Crucibles serve as the fundamental barrier between a sample and the destructive environment of a high-temperature furnace. In laboratory applications, their specific utility lies in their ability to maintain structural integrity while effectively containing samples during intensive thermal processes such as melting, sintering, or calcination.
Crucibles are not merely containers; they are active components in thermal analysis that preserve sample purity and ensure data accuracy. They protect materials during extreme heating while facilitating the precise transfer of thermal energy required for analytical testing.

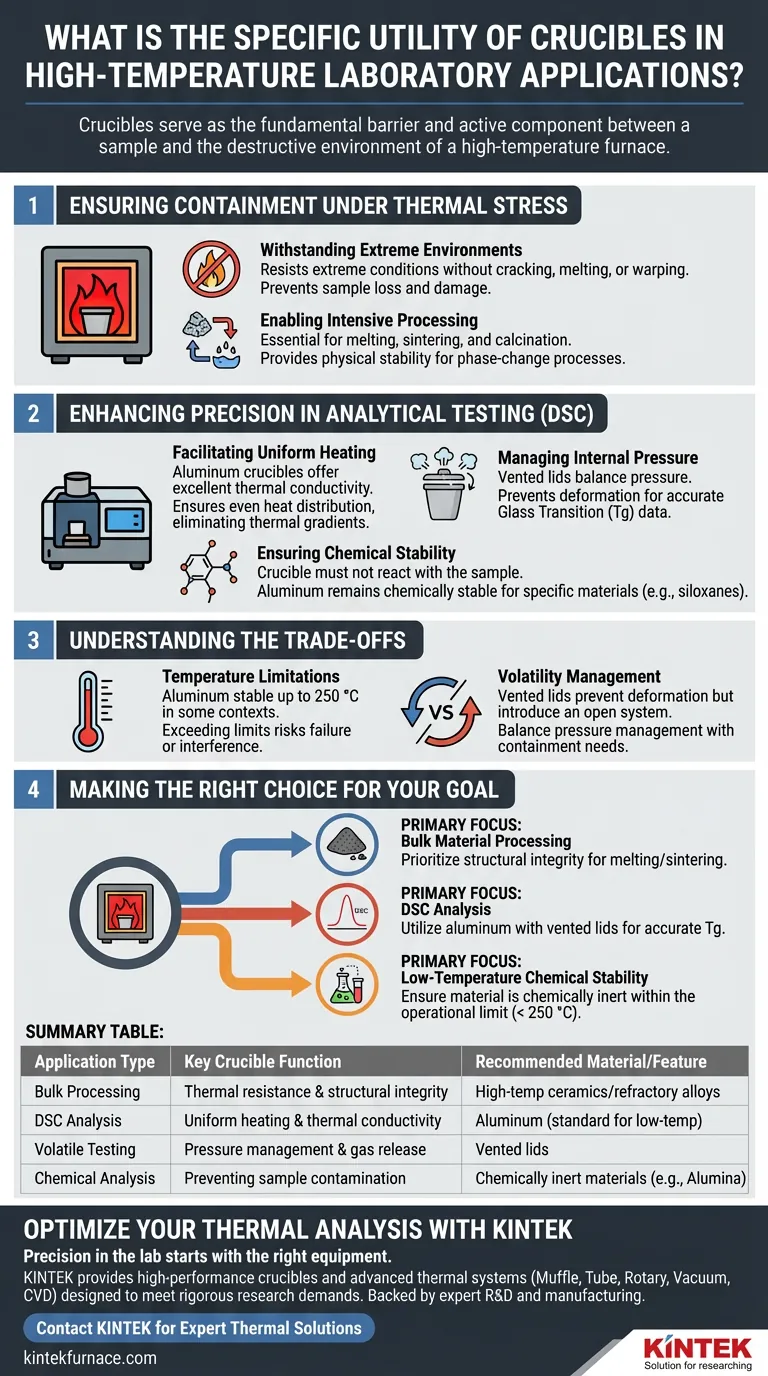
Ensuring Containment Under Thermal Stress
Withstanding Extreme Environments
The primary function of a crucible is to survive conditions that would destroy standard laboratory glassware.
They are engineered to resist extreme thermal conditions without cracking, melting, or warping.
This ensures the vessel remains intact, preventing sample loss or damage to the furnace system during operation.
