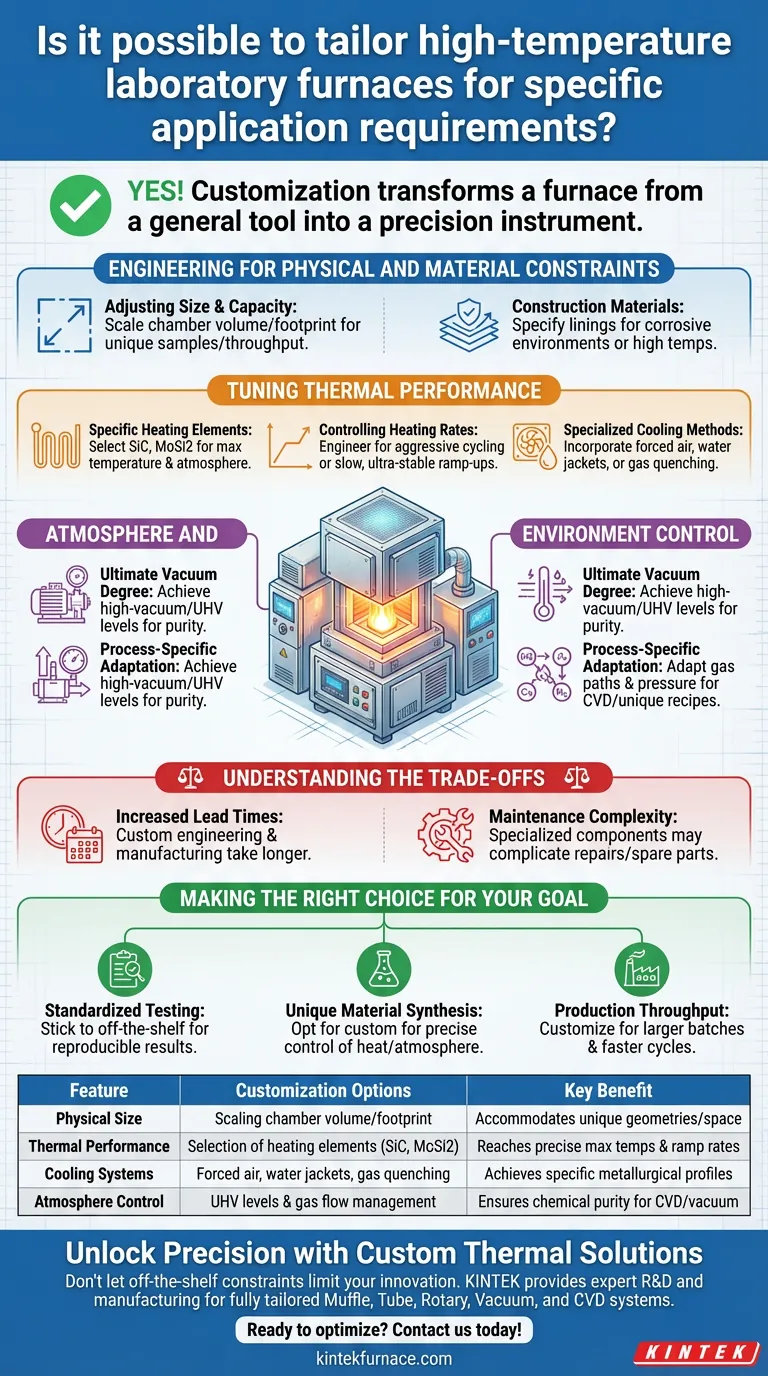
Yes, high-temperature laboratory furnaces can be fully tailored to specific application requirements. Whether utilizing Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, manufacturers can engineer equipment to match unique operational demands. This ensures the furnace aligns precisely with your technical specifications rather than forcing your process to fit standard off-the-shelf constraints.
Customization transforms a furnace from a general tool into a precision instrument. By modifying critical parameters—from heating elements to vacuum degrees—you ensure the equipment supports the exact thermodynamics and throughput required for your specific research or production goals.

Engineering for Physical and Material Constraints
Standard dimensions often fail to accommodate unique sample geometries or laboratory spatial limitations. Customization addresses these physical barriers.
Adjusting Size and Capacity
You are not limited to catalog dimensions. The physical footprint and internal chamber volume can be scaled up or down.
This allows you to accommodate specific sample sizes or increase batch capacity for higher throughput.
Construction Materials
The materials used to build the furnace body and insulation can be specified based on your environment.
