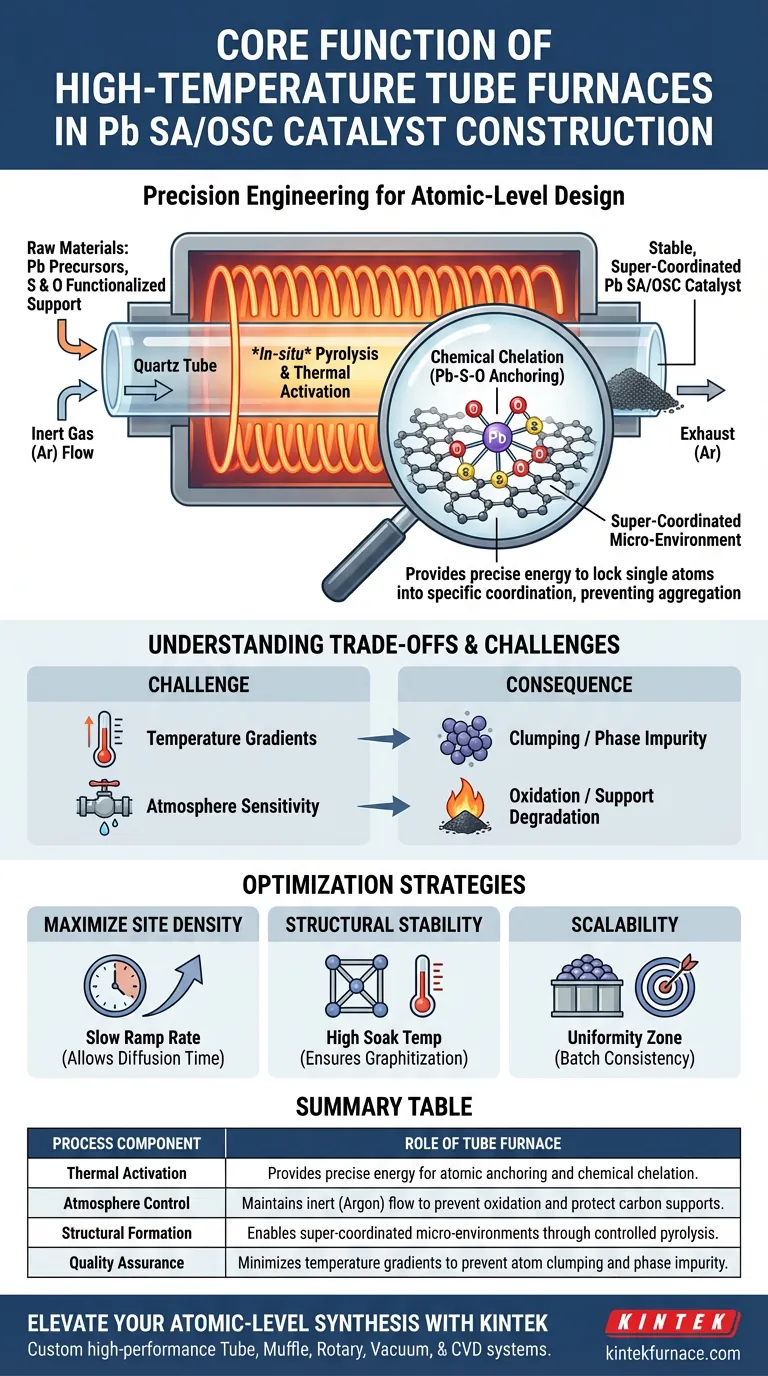
The primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in constructing Pb SA/OSC catalysts is to provide a strictly controlled thermal and atmospheric environment that enables in-situ pyrolysis. Specifically, it facilitates the chemical chelation of lead (Pb) cations with sulfur (S) and oxygen (O) functional groups on a support material. This process anchors the atoms individually, creating a stable, super-coordinated micro-environment.
Core Insight: The tube furnace acts as a precision engineering tool, not just a heater. It supplies the exact activation energy required to lock single atoms into a specific sulfur-oxygen coordination structure, preventing them from aggregating into clumps while preserving their catalytic activity.

Engineering the Atomic Micro-Environment
The synthesis of sulfur and oxygen super-coordinated single-atom catalysts (Pb SA/OSC) is a delicate thermodynamic process. The tube furnace serves as the reactor that drives the fundamental chemistry required to stabilize individual atoms.
