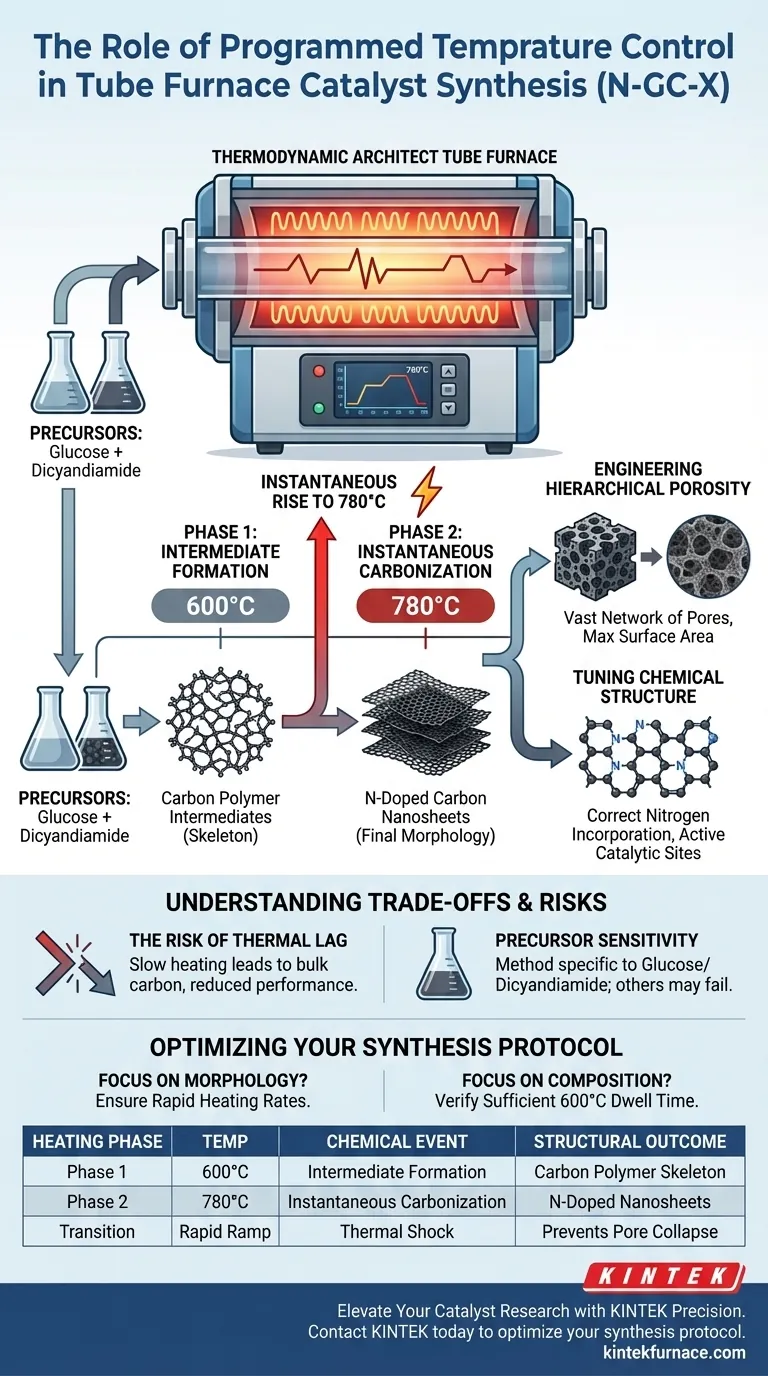
The primary role of programmed temperature control in this context is to act as a thermodynamic architect. In the synthesis of N-GC-X catalysts, the tube furnace does not simply heat materials; it executes a precise, two-stage thermal strategy. This regulation governs the pyrolysis of precursors—specifically glucose and dicyandiamide—to ensure they evolve into nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets with a specific, highly developed pore structure.
Core Takeaway Programmed temperature control is the mechanism that enables a critical two-phase reaction: creating polymer intermediates at 600°C and then instantly carbonizing them at 780°C. Without this specific thermal trajectory, the precursors would fail to form the hierarchical porosity and chemical structure required for high-performance catalysis.

The Two-Stage Heating Strategy
The effectiveness of the N-GC-X catalyst is entirely dependent on a split-phase thermal treatment. The tube furnace’s programming capability allows for two distinct thermodynamic events to occur in sequence.
