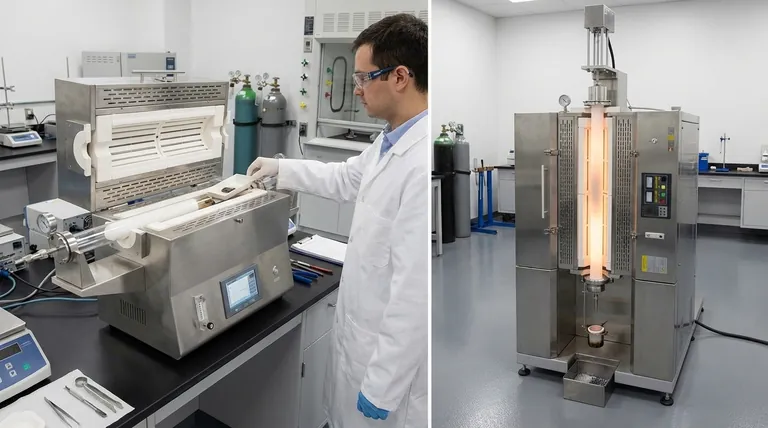
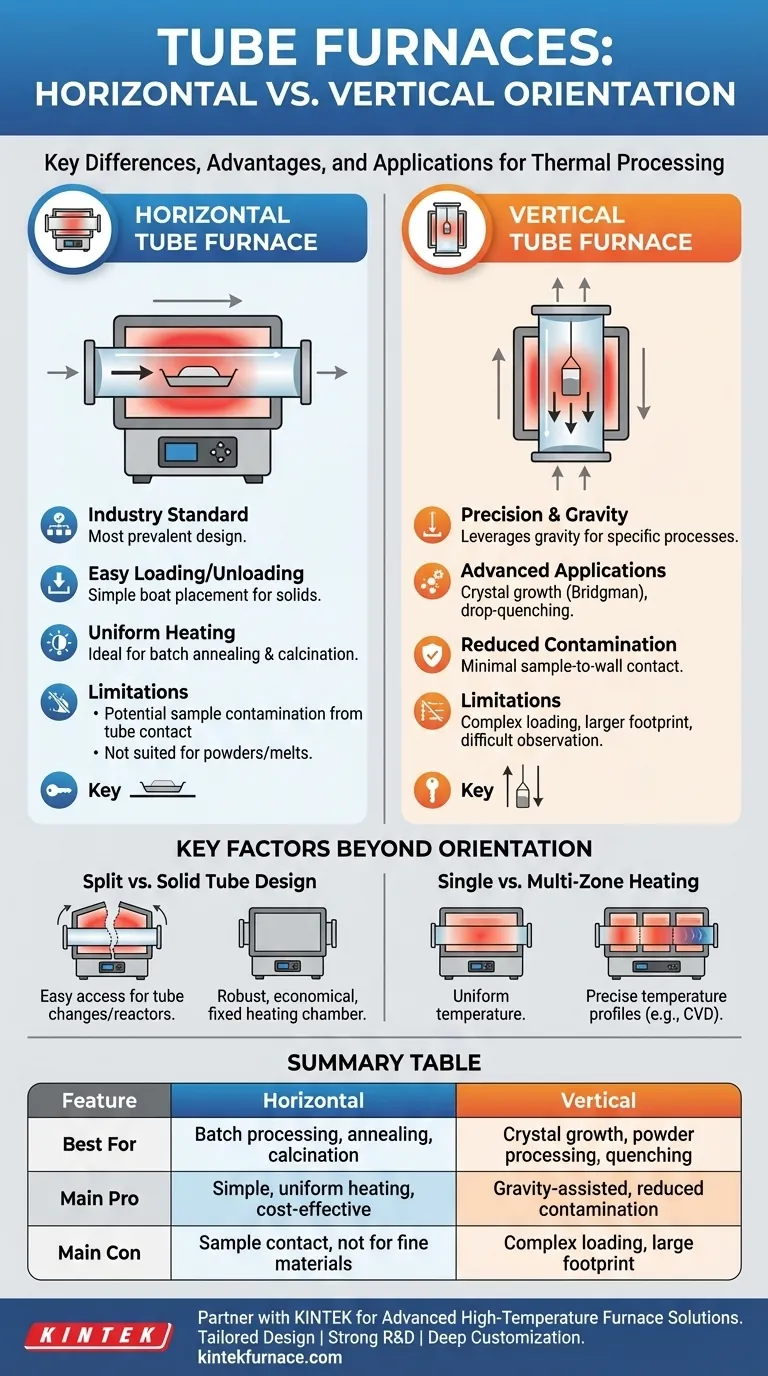
When classifying tube furnaces by their orientation, the two principal designs are the Horizontal Tube Furnace and the Vertical Tube Furnace. Each configuration is engineered to serve distinct process requirements, with the choice depending entirely on the nature of the sample and the desired thermal treatment. Horizontal furnaces are the most common, while vertical designs solve specific challenges related to gravity, atmosphere, and material form.
