Tube furnace oxidation simulation facilities provide a controlled and reliable method for assessing high-temperature durability by maintaining stable gas flow rates and specific chemical compositions over extended periods, often up to 1000 hours. This precision allows researchers to accurately replicate and analyze the complex material degradation behaviors that occur during actual long-term service.
By maintaining environmental stability over long durations, these facilities reveal critical failure mechanisms—such as oxide scale spallation and chromium depletion—that are often undetectable in shorter or less controlled experiments.
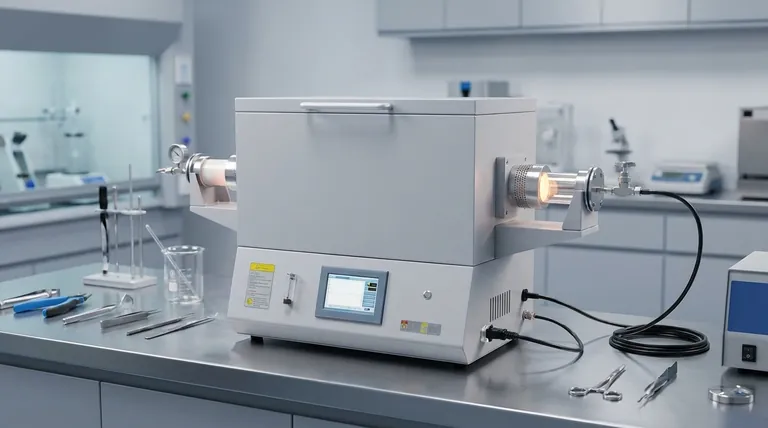

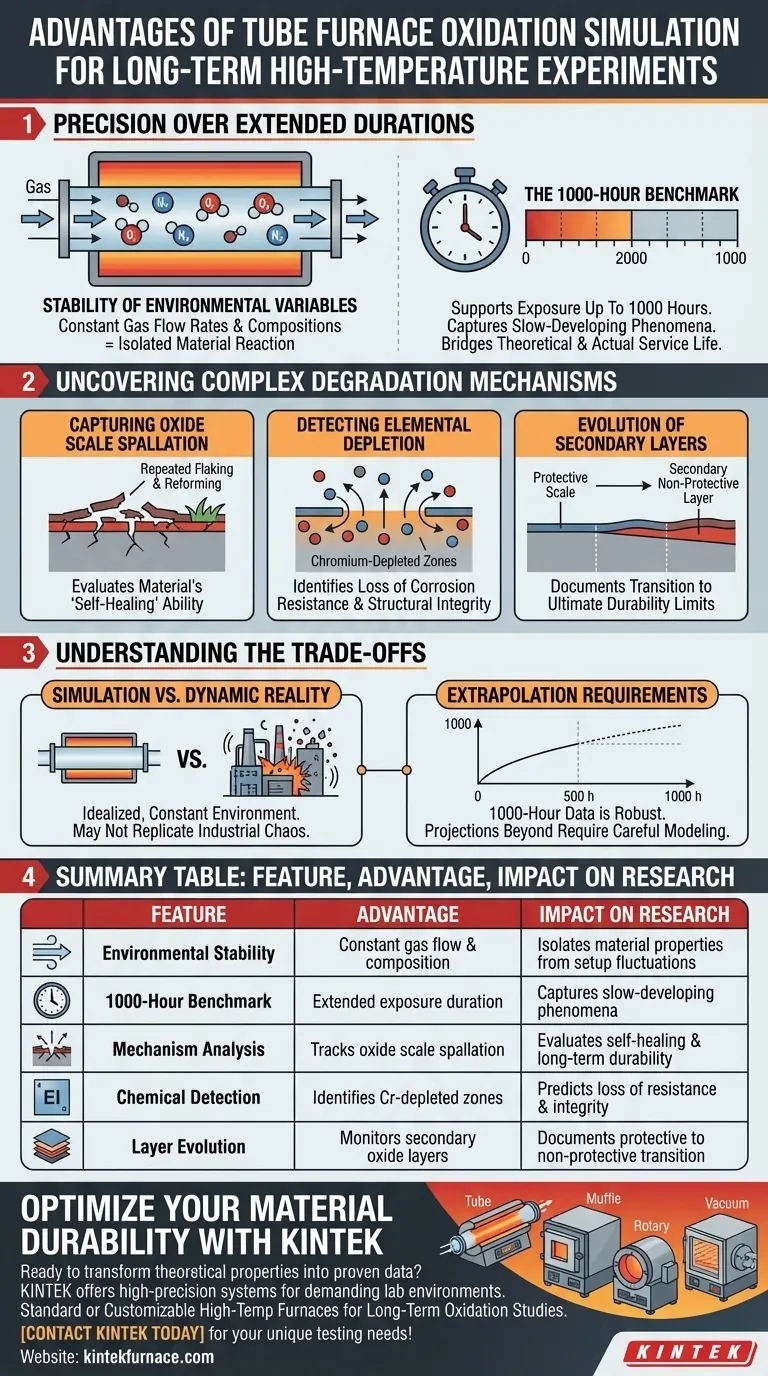
Precision Over Extended Durations
Stability of Environmental Variables
The primary advantage of a tube furnace facility is the rigorous control of the testing environment.