Facilitating Atomic-Level Anchoring
For single-atom catalysts to function, the metal atoms must be firmly "anchored" to the support material.
The high-temperature environment provides the necessary thermal activation energy to drive chemical bonding.
Under these conditions, lead cations react chemically with sulfur and oxygen species. This creates a chelated structure where the metal atom is held firmly in place by the surrounding non-metal atoms.
Establishing the Inert Atmosphere
The synthesis process cannot occur in open air, as oxygen would degrade the carbon-based support or alter the oxidation state of the metal incorrectly.
The tube furnace allows for a constant flow of inert gas, typically argon.
This creates a stable, non-reactive envelope that protects the materials during the high-heat phase, ensuring that the chemical changes are strictly limited to the desired pyrolysis and coordination reactions.
Creating the Super-Coordinated Structure
The "super-coordinated" nature of the Pb SA/OSC catalyst refers to a specific, high-density bonding arrangement around the lead atom.
The precise temperature control curve of the furnace ensures that the material reaches the exact point required to form these complex bonds without destroying the underlying framework.
This results in a micro-environment that remains stable even under high-temperature catalytic operations later on.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the high-temperature tube furnace is the gold standard for this synthesis, accurate operation is critical to avoid compromising the material.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Gradients
The core advantage of a tube furnace is its ability to minimize temperature gradients along the tube length.
However, if the "soak time" (duration at peak temperature) or heating ramp rates are miscalculated, thermal gradients can still occur.
Inconsistent heating leads to "phase impurity," where some lead atoms fail to anchor and instead clump together, ruining the single-atom properties.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The process relies entirely on the purity of the inert atmosphere.
Any leak or fluctuation in the argon flow allows oxygen to enter the chamber at high temperatures.
This results in the combustion of the support material or the formation of unwanted metal oxides rather than the target super-coordinated active sites.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
Success in synthesizing Pb SA/OSC materials depends on how you program and utilize the tube furnace capabilities.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Site Density: Prioritize a slow ramp rate to allow sufficient time for the lead cations to diffuse and find available sulfur/oxygen anchoring sites before pyrolysis is complete.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Ensure the "soak" temperature is high enough to fully graphitize the carbon support, which locks the super-coordinated structure in place for long-term durability.
- If your primary focus is Scalability: Focus on the "uniformity zone" of your specific furnace; only place samples in the center region where the temperature deviation is negligible to ensure batch consistency.
By strictly controlling the thermal curve and atmospheric purity, you transform the tube furnace from a simple heater into an instrument of atomic-level design.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role of Tube Furnace in Catalyst Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Thermal Activation | Provides precise energy for atomic anchoring and chemical chelation. |
| Atmosphere Control | Maintains inert (Argon) flow to prevent oxidation and protect carbon supports. |
| Structural Formation | Enables super-coordinated micro-environments through controlled pyrolysis. |
| Quality Assurance | Minimizes temperature gradients to prevent atom clumping and phase impurity. |
Elevate Your Atomic-Level Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal engineering is the difference between a successful single-atom catalyst and a failed batch. At KINTEK, we understand the rigorous demands of material science. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to your specific research needs.
Whether you are synthesizing super-coordinated catalysts or advanced nanomaterials, our furnaces provide the temperature uniformity and atmospheric integrity your work deserves. Partner with KINTEK today for your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Xiao Zhou, Han‐Qing Yu. Constructing sulfur and oxygen super-coordinated main-group electrocatalysts for selective and cumulative H2O2 production. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44585-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in Silicon/Hard Carbon synthesis? Master Battery Anode Production
- What are the advantages of using a tube furnace with nitrogen flow? Precision Engineering for High-Temp Pyrolysis
- Why is a controlled atmosphere tube furnace essential for YBCO? Master Oxygen Stoichiometry for Superconductivity
- How does a tubular furnace work? Achieve Precise, Uniform Heat for Your Lab
- What is the function of a dual-zone tube furnace in LPCVD? Master Precise MnSe Nanosheet Synthesis
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What role does a tube furnace play in evaluating modified birnessite catalysts? Optimize VOC Degradation Activity
- What are the primary applications of tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing



