The decision between a horizontal or vertical tube furnace is not about which is "better," but which is best suited for your specific process. Horizontal furnaces excel at batch processing and uniform heating along a sample's length, while vertical furnaces are ideal for gravity-assisted processes and minimizing contamination.

Understanding the Primary Orientations
The physical orientation of the process tube is the most fundamental design choice, directly influencing how a sample is heated, how it interacts with the furnace, and how process gases flow around it.
The Horizontal Tube Furnace: The Industry Standard
A horizontal tube furnace features a process tube that lies flat, parallel to the ground. This is the most prevalent design due to its simplicity and versatility.
Samples are typically placed in a ceramic or quartz "boat" and pushed into the center of the heated zone. This configuration makes loading and unloading straightforward for solid materials.
The primary advantage is achieving a highly uniform temperature zone along the length of the tube, which is ideal for annealing, calcination, and other batch-processing applications.
The Vertical Tube Furnace: Precision and Gravity
In a vertical tube furnace, the process tube is oriented upright. This design leverages gravity, making it uniquely suited for specific, advanced applications.
It is essential for processes like crystal growth (e.g., the Bridgman method), where a substance is slowly lowered through a temperature gradient. It's also ideal for drop-quenching experiments, where a sample can be quickly dropped from the hot zone into a quenching medium below.
Furthermore, vertical orientation is superior for processing fine powders or liquids, as gravity helps contain them. It also minimizes sample contact with the tube walls, reducing potential contamination.
Key Factors Beyond Orientation
While orientation is a primary classifier, other design features are equally critical to a furnace's capability. These choices are often independent of whether the furnace is horizontal or vertical.
Split vs. Solid Tube Design
A split tube furnace is hinged, allowing it to open like a clamshell. This provides easy access to the process tube, which is useful for quickly changing tubes or accommodating reactors with complex connections.
A solid tube furnace has a fixed heating chamber, and the process tube must be slid in from the ends. These designs are generally more robust and economical.
Single vs. Multi-Zone Heating
A single-zone furnace is designed to create one stable, uniform temperature area in the center.
A multi-zone furnace has two or more independently controlled heating sections. This allows a user to create a precise temperature gradient along the length of the tube, which is critical for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and certain types of crystal growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an orientation requires acknowledging the inherent compromises of each design. What makes one ideal for a specific task makes it less suitable for another.
Horizontal Furnace Limitations
The primary drawback is sample contact. A sample resting on the bottom of the tube can lead to contamination or unwanted reactions with the tube material.
Convection currents can also create a slight temperature difference between the top and bottom of the process tube, which can be a factor in highly sensitive processes.
Finally, they are generally unsuitable for processing fine powders or melts, which cannot be easily contained.
Vertical Furnace Considerations
Loading and unloading can be more complex, often requiring specialized crucibles, suspension wires, or sample holders to position the material correctly in the hot zone.
The physical footprint, particularly the height requirement, can be a significant facility constraint.
Observing the sample during processing is often more difficult in a vertical setup compared to the direct line-of-sight available in many horizontal designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated by the physics of your process and the form of your material.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose batch processing of solid samples: A horizontal tube furnace is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is crystal growth, powder processing, or minimizing sample contamination: A vertical tube furnace offers superior control by leveraging gravity and reducing contact with the tube walls.
- If your primary focus is creating a precise temperature gradient for CVD or similar processes: You must prioritize a multi-zone furnace, and the orientation will depend on your specific material handling needs.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace orientation is the first step in designing a thermal process that is both repeatable and reliable.
Summary Table:
| Orientation | Key Applications | Main Advantages | Main Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Batch processing, annealing, calcination | Easy loading/unloading, uniform heating, cost-effective | Potential sample contamination, not ideal for powders/liquids |
| Vertical | Crystal growth, powder processing, drop-quenching | Gravity-assisted processes, reduced contamination, better for fine materials | Complex loading, larger footprint, difficult observation |
Struggling to choose the right tube furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique experimental requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can help you select or design the perfect horizontal or vertical tube furnace to enhance your process efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