Enabling Intensive Processing
Crucibles provide the physical stability required for aggressive phase-change processes.
They are essential for melting, sintering, and calcination, holding the material securely as it undergoes physical or chemical transformation.
This containment allows researchers to process materials safely at temperatures required to alter their fundamental properties.
Enhancing Precision in Analytical Testing (DSC)
Facilitating Uniform Heating
In applications like Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), the material of the crucible dictates the quality of the data.
Aluminum crucibles, for instance, offer excellent thermal conductivity.
This ensures the heat is distributed evenly throughout the sample, eliminating thermal gradients that could skew test results.
Managing Internal Pressure
Specific crucible designs utilize vented lids to mechanically balance internal and external pressures.
This feature prevents the crucible from deforming due to the build-up of volatile components evolved during heating.
By maintaining the vessel's shape, vented lids ensure the acquisition of accurate Glass Transition (Tg) data.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
For accurate analysis, the crucible must not chemically react with the sample.
Aluminum crucibles remain chemically stable when testing specific materials, such as siloxane mixtures.
This inertness preserves the chemical composition of the sample, ensuring that the observed thermal events are inherent to the material and not artifacts of a reaction with the container.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Limitations
While versatile, specific crucible materials have defined thermal ceilings.
For example, while aluminum offers superior conductivity, it is chemically stable only up to 250 °C in certain contexts.
Exceeding this limit can lead to vessel failure or chemical interference, necessitating the use of alternative materials for higher-temperature studies.
Volatility Management
While vented lids solve pressure issues, they introduce an open system.
This design is excellent for preventing deformation but may not be suitable if the goal is to completely retain all volatile mass.
You must choose between pressure, balance, and complete containment based on the specific analytical data you require.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible requires balancing thermal endurance with analytical precision.
- If your primary focus is bulk material processing: Prioritize crucibles designed for maximum structural integrity to withstand the prolonged heat of melting or sintering without failure.
- If your primary focus is Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC): Utilize aluminum crucibles with vented lids to ensure uniform heating and pressure balance for accurate Glass Transition (Tg) measurements.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature chemical stability: Ensure the crucible material remains inert relative to your sample (e.g., siloxanes) within the operational limit (e.g., < 250 °C).
The utility of a crucible is defined not just by its ability to hold a sample, but by its ability to disappear—chemically and physically—leaving only the true properties of your material to be measured.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key Crucible Function | Recommended Material/Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Processing | Thermal resistance & structural integrity | High-temp ceramics/refractory alloys |
| DSC Analysis | Uniform heating & thermal conductivity | Aluminum (standard for low-temp) |
| Volatile Testing | Pressure management & gas release | Vented lids |
| Chemical Analysis | Preventing sample contamination | Chemically inert materials (e.g., Alumina) |
Optimize Your Thermal Analysis with KINTEK
Precision in the lab starts with the right equipment. KINTEK provides high-performance crucibles and advanced thermal systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of your research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of laboratory equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which can be customized to your specific high-temperature needs.
Don't let subpar containment compromise your data accuracy. Ensure your materials are processed with the highest structural integrity and chemical stability today.
Contact KINTEK for Expert Thermal Solutions
Visual Guide
References
- Preparation and Characterization of Nanogold/Silica/Epoxy Acrylate Flame‐Retardant Coatings. DOI: 10.1002/slct.202405128
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a FeCrAl alloy crucible used in CDM experiments? The Key to High-Temperature Stability
- Why is a vacuum suction system required during the exhaust stage of rice straw-based charcoal carbonization?
- Why is the precise regulation of oxygen ratios via mass flow controllers critical for MCTV catalyst yield?
- What is the necessity of configuring non-contact infrared pyrometers for temperature monitoring? Ensure Sintering Precision
- What is the function of a high-precision mass flow controller (MFC) in CdS nanobelt vapor deposition?
- What role do graphite molds play in graphite flake alignment? Engineered Precision for High Thermal Conductivity
- Why is a vacuum pump necessary for bio-adsorbent performance assessments? Ensuring Industrial Viability in VSA
- What is the role of a quartz reactor within a vacuum distillation apparatus for metal recovery? Unlocking Efficient High-Purity Extraction



















