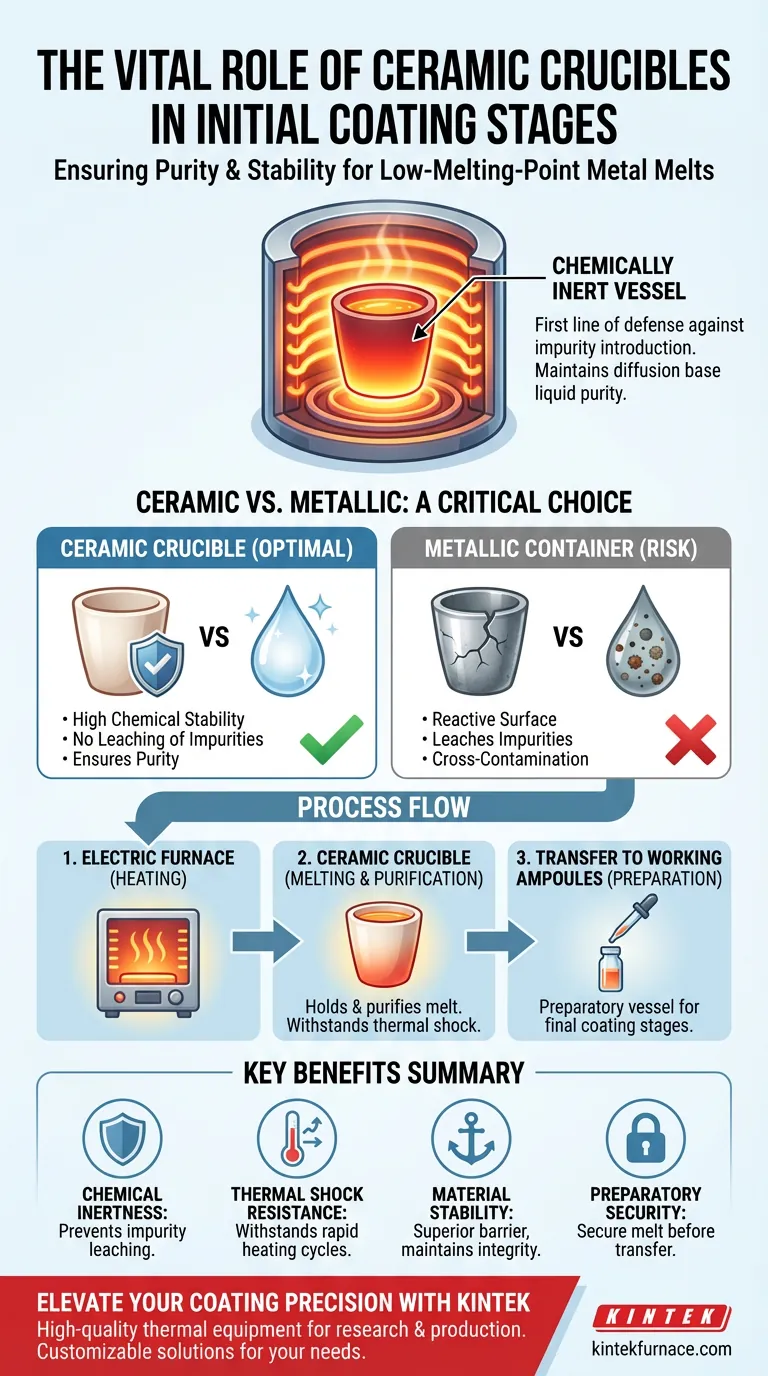
In the initial stages of the coating process, ceramic crucibles act as chemically inert vessels designed to melt low-melting-point metals without compromising their composition. Used primarily within electric furnaces, these crucibles serve as the first line of defense against impurity introduction, ensuring the raw material remains uncontaminated before it proceeds to subsequent processing steps.
The core function of the ceramic crucible is to guarantee the high purity of the diffusion base liquid by acting as a chemically stable barrier that prevents the specific impurities common to metallic containers.
