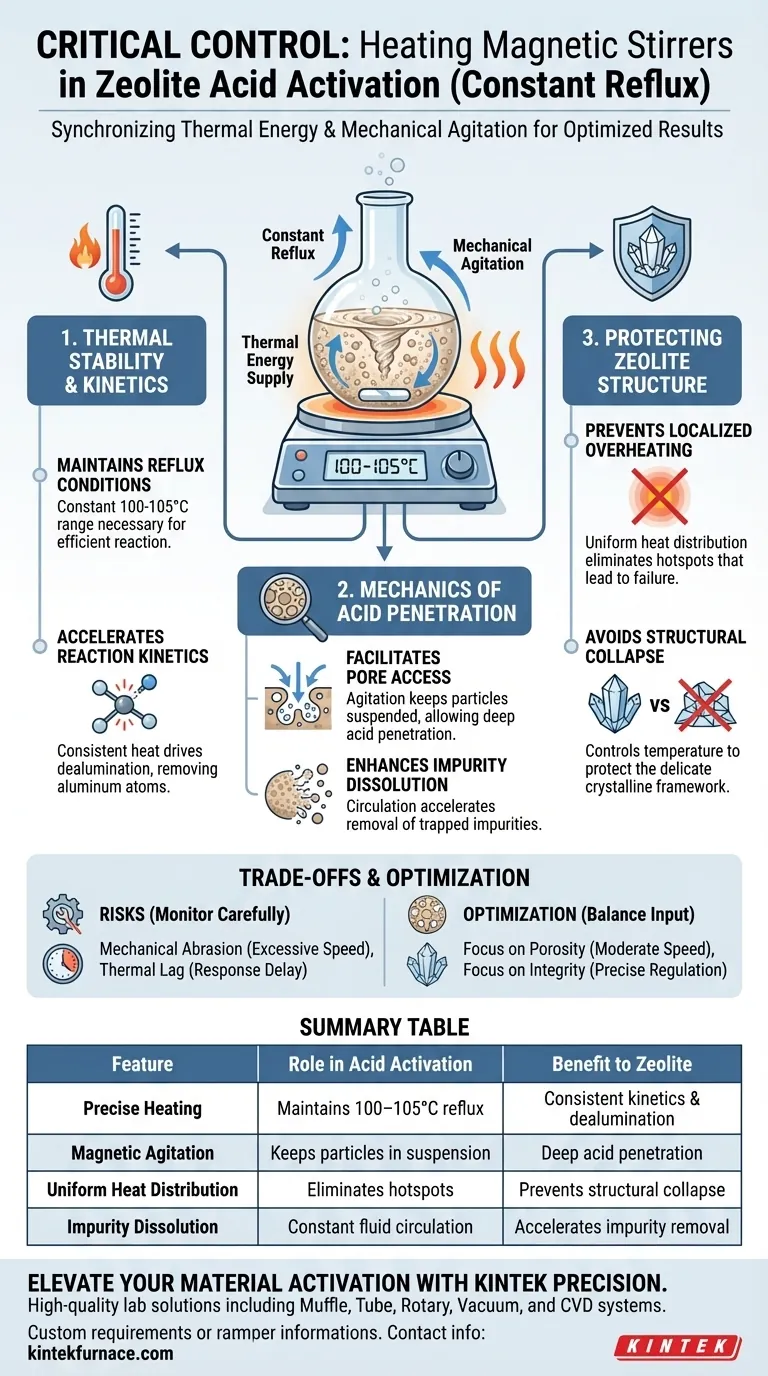
A heating magnetic stirrer is the critical control mechanism in the acid activation of zeolites, serving to synchronize thermal energy with mechanical agitation. By maintaining a constant reflux temperature (typically 100–105°C), it ensures the acid solution thoroughly penetrates the zeolite pores while preventing the structural damage often caused by uneven heating.
The device functions as a kinetic stabilizer, ensuring the zeolite suspension remains homogeneous and the thermal supply remains constant. This balance is required to accelerate dealumination and impurity removal without risking the collapse of the zeolite’s crystalline framework.

The Role of Thermal Stability
Maintaining Reflux Conditions
The acid activation process generally requires temperatures near the boiling point of the solution.
The heating magnetic stirrer maintains the system specifically between 100–105°C. This ensures the solution remains at a constant reflux state, which is necessary for the reaction to proceed efficiently in a round-bottom flask.
