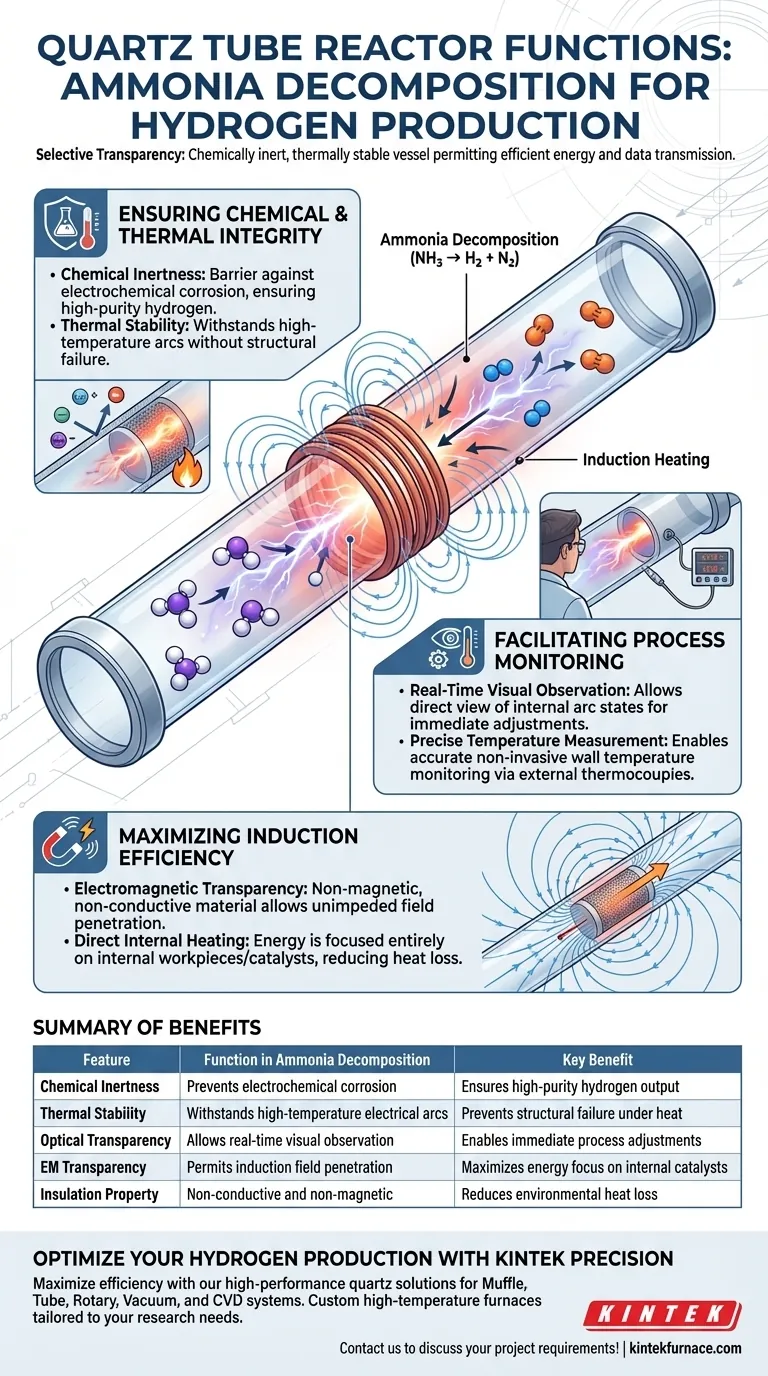
The primary function of a quartz tube reactor in ammonia decomposition is to act as a chemically inert and thermally stable containment vessel that permits the efficient transmission of energy and data. By utilizing quartz, the system can withstand the harsh conditions of high-temperature plasma while remaining transparent to both visual inspection and electromagnetic fields, ensuring energy is directed solely at the reaction rather than the reactor walls.
The core value of a quartz reactor lies in its "selective transparency." It physically contains the harsh ammonia decomposition process but remains invisible to electromagnetic induction fields and optical monitoring instruments, allowing for maximum efficiency and precise control.

