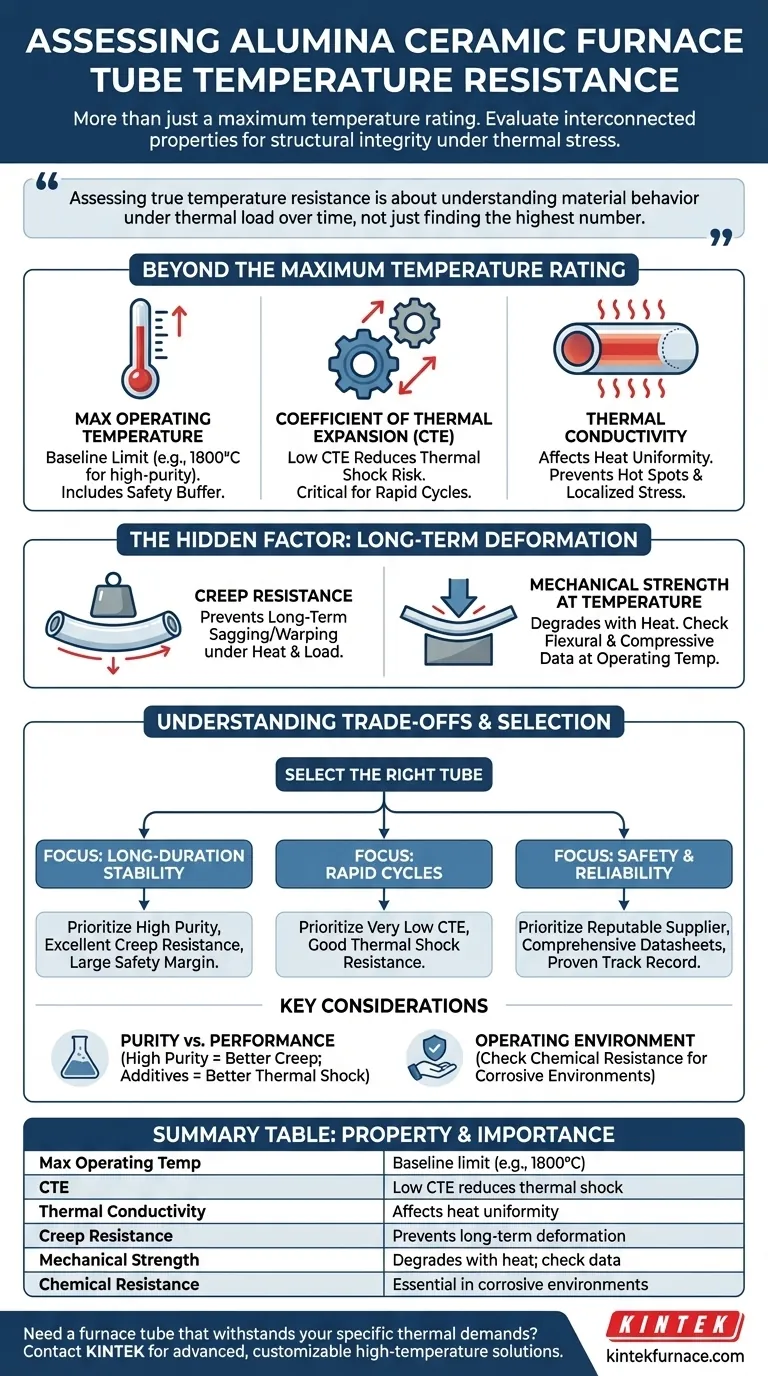
To assess the temperature resistance of an alumina ceramic furnace tube, you must evaluate a set of interconnected properties provided by the manufacturer. This goes beyond a single "maximum temperature" rating and includes the coefficient of thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, and long-term creep resistance. These specifications collectively determine the tube's ability to maintain its structural integrity under the thermal stresses of your specific application.
Assessing true temperature resistance is not about finding the highest number on a datasheet. It's about understanding how the material behaves under thermal load over time, ensuring the furnace tube will not crack, deform, or fail when subjected to your process's unique heating and cooling cycles.

