your unique experimental needs.
Ready to elevate your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK Experts Today
Visual Guide
References
- Haoteng Zhang, Chunjiang Yu. Experimental Study on Single-Particle Combustion Characteristics of Large-Sized Wheat Straw in a Drop Tube Furnace. DOI: 10.3390/en18153968
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do vertical fluidized bed tube furnaces contribute to the new energy field? Unlock Next-Gen Energy Material Development
- What are the possible configurations of heated sections in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Setup for Your Process
- What are the types of Tube Furnaces based on orientation? Horizontal vs. Vertical for Optimal Thermal Processing
- How does a Drop Tube Furnace (DTF) contribute to evaluating the combustion of reducing agents? Optimize Furnace Performance
- What technical advantages do three-zone tube furnaces offer? Superior Temperature Control and Flexibility
- What are the common applications of alumina tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in Materials Processing
- Why use stainless steel or nickel foil liners in tube furnaces? Protect Your Equipment During KOH Activation
- What role do industrial tube furnaces play in the oxidation of NiCrAl alloys? Precise Stability for Reliable Data



