Accelerating Reaction Kinetics
A stable thermal supply is not just about reaching a temperature; it is about holding it precisely.
Consistent heat input drives the dealumination process, where aluminum atoms are removed from the zeolite framework. Without this steady energy, the reaction rate would fluctuate, leading to incomplete activation.
Mechanics of Acid Penetration
Facilitating Pore Access
Zeolites are defined by their porous structure.
The magnetic stirrer keeps the zeolite particles in a constant state of suspension. This agitation allows the acid solution to effectively penetrate the zeolite pores, rather than reacting only with the external surface of settled particles.
Enhancing Impurity Dissolution
Acid activation is also a purification step.
The combination of heat and movement accelerates the dissolution of impurities trapped within the zeolite matrix. Continuous circulation ensures that fresh acid constantly contacts the material, preventing saturation layers from forming around the particles.
Protecting the Zeolite Structure
Preventing Localized Overheating
One of the greatest risks in heating heterogeneous mixtures is the formation of "hotspots."
If the suspension is not stirred, heat accumulates at the bottom of the flask, creating temperatures far exceeding the target range. The magnetic stirrer eliminates this by distributing heat evenly throughout the fluid.
Avoiding Structural Collapse
Zeolite frameworks are sensitive to extreme thermal shock.
Localized overheating can cause the delicate porous structure of the zeolite to collapse, rendering it useless. By strictly controlling the temperature distribution, the stirrer protects the integrity of the crystal lattice during the aggressive acid treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Abrasion Risks
While agitation is necessary, excessive stirring speed can be detrimental.
If the magnetic bar spins too aggressively, it may physically grind the zeolite particles against the flask wall. This can alter particle size distribution unintendedly, affecting filtration and flow properties downstream.
Thermal Lag
Heating mantles or plates associated with magnetic stirrers often have a response delay.
Because the heat must transfer through the glassware to the liquid, there is a risk of temperature overshoot if the controller is not precise. This requires careful monitoring during the initial ramp-up to the 100–105°C range.
Optimizing the Activation Process
To achieve high-quality activated zeolites, you must balance thermal input with physical suspension.
- If your primary focus is maximum porosity: Maintain a moderate stirring speed to ensure full acid penetration into the pores without grinding the particles.
- If your primary focus is crystalline integrity: Prioritize precise temperature regulation to prevent hotspots that lead to structural collapse.
Success relies on using the stirrer not just as a mixer, but as a tool to guarantee a uniform thermal environment for every single particle.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Acid Activation | Benefit to Zeolite |
|---|---|---|
| Precise Heating | Maintains 100–105°C reflux | Ensures consistent reaction kinetics and dealumination |
| Magnetic Agitation | Keeps particles in suspension | Facilitates deep acid penetration into porous structures |
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Eliminates localized hotspots | Prevents thermal shock and crystalline framework collapse |
| Impurity Dissolution | Constant fluid circulation | Accelerates removal of trapped impurities from the matrix |
Elevate Your Material Activation with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect balance of thermal stability and mechanical agitation is critical for high-quality zeolite activation. At KINTEK, we understand that precision is non-negotiable in your research and production.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of lab solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized high-temperature furnaces. Whether you require standard equipment or a fully customizable system tailored to your unique chemical processing needs, KINTEK provides the reliability your lab deserves.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Sandugash Tanirbergenova, З. А. Мансуров. Effect of Acid Treatment on the Structure of Natural Zeolite from the Shankhanai Deposit. DOI: 10.3390/pr13092896
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump create negative pressure? Discover the Liquid-Ring Mechanism for Efficient Lab Vacuum
- How can the temperature resistance of alumina ceramic furnace tubes be assessed? Ensure Long-Term Reliability in Your Lab
- Is it possible to tailor high-temperature laboratory furnaces? Custom Engineering for Unique Research Needs
- What are the main composition percentages of alumina tubes? Optimize Performance for High-Temperature Applications
- What are the primary functions of a quartz tube reactor? Enhance Hydrogen Production and Induction Efficiency
- What function do graphite chill plates or chill rings perform? Master Single-Crystal Blade Directional Solidification
- Why is a tantalum (Ta) crucible essential for Li3-3xScxSb sintering? Ensure Pure Phase Stability at 1143 K
- What is the purpose of configuring a hot gas filter within a Catalytic Hydropyrolysis (CHP) process? Ensure Reactor Life



















