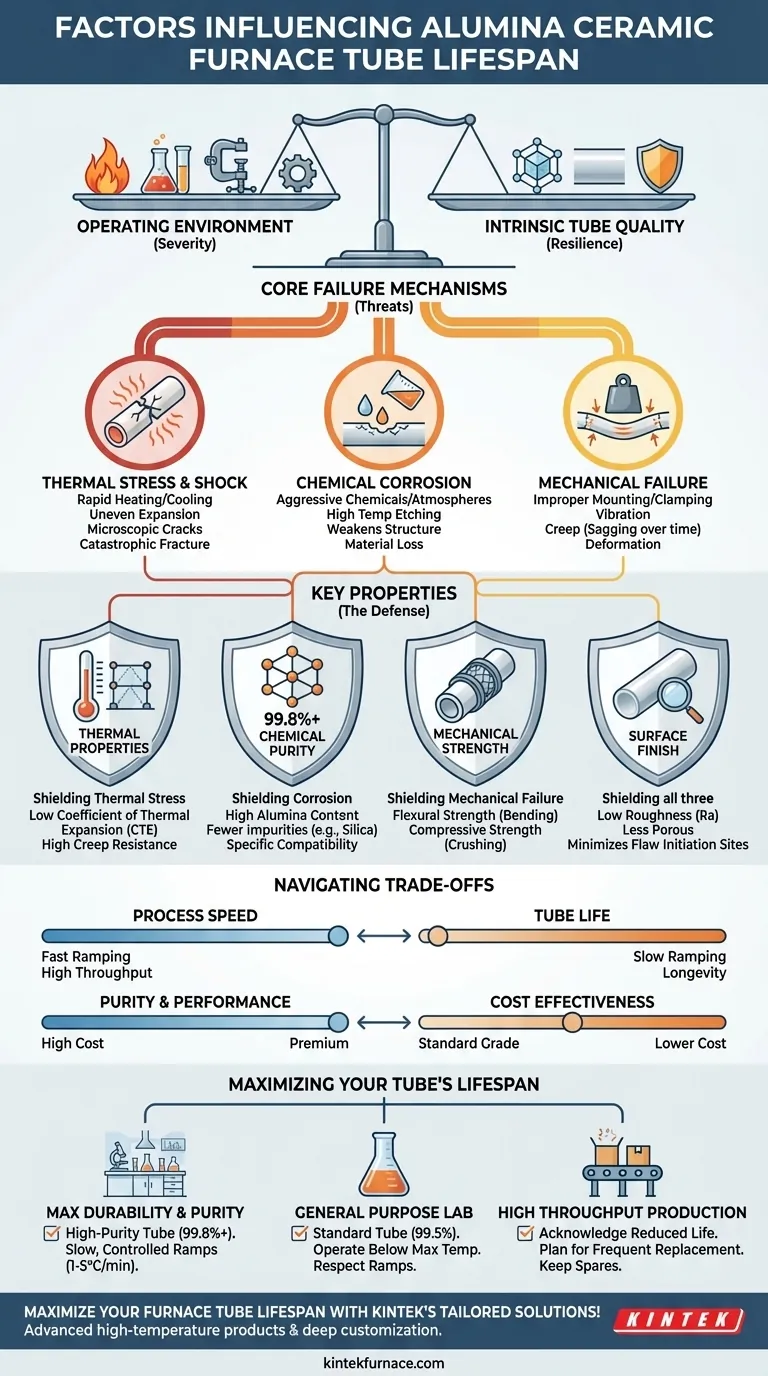
At its core, the lifespan of an alumina ceramic furnace tube is determined by a balance between the severity of its operating environment and the intrinsic quality of the tube itself. Key factors influencing its longevity include the operating temperature and heating/cooling rates, chemical interactions within the furnace, and the presence of mechanical stress.
The ultimate lifespan of a furnace tube is not a fixed attribute but an outcome. It is dictated by the continuous battle between the material's inherent resistance and the cumulative damage from thermal, chemical, and mechanical stresses imposed by your specific process.

The Core Failure Mechanisms
To extend the life of a furnace tube, you must first understand how it fails. Degradation is rarely sudden; it is a gradual process driven by three primary factors.
Thermal Stress and Shock
The most common cause of failure is thermal stress. Alumina has excellent high-temperature stability, but it is a brittle ceramic.
