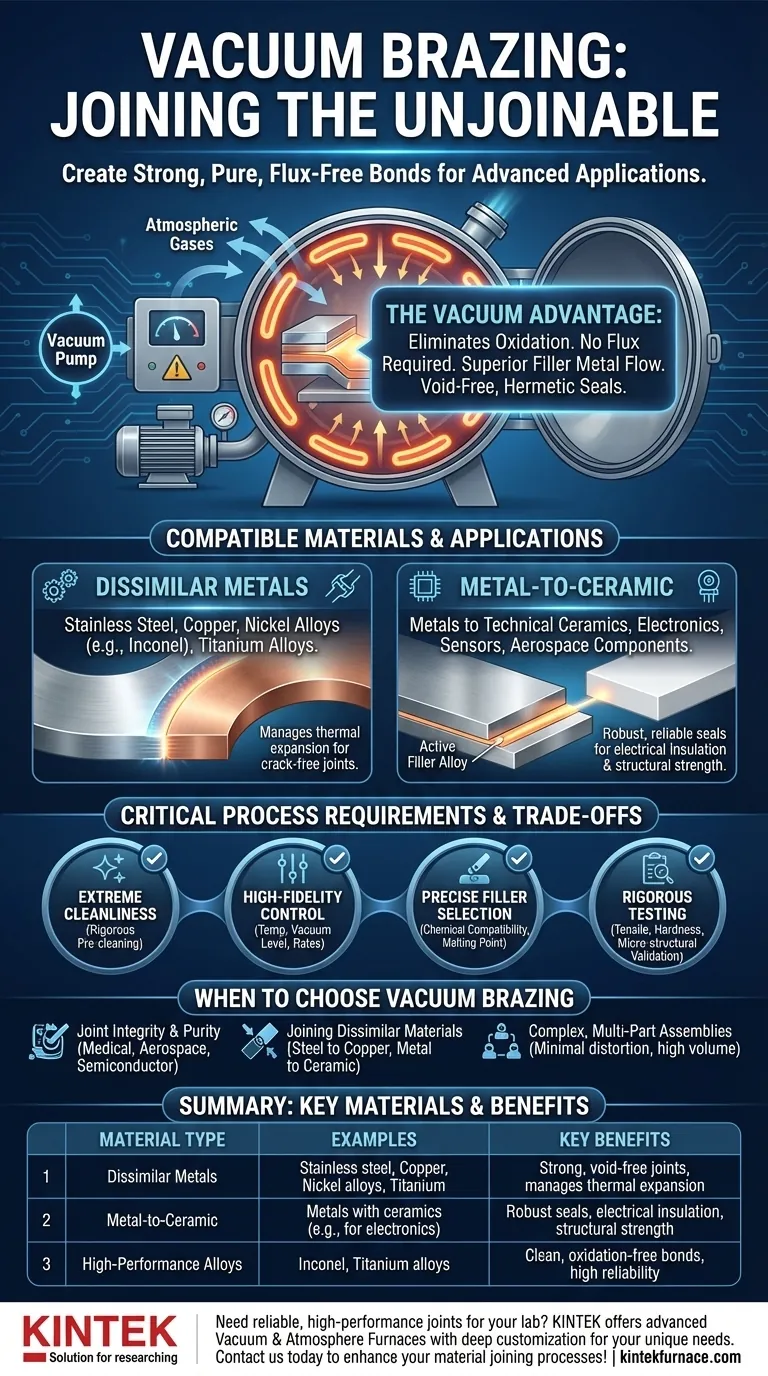
In short, vacuum brazing excels at joining a wide range of materials, particularly dissimilar metals and metal-to-ceramic combinations. It is frequently used for high-performance alloys such as stainless steel, nickel alloys, titanium, and copper, creating strong, clean joints that are often impossible to achieve with other methods.
The true advantage of vacuum brazing is not just the list of materials it can join, but its ability to create exceptionally pure, flux-free bonds between challenging and dissimilar materials. The process is chosen when joint integrity and performance are non-negotiable.

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
The "vacuum" in vacuum brazing is the key to its unique capabilities. By removing atmospheric gases from a sealed furnace, the process fundamentally changes how materials can be joined.
Eliminating Oxidation Without Flux
In traditional brazing, a chemical agent called flux is required to clean the surfaces and prevent oxidation when heat is applied. A vacuum environment makes this unnecessary.
With virtually no oxygen present, oxides cannot form on the metal surfaces, ensuring they remain perfectly clean for the brazing filler metal to adhere to.
Enhancing Filler Metal Flow
Because the base material surfaces are atomically clean, the molten filler metal can flow smoothly and completely into the joint through capillary action.
This results in a void-free, exceptionally strong, and hermetically sealed bond that covers the entire joint interface.
A Closer Look at Compatible Materials
Vacuum brazing's versatility comes from its ability to handle materials with different chemical and physical properties.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
The process is a premier solution for joining metals that are difficult or impossible to weld together. Common combinations include:
- Stainless Steel
- Copper
- Nickel-based alloys (e.g., Inconel)
- Titanium alloys
The controlled heating and cooling cycles in a vacuum furnace help manage the different thermal expansion rates of these metals, reducing stress and preventing cracks.
Integrating Metals and Ceramics
One of the most powerful applications of vacuum brazing is joining metals to ceramics. This is critical for creating components that require both electrical insulation and structural strength.
With the careful selection of an active filler alloy, the braze material can chemically bond to the ceramic surface, creating a robust, reliable seal used in electronics, sensors, and aerospace components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Requirements
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a precise and demanding process. Success is not just about choosing the right materials, but about controlling the entire environment.
The Necessity of Extreme Cleanliness
The process is highly sensitive to contamination. Any oils, dirt, or other residues on the parts will vaporize in the vacuum and can ruin the braze.
This is why rigorous pre-cleaning of parts and assembly in a controlled, clean environment are absolute prerequisites for a successful outcome.
High-Fidelity Process Control
Success depends on high-quality equipment. A high-vacuum furnace is required to achieve the necessary purity, and process variables like temperature, heating/cooling rates, and vacuum level must be precisely controlled.
Careful Filler Metal Selection
The filler metal is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It must be chemically compatible with both base materials and have a melting point that is suitable for the application without damaging the parts being joined.
The Importance of Rigorous Testing
Given the critical applications where vacuum brazing is used, finished assemblies must be validated. Facilities for tensile testing, hardness testing, and micro-structural analysis are essential to verify the integrity and strength of every joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting vacuum brazing depends entirely on your project's technical demands.
- If your primary focus is joint integrity and purity: This process is unmatched for creating flux-free, strong bonds, making it essential for medical, aerospace, and semiconductor applications.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (e.g., steel to copper or metal to ceramic): Vacuum brazing is one of the most reliable methods for creating a robust bond between materials that cannot be welded.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, multi-part assemblies: The process allows for the simultaneous joining of dozens or even hundreds of joints in a single furnace cycle, producing a clean, finished assembly with minimal distortion.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum brazing is a decision to prioritize final component performance and reliability over process simplicity.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dissimilar Metals | Stainless steel, Copper, Nickel alloys, Titanium | Strong, void-free joints, manages thermal expansion |
| Metal-to-Ceramic | Metals with ceramics (e.g., for electronics) | Robust seals, electrical insulation, structural strength |
| High-Performance Alloys | Inconel, Titanium alloys | Clean, oxidation-free bonds, high reliability |
Need reliable, high-performance joints for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for vacuum brazing and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material joining processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















