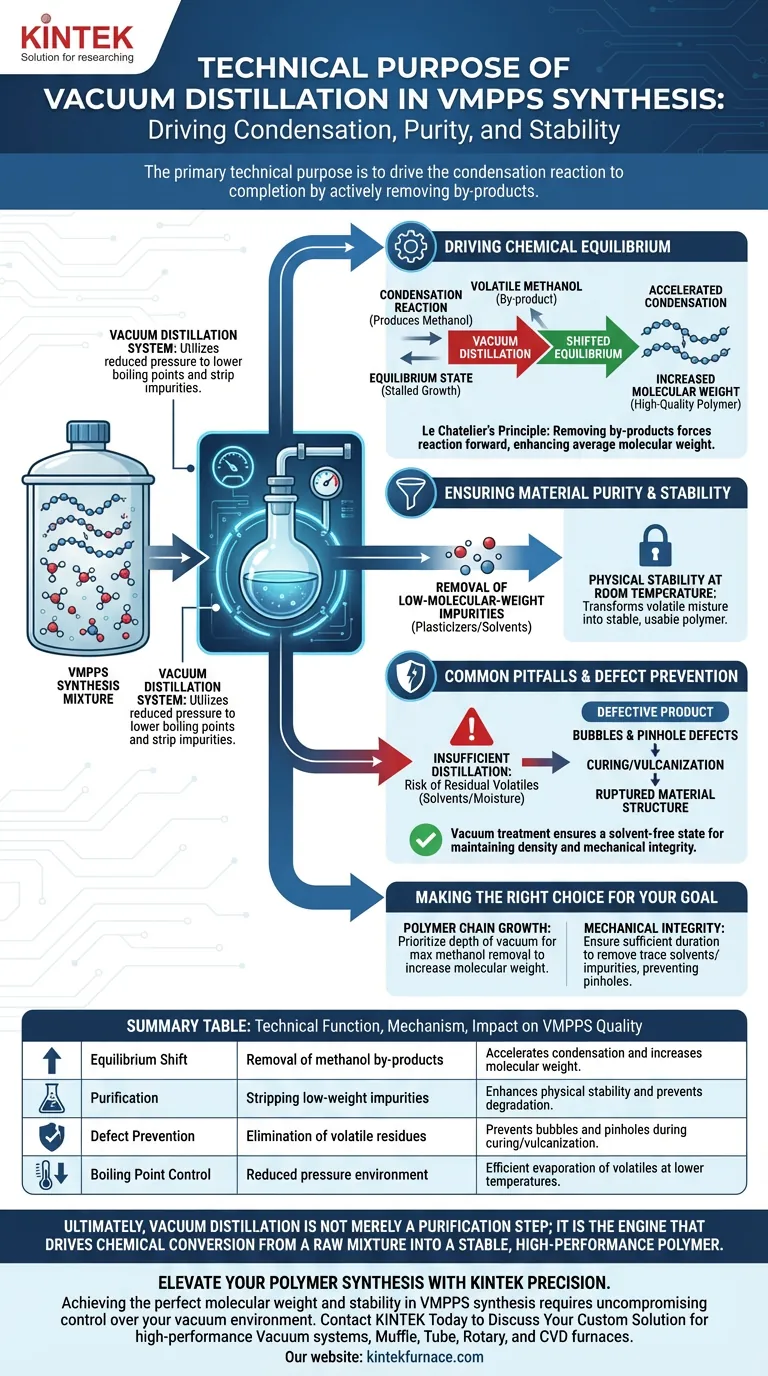
The primary technical purpose of using a vacuum distillation system in VMPPS synthesis is to drive the condensation reaction to completion by actively removing by-products. Specifically, the system utilizes reduced pressure to lower the boiling points of impurities—such as methanol and unreacted low-molecular-weight compounds—allowing them to be stripped from the polymer matrix efficiently.
By continuously removing volatile by-products, the vacuum distillation process forces a chemical equilibrium shift that is essential for synthesizing high-quality polymers. This step is the defining factor in achieving the target average molecular weight and ensuring the physical stability of the material at room temperature.
Driving Chemical Equilibrium
Le Chatelier’s Principle in Action
The synthesis of Vinyl Methyl Phenyl Polysiloxane (VMPPS) relies on a condensation reaction that generates by-products, notably methanol.
If these by-products remain in the system, the reaction reaches an equilibrium state where polymer growth stalls.