Rapid heating or cooling creates a temperature gradient across the tube wall, causing uneven expansion or contraction. This internal stress can lead to microscopic cracks that eventually grow and cause a catastrophic fracture. This phenomenon is known as thermal shock.
Chemical Corrosion
While alumina is highly resistant to most acids, alkalis, and solvents, it is not invincible. The operational environment must be compatible with the material.
Certain aggressive chemicals or atmospheres, especially at high temperatures, can slowly etch away at the ceramic surface. This corrosion weakens the tube's structure, making it more susceptible to mechanical or thermal failure.
Mechanical Failure
Mechanical stress can arise from several sources. Improper mounting, excessive clamping force, or vibration can introduce localized stress points.
At very high temperatures, the material's own weight can cause it to sag or deform over time, a process known as creep. This is particularly relevant for long, horizontally mounted tubes that are not adequately supported.
Key Properties That Determine Resilience
Understanding the failure mechanisms allows you to evaluate a tube based on the properties that directly counter them. When specifying a tube, look beyond the simple "alumina" label.
Thermal Properties
A manufacturer's data sheet will specify the maximum operating temperature, but you must also consider properties that dictate resistance to thermal stress.
Look for the coefficient of thermal expansion (lower is better for resisting stress) and creep resistance, which indicates the material's ability to resist deformation under high heat and load.
Chemical Purity and Compatibility
The purity of the alumina (e.g., 99.5% vs. 99.8%) has a significant impact on its chemical resistance. Higher purity generally means fewer impurities (like silica) that can act as weak points for chemical attack.
Always verify the tube's documented resistance to the specific chemicals, gases, or melts used in your process.
Mechanical Strength
Key specifications include flexural strength (resistance to bending) and compressive strength (resistance to crushing). These values tell you how well the tube can withstand the physical loads of its installation and operation. Hardness indicates its resistance to surface abrasion.
The Overlooked Factor: Surface Finish
A tube's surface finish, often measured by a roughness value (Ra), is critical. A smoother, less porous surface is easier to clean, minimizes the risk of process contamination, and reduces the number of microscopic surface flaws.
These flaws can act as initiation sites for cracks, making a tube with a poor surface finish more vulnerable to thermal shock and mechanical stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting and operating a furnace tube involves balancing performance, cost, and lifespan. Awareness of these trade-offs is crucial for making informed decisions.
Purity vs. Cost
Higher-purity alumina offers superior thermal and chemical resistance, but it comes at a premium price. For less demanding applications, a standard-grade tube may provide an acceptable lifespan at a lower cost.
Process Speed vs. Tube Life
The most significant operational trade-off is between process speed and tube longevity. Using aggressive heating and cooling rates (fast ramping) will shorten the tube's life due to increased thermal shock, but it may be necessary for high-throughput requirements.
The Supplier Variable
Not all manufacturers produce alumina of the same quality, even if the purity percentage is identical. A reputable supplier with strong quality assurance, transparent technical data, and a long track record provides confidence that the specified properties are consistent and reliable.
Maximizing Your Tube's Lifespan
Your operational protocol is as important as your initial material selection. Use these guidelines to make the right choice and implement best practices.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and process purity: Invest in a high-purity (99.8%+) tube from a reputable supplier and strictly adhere to slow, controlled heating and cooling rates (typically 1-5°C per minute).
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work: A standard 99.5% alumina tube is often sufficient, but always operate well below the specified maximum temperature and respect the manufacturer's recommended ramp rates.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: Acknowledge that rapid thermal cycling will reduce lifespan. Factor in the cost of more frequent tube replacement and consider keeping spares on hand to minimize downtime.
By understanding the interplay of material science and operational discipline, you gain direct control over the reliability and longevity of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stress | Rapid heating/cooling causing cracks | High - leads to fracture |
| Chemical Corrosion | Attack by aggressive substances | Medium - weakens structure |
| Mechanical Stress | Improper mounting or vibration | Medium - causes localized damage |
| Material Purity | Higher purity (e.g., 99.8% alumina) | High - improves resistance |
| Surface Finish | Smoother surfaces reduce flaws | Medium - minimizes crack initiation |
Maximize your furnace tube lifespan with KINTEK's tailored solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability and efficiency. Don't let tube failures disrupt your workflow—contact us today for expert advice and reliable support!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