Phase 1: Intermediate Formation at 600°C
The first stage involves heating the precursors to a steady 600°C.
During this phase, glucose and dicyandiamide undergo a specific chemical transformation. They do not immediately carbonize; instead, they react to form carbon polymer intermediates. This step creates the structural "skeleton" required for the final catalyst.
Phase 2: Instantaneous Rise to 780°C
The second stage requires a rapid thermal shift. The programming triggers an instantaneous temperature increase from 600°C to 780°C.
This sudden jump forces the intermediates to undergo rapid pyrolysis and carbonization. It is this specific thermal shock that locks in the material's final morphology.
Why Precise Regulation Matters
The tube furnace provides the stable environment necessary to execute this complex recipe without deviation.
Engineering Hierarchical Porosity
The ultimate goal of this thermal process is to create hierarchical porosity.
By controlling the transition between intermediate formation and final carbonization, the furnace prevents the collapse of the material's structure. This results in N-doped carbon nanosheets that possess a vast network of pores, which is essential for maximizing surface area.
Tuning Chemical Structure
Temperature precision directly impacts the chemical composition of the final product.
The specific heating profile ensures the correct incorporation of nitrogen into the carbon lattice. This "doping" creates active sites within the carbon nanosheets, which are the engines driving catalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While programmed temperature control offers high precision, it introduces specific sensitivities to the manufacturing process.
The Risk of Thermal Lag
The process relies on an "instantaneous" rise to 780°C.
If the tube furnace cannot ramp up temperature fast enough, the reaction pathway alters. Slow heating between the two stages may lead to bulk carbonization rather than the formation of nanosheets, significantly reducing catalytic performance.
Precursor Sensitivity
The thermodynamic conditions are tuned specifically for glucose and dicyandiamide.
This method is highly specific to these precursors. Attempting to use this exact temperature program with different carbon or nitrogen sources without adjustment may result in incomplete carbonization or unstable structures.
Optimizing Your Synthesis Protocol
To replicate the high-performance characteristics of N-GC-X catalysts, you must align your equipment capabilities with the chemical requirements of the precursors.
- If your primary focus is Structural Morphology: Ensure your furnace is capable of rapid heating rates to achieve the "instantaneous" transition from 600°C to 780°C required for nanosheet formation.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Composition: Verify that the dwell time at 600°C is sufficient for the glucose and dicyandiamide to fully convert into polymer intermediates before the temperature spike.
Success in this synthesis depends not just on reaching high temperatures, but on the precision of the journey between them.
Summary Table:
| Heating Phase | Temperature | Chemical Event | Structural Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | 600°C | Intermediate Formation | Creates the carbon polymer structural "skeleton" |
| Phase 2 | 780°C | Instantaneous Carbonization | Triggers rapid pyrolysis to form N-doped nanosheets |
| Transition | Rapid Ramp | Thermal Shock | Prevents pore collapse and locks in morphology |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
Precision is the difference between bulk carbon and high-performance N-doped nanosheets. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces designed to execute the complex thermal trajectories your synthesis demands.
Whether you require rapid ramp rates for thermal shock or stable dwell times for polymer formation, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique lab needs. Contact KINTEK today to optimize your synthesis protocol and ensure your materials achieve the hierarchical porosity they deserve.
Visual Guide
References
- Ganchang Lei, Lilong Jiang. Atom-economical insertion of hydrogen and sulfur into carbon–nitrogen triple bonds using H<sub>2</sub>S <i>via</i> synergistic C–N sites. DOI: 10.1039/d5ey00110b
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in Leidenfrost experiments? Preheating with Precision & Protection
- What is the core function of a high-temperature tube furnace in Pb SA/OSC construction? Precision Atomic Engineering
- How do tube furnaces function and where are they used? Discover Precision Heating Solutions
- What are the advantages of using tube furnace oxidation simulation facilities? Enhance Your High-Temp Material Testing
- What types of tube materials are available for tube furnaces and what are their temperature limits? Choose the Right Material for Your Lab
- What are the common applications of tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- Why are quartz or alumina tubes used in tube furnaces? Key Benefits for High-Temp Processes
- What is the function of a fast-response photoelectric sensor system? Precision Ignition Timing in Tube Furnaces



