Beyond the "Maximum Temperature" Rating
The advertised maximum operating temperature is a critical starting point, but it doesn't tell the whole story. Real-world performance depends on how the tube handles changes in temperature and maintains its physical form.
The Maximum Operating Temperature: Your Baseline
This value, often up to 1800°C for high-purity alumina, represents the absolute limit the material can withstand.
For safety and longevity, you must choose a tube with a rating significantly higher than your intended operating temperature. This buffer accounts for potential temperature overshoots and material degradation over time.
Thermal Shock and the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
The CTE measures how much the ceramic expands when heated and contracts when cooled. A low CTE is highly desirable.
A tube with a high CTE is more susceptible to thermal shock—cracking caused by rapid temperature changes. If your process involves fast heating or cooling rates, a low and well-documented CTE is a non-negotiable parameter.
Heat Uniformity and Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity indicates how efficiently heat transfers through the tube material.
While alumina is a thermal insulator, its conductivity affects the temperature uniformity inside the furnace. Consistent conductivity ensures even heating and prevents "hot spots" that can create localized stress on the tube wall, leading to premature failure.
The Hidden Factor: Long-Term Deformation Under Heat
Many failures do not happen instantly but occur over hundreds or thousands of hours of operation. This slow deformation under heat and load is a critical, often overlooked, aspect of temperature resistance.
Understanding Creep Resistance
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress, even at temperatures below its melting point.
For a furnace tube, this stress can simply be its own weight over a long span. Excellent creep resistance ensures the tube will not sag, bend, or warp over its operational lifespan at high temperatures, which is essential for maintaining process integrity.
The Role of Mechanical Strength at Temperature
Key mechanical properties include flexural strength (resistance to bending) and compressive strength (resistance to crushing).
It is crucial to understand that these properties degrade as temperature increases. A simple room-temperature strength value is insufficient. A reliable manufacturer will provide data on how the tube's mechanical strength behaves at elevated operating temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right tube involves balancing performance characteristics against the demands of your application and budget.
Purity vs. Performance
Higher alumina purity (e.g., 99.7%+) generally correlates with better creep resistance and a higher maximum operating temperature.
However, certain additives in lower-purity grades can sometimes improve thermal shock resistance. You must weigh the need for absolute temperature stability against the demands of your heating and cooling cycles.
The Operating Environment Matters
The tube's temperature resistance is only valid in an environment it can tolerate.
If your process involves corrosive chemicals, acids, or alkalis, you must verify the tube's chemical resistance. Chemical attack can degrade the ceramic, severely compromising its structural integrity and lowering its effective temperature resistance.
Supplier Data and Reliability
The specifications are only as trustworthy as the supplier who provides them.
A reputable supplier will offer comprehensive datasheets, quality assurance documentation, and available technical support. Evaluating supplier reliability is a crucial step in ensuring the product you receive matches the performance you expect.
How to Select the Right Tube for Your Application
Use your specific process requirements to prioritize the following technical specifications.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature stability for long-duration processes: Prioritize a tube with the highest alumina purity, excellent documented creep resistance, and a large safety margin on the maximum operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles: Prioritize a tube with a very low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and good thermal shock resistance specifications.
- If your primary focus is overall safety and long-term reliability: Prioritize a reputable supplier who provides comprehensive datasheets detailing mechanical properties at elevated temperatures and has a proven track record of quality.
Ultimately, a truly temperature-resistant tube is one whose properties are holistically matched to the demands of your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Importance for Temperature Resistance |
|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Baseline limit, often up to 1800°C for high-purity alumina |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) | Low CTE reduces thermal shock risk from rapid temperature changes |
| Thermal Conductivity | Affects heat uniformity, preventing hot spots and stress |
| Creep Resistance | Prevents long-term deformation like sagging under heat and load |
| Mechanical Strength at Temperature | Degrades with heat; check flexural and compressive strength data |
| Chemical Resistance | Essential in corrosive environments to maintain integrity |
Need a furnace tube that withstands your specific thermal demands? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing safety and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored alumina ceramic tubes can optimize your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