If your process involves corrosive byproducts, you can request lining materials that resist chemical degradation better than standard fiber or brick.
Tuning Thermal Performance
The core function of a furnace is thermal management. Customization allows you to dictate exactly how heat is applied and removed.
Specific Heating Elements
You can select the type of heating elements used (e.g., Silicon Carbide, Molybdenum Disilicide) to achieve specific maximum temperatures.
This choice also influences the longevity of the furnace under specific atmosphere conditions.
Controlling Heating Rates
For processes requiring rapid thermal cycling, the power supply and element configuration can be engineered for aggressive heating rates.
Conversely, for delicate materials, systems can be tuned for slow, ultra-stable ramp-ups to prevent thermal shock.
Specialized Cooling Methods
Standard furnaces often rely on natural cooling, which may be too slow for some metallurgical processes.
Custom units can incorporate forced air, water cooling jackets, or inert gas quenching to achieve precise cooling profiles.
Atmosphere and Environment Control
Advanced applications often require strict control over the reaction environment, particularly in Vacuum and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) systems.
Ultimate Vacuum Degree
For vacuum furnaces, the "ultimate vacuum degree" is a customizable parameter.
You can specify the pump system to achieve high-vacuum or ultra-high-vacuum levels depending on the purity requirements of your melt or heat treatment.
Process-Specific Adaptation
Systems like CVD furnaces can be adapted for specific gas flow paths and pressure management.
This flexibility ensures the equipment supports your unique chemical recipes and production processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While customization offers precision, it introduces specific challenges that must be weighed against the benefits of standard models.
Increased Lead Times
Custom engineering requires design verification and specialized manufacturing.
Expect significantly longer delivery times compared to off-the-shelf units that are in stock or pre-assembled.
Maintenance Complexity
Standard furnaces use ubiquitous parts that are easy to source.
Custom units may utilize specialized components, potentially complicating repairs and increasing the lead time for spare parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Before commissioning a custom build, evaluate your project's specific constraints to determine if the investment yields the necessary return.
- If your primary focus is Standardized Testing: Stick to off-the-shelf models to ensure your results are easily reproducible by other labs using standard equipment.
- If your primary focus is Unique Material Synthesis: Opt for customization to gain precise control over heating rates, atmosphere, and vacuum levels that standard units cannot achieve.
- If your primary focus is Production Throughput: Customize the chamber size and cooling systems to maximize batch sizes and reduce cycle times.
Customization is not just about fitting a space; it is about engineering the equipment to remove variables and guarantee process integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Customization Options | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Size | Scaling chamber volume and footprint | Accommodates unique sample geometries and lab space |
| Thermal Performance | Selection of heating elements (SiC, MoSi2) | Reaches precise max temperatures and ramp rates |
| Cooling Systems | Forced air, water jackets, gas quenching | Achieves specific metallurgical cooling profiles |
| Atmosphere Control | UHV levels and gas flow management | Ensures chemical purity for CVD and vacuum processes |
Unlock Precision with Custom Thermal Solutions
Don’t let off-the-shelf constraints limit your innovation. KINTEK provides expert R&D and manufacturing to deliver fully tailored Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed specifically for your unique process requirements. Whether you need specialized atmosphere control or unique chamber dimensions, our engineering team is ready to build your ideal solution.
Ready to optimize your lab's performance? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Manaswini Sahoo, G. Allodi. Ubiquitous Order‐Disorder Transition in the Mn Antisite Sublattice of the (MnBi<sub>2</sub>Te<sub>4</sub>)(Bi<sub>2</sub>Te<sub>3</sub>)<sub><i>n</i></sub> Magnetic Topological Insulators. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202402753
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which industries commonly use graphite crucible furnaces? Essential for High-Temp, High-Purity Processes
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during the SPS sintering process of Al2O3-TiC? Unlock Process Efficiency
- How do high-precision mass flow controllers contribute to studying the oxidation behavior of lignite?
- What role does a quartz substrate holder play in MoS2 growth? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precision Hardware
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for Li2Mg3Ti(1-x)ZrxO6 sintering? Ensure Dielectric Excellence
- What are the advantages of using high-purity platinum crucibles? Ensure Absolute Data Integrity in Magnetite Oxidation
- What are alumina ceramic tubes and why are they considered advanced ceramics? Discover High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is a laboratory-grade high-pressure reactor essential for TiO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Purity and Efficiency



