Accelerating Condensation
Vacuum distillation disrupts this equilibrium by creating a reduced-pressure environment.
This lowers the boiling point of the methanol, allowing it to evaporate rapidly. As the by-product is physically removed, the reaction acts to replace it, effectively accelerating the forward reaction and promoting more complete condensation.
Increasing Molecular Weight
The direct result of this equilibrium shift is the continuous growth of polymer chains.
Without effective vacuum distillation, the polymer chains remain short. The process is therefore critical for enhancing the average molecular weight to meet technical specifications.
Ensuring Material Purity and Stability
Removal of Low-Molecular-Weight Impurities
Beyond reaction by-products, the synthesis mixture contains unreacted oligomers or low-molecular-weight impurities.
Vacuum distillation strips these volatile components out of the bulk material. This purification is necessary because these impurities act as plasticizers that can degrade the mechanical properties of the final product.
Physical Stability at Room Temperature
A VMPPS system that retains impurities or solvents is often unstable.
The primary reference indicates that thoroughly removing these components ensures the physical stability of the resulting polysiloxane when stored at room temperature. It transforms a volatile mixture into a stable, usable polymer.
Common Pitfalls and Defect Prevention
The Risk of Residual Volatiles
If the vacuum distillation process is insufficient, trace volatiles (including solvents or moisture) remain trapped within the viscous polymer matrix.
While final drying (often via vacuum oven) captures trace residues, the bulk distillation phase does the heavy lifting. Failure here overburdens downstream drying processes.
Preventing Structural Defects
The presence of trapped volatiles is a primary cause of bubbles or pinhole defects during subsequent curing or vulcanization stages.
As noted in supplementary contexts regarding vacuum treatment, ensuring a solvent-free state is vital for maintaining density and mechanical integrity. If these volatiles boil off during the final application (such as high-temperature vulcanization), they rupture the material structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your VMPPS synthesis, assess your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is Polymer Chain Growth: Prioritize the depth of the vacuum and temperature control to maximize the removal of methanol, which directly drives the equilibrium toward higher molecular weights.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Integrity: Ensure the distillation duration is sufficient to remove not just reaction by-products, but all trace solvents and low-molecular-weight impurities to prevent pinholes and bubbles during curing.
Ultimately, vacuum distillation is not merely a purification step; it is the engine that drives the chemical conversion from a raw mixture into a stable, high-performance polymer.
Summary Table:
| Technical Function | Mechanism | Impact on VMPPS Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium Shift | Removal of methanol by-products | Accelerates condensation and increases molecular weight |
| Purification | Stripping low-weight impurities | Enhances physical stability and prevents degradation |
| Defect Prevention | Elimination of volatile residues | Prevents bubbles and pinholes during curing/vulcanization |
| Boiling Point Control | Reduced pressure environment | Efficient evaporation of volatiles at lower temperatures |
Elevate Your Polymer Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect molecular weight and stability in VMPPS synthesis requires uncompromising control over your vacuum environment. At KINTEK, we understand the critical role that specialized distillation and thermal equipment play in driving chemical equilibrium and material purity.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer high-performance Vacuum systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD furnaces—all fully customizable to meet the unique demands of your lab. Whether you are scaling up production or refining complex polysiloxane formulations, our systems ensure maximum efficiency and defect-free results.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature lab processes?
Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Ao Liu, Chaocan Zhang. A High-Temperature-Resistant and Conductive Flexible Silicone Rubber with High Phenyl Content Based on Silver-Coated Glass Fibers. DOI: 10.3390/polym17091187
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be joined using vacuum brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean Bonds for Dissimilar Materials
- What types of quenching methods are available in a vacuum furnace? Optimize Hardening with Oil or Gas Quenching
- What role does a vacuum chamber play in the Flash Joule Heating (FJH) process for LIG? Master Graphene Synthesis
- What is the function of a vacuum oven in TiN/MoS2 coating? Master the Curing Process for Superior Film Integrity
- Why is a high-pressure reactor core equipment for hydrothermal carbonization? Unlock Superior Carbon Skeletons
- What evidence does vacuum tensile testing equipment provide for hydrogen embrittlement? Discover Gas Release Secrets
- How does a vacuum drying oven ensure efficient encapsulation? Master Vacuum Impregnation for Phase Change Materials
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum dryer for cerium oxide nanoparticles? Preserve Integrity & Prevent Oxidation



