Preserving Chemical Purity
The Barrier Against Contamination
The most critical role of the ceramic crucible is to prevent the low-melting-point melt from interacting with its containment vessel.
Superiority Over Metallic Containers
Standard metallic containers often leach impurities into the melt during the heating process. Ceramic crucibles utilize their high chemical stability and inertness to eliminate this risk entirely.
Ensuring Base Liquid Quality
By maintaining this inert environment, the crucible ensures the diffusion base liquid reaches the necessary purity standards required for the coating application.
Thermal Performance in Electric Furnaces
Managing Thermal Shock
The melting process involves significant temperature fluctuations. Ceramic crucibles are selected for their excellent thermal shock resistance, allowing them to withstand the rapid heating cycles of electric furnaces without fracturing.
Stability During Melting
This thermal stability ensures that the physical integrity of the container remains intact throughout the melting phase. This reliability is essential for safely containing the molten metal until it is ready for transfer.
The Process Context
Preparation for Transfer
The crucible is not the final destination for the melt; it is a preparatory vessel. Its role is to hold and purify the melt specifically before it is transferred to working ampoules.
The Initial Stage Foundation
Success in the later stages of coating depends heavily on this initial step. If the melt is contaminated in the furnace, the quality of the final coating is compromised regardless of how well the working ampoules function.
Understanding the Risks of Alternatives
The Pitfall of Reactivity
The primary trade-off to understand is the risk associated with non-ceramic alternatives. Using a reactive container, such as a standard metal crucible, introduces a high probability of elemental cross-contamination.
Impact on Coating Integrity
While metallic containers might offer different handling properties, their lack of chemical inertness makes them unsuitable for applications where the purity of the diffusion base liquid is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your coating process yields consistent, high-quality results, consider the following regarding your equipment selection:
- If your primary focus is Purity: Prioritize ceramic crucibles to exploit their chemical inertness and prevent impurity leaching from the container walls.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Rely on the thermal shock resistance of ceramics to withstand the rapid heating cycles of electric furnaces without structural failure.
The choice of a ceramic crucible is a foundational decision to secure the chemical integrity of your melt from the very first moment of heating.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit in Initial Coating Stages |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents impurity leaching and ensures diffusion base liquid purity. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating cycles in electric furnaces without fracturing. |
| Material Stability | Acts as a superior barrier compared to reactive metallic containers. |
| Preparatory Security | Maintains melt integrity before transfer to working ampoules. |
Elevate Your Coating Precision with KINTEK
Don't let impurities compromise your coating integrity. At KINTEK, we understand that high-quality results begin with superior thermal equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique research or production needs.
Whether you are melting low-melting-point metals or developing advanced thin films, our solutions provide the thermal stability and purity your application demands. Contact us today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Ismatov Jumaniez Faizullaevich. Mplementation Of The Process Of High Temperature Diffusion Treatment. DOI: 10.37547/ajast/volume05issue11-22
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a rotary evaporator in the recovery of formic acid lignin? Preserve Quality & Boost Efficiency
- How can the temperature resistance of alumina ceramic furnace tubes be assessed? Ensure Long-Term Reliability in Your Lab
- How do graphite molds in SPS affect maraging steel? Managing Carbon Diffusion for Precise Sintering Results
- Why is a heating magnetic stirrer used for the acid activation of zeolites? Precision in Thermal & Kinetic Control
- What is the purpose of applying Boron Nitride (BN) to graphite molds in Mg3Sb2 VHP? Ensure Purity & Easy Demolding
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump create negative pressure? Discover the Liquid-Ring Mechanism for Efficient Lab Vacuum
- What is the specific significance of using high-purity corundum crucibles in oxidation weight gain experiments?
- What is the function of a graphite crucible with a threaded lid? Key to Successful Mg3Sb2 Synthesis



