Ensuring Chemical and Thermal Integrity
Preventing Electrochemical Corrosion
In ammonia decomposition, particularly those systems utilizing plasma, the reaction environment is highly aggressive. The quartz tube provides excellent chemical inertness, functioning as a barrier that prevents electrochemical corrosion. This is critical for maintaining the purity of the hydrogen output and extending the lifespan of the reactor under high-temperature conditions.
Withstanding High-Temperature Arcs
The decomposition process often involves electrical arcs that generate intense localized heat. The quartz material offers high thermal stability, allowing the reactor to withstand the extreme temperatures produced by these internal electrical arcs without structural failure or degradation.
Facilitating Process Monitoring
Real-Time Visual Observation
Unlike metallic reactors, the optical transparency of quartz allows operators to view the interior of the chamber directly. This permits real-time observation of internal arc states, enabling immediate adjustments to maintain process stability.
Precise Temperature Measurement
The transparency and thermal properties of the tube allow for accurate external monitoring. Thermocouples can be attached to the exterior wall to perform precise wall temperature monitoring, providing critical data on the thermal profile of the reaction zone without breaching the containment.
Maximizing Induction Efficiency
Electromagnetic Transparency
When induction heating is used to drive the decomposition, the reactor material must not interfere with the magnetic field. Quartz is non-magnetic and non-conductive, making it electromagnetically transparent. This allows electromagnetic waves to penetrate the tube wall without resistance or energy loss.
Direct Internal Heating
Because the quartz tube does not shield the field or generate its own heat via induction, energy is focused entirely on the internal metal workpieces or catalysts. This direct heating mechanism significantly reduces environmental heat loss and increases the overall thermal efficiency of the hydrogen production system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The "Cold Wall" Implication
While the lack of self-heating in induction systems is an efficiency benefit, it creates a specific thermal profile. Because the quartz does not generate heat when exposed to the induction field, the system relies entirely on the internal workpieces or catalysts to generate the necessary thermal energy. This requires careful internal design to ensure the catalyst bed is heated uniformly, as it cannot rely on conductive heat transfer from a heated reactor wall.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a quartz tube reactor is a strategic decision based on the specific heating method and monitoring requirements of your ammonia decomposition system.
- If your primary focus is Induction Heating Efficiency: Choose quartz to ensure electromagnetic waves penetrate directly to the catalyst, eliminating energy waste on heating the reactor vessel itself.
- If your primary focus is Process Control and Safety: Leverage the optical transparency of quartz to enable visual monitoring of arc stability and non-invasive temperature sensing.
By utilizing quartz, you convert the reactor vessel from a passive container into an active component that enhances both the visibility and energy efficiency of hydrogen production.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Ammonia Decomposition | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents electrochemical corrosion | Ensures high-purity hydrogen output |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands high-temperature electrical arcs | Prevents structural failure under heat |
| Optical Transparency | Allows real-time visual observation | Enables immediate process adjustments |
| EM Transparency | Permits induction field penetration | Maximizes energy focus on internal catalysts |
| Insulation Property | Non-conductive and non-magnetic | Reduces environmental heat loss |
Optimize Your Hydrogen Production with KINTEK Precision
Maximize your ammonia decomposition efficiency with our high-performance quartz solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of lab equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you need standard quartz tube reactors or a fully customizable high-temperature furnace tailored to your unique research needs, our team delivers the durability and precision your lab requires.
Ready to enhance your thermal efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Zeyu Lin, Bo Liang. Ammonia-Fueled Tubular Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Using a Plasma-Enhanced Cracking Reactor. DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c03027
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How do Mass Flow Controllers (MFC) contribute to the repeatability of In2Se3 synthesis? Master CVD Process Stability
- What roles do the Stockbarger method and vacuum-sealed quartz ampoules play in NaCl:Li and KCl:Na crystal growth?
- What is the function of an in-situ heating holder in the study of Peierls transitions in NaRu2O4? Dynamic Lab Insights
- What factors influence the lifespan of alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Maximize Durability and Performance
- Why use a fusion furnace and platinum crucibles for XRF analysis of magnesium slag? Ensure Accurate Results
- How are quartz tubes used in laboratory applications? Essential for High-Temp, High-Purity Processes
- What is the role of a BN crucible in Ca0.5Sr0.5AlSiN3:Eu2+ synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Nitride Phosphors
- What are the key characteristics of the alumina furnace tube? Essential for High-Temp Lab Success



