By maintaining stable gas flow rates and compositions, the facility ensures that the test conditions remain constant. This isolates the material's reaction to the environment, ensuring that observed degradation is due to the material's properties rather than fluctuations in the test setup.
The 1000-Hour Benchmark
Material degradation is often cumulative and non-linear.
These facilities support exposure testing for durations up to 1000 hours. This extended timeframe is critical for observing slow-developing phenomena that short-term tests will inevitably miss. It bridges the gap between theoretical resistance and actual service life performance.
Uncovering Complex Degradation Mechanisms
Capturing Oxide Scale Spallation
In real-world applications, protective oxide layers do not remain static; they grow, stress, and break.
Tube furnace simulations allow for the observation of repeated oxide scale spallation. This mimics the cycle where protective layers flake off and reform, providing data on the material's ability to "heal" itself over time or if it will suffer accelerated attack.
Detecting Elemental Depletion
High-temperature environments often cause vital alloying elements to migrate or evaporate.
Long-term simulations facilitate the formation and detection of chromium-depleted zones. Identifying these zones is essential, as the loss of chromium significantly reduces a material's corrosion resistance and structural integrity.
Evolution of Secondary Layers
A material's surface chemistry changes significantly as it ages.
These facilities capture the evolution of secondary non-protective oxide layers. Documenting the transition from a protective scale to a non-protective one provides a comprehensive evaluation of the material's ultimate durability limits.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simulation vs. Dynamic Reality
While the stability of gas flow is an advantage for scientific reproducibility, it is also a limitation.
A tube furnace creates an idealized, constant environment. It may not fully replicate the chaotic fluctuations, mechanical vibrations, or particulate erosion present in dynamic industrial operations.
Extrapolation Requirements
Testing for 1000 hours provides a robust dataset, but it is not infinite.
For components intended to last tens of thousands of hours, researchers must still rely on extrapolation. The data gathered is highly accurate for the test period, but projecting beyond the 1000-hour mark requires careful modeling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding if a tube furnace simulation is appropriate for your materials testing, consider your specific analytical needs:
- If your primary focus is failure mechanism analysis: Use these facilities to isolate and identify specific degradation causes, such as chromium depletion or spallation, in a noise-free environment.
- If your primary focus is service life modeling: Utilize the 1000-hour stability data to validate predictive models regarding the formation of secondary oxide layers.
Ultimately, these facilities offer the necessary stability and duration to transform theoretical material properties into proven durability data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage | Impact on Research |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Stability | Constant gas flow & composition | Isolates material properties from setup fluctuations |
| 1000-Hour Benchmark | Extended exposure duration | Captures slow-developing phenomena missed by short tests |
| Mechanism Analysis | Tracks oxide scale spallation | Evaluates self-healing ability and long-term durability |
| Chemical Detection | Identifies chromium-depleted zones | Predicts loss of corrosion resistance and integrity |
| Layer Evolution | Monitors secondary oxide layers | Documents the transition from protective to non-protective scales |
Optimize Your Material Durability with KINTEK
Ready to transform theoretical material properties into proven durability data? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding lab environments. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customizable high-temp furnace for long-term oxidation studies, our solutions provide the stability and control your research requires.
Take the next step in your high-temperature analysis—Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique testing needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Anna M. Manzoni, Christiane Stephan‐Scherb. High‐Temperature Oxidation of the CrFeNi Medium‐Entropy Alloy. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202500400
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of an industrial programmable tube furnace? Master Titania-Carbon Synthesis with Precision
- What is an alumina tube furnace? Essential for High-Temp, Contamination-Free Material Processing
- How are wafers loaded and unloaded in a vertical tube furnace? Achieve Precision and Purity in Wafer Processing
- What is the purpose of introducing nitrogen flow into a tube furnace? Optimize Your Activated Carbon Calcination
- What core process conditions does a vacuum tube furnace provide for FeCoNiCrAl coatings? Expert Annealing Guide
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the pore regulation of carbon nanofibers? Precision Engineering
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace in the annealing treatment of ZnIn electrodes?
- What are the methods for treating exhaust gas using a tube furnace? Safely Neutralize Hazards in Your Lab



















