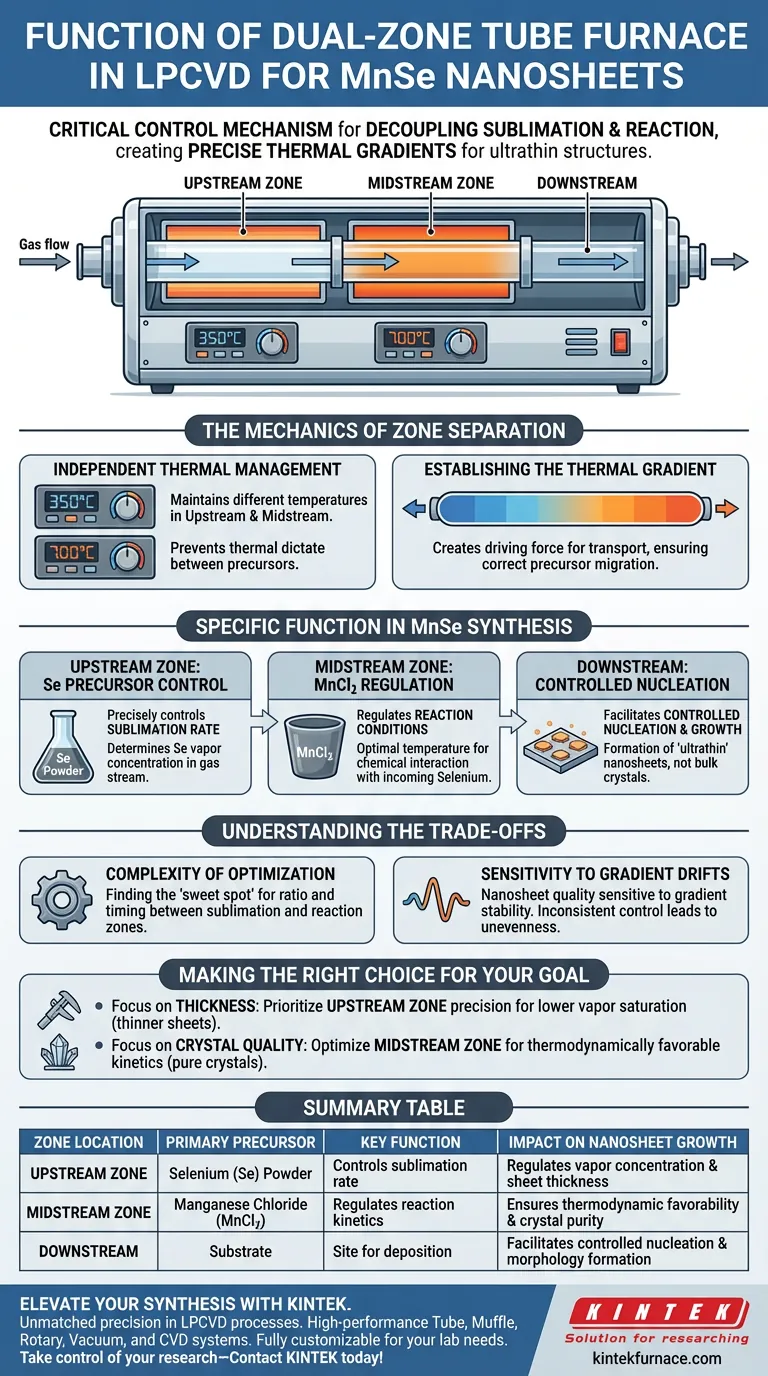
The dual-zone tube furnace serves as the critical control mechanism in the Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) of MnSe nanosheets, providing two independently regulated thermal environments within a single system. Its primary function is to decouple the sublimation rate of the selenium precursor from the reaction conditions of the manganese precursor, allowing for the precise thermal gradient required to synthesize ultrathin nanosheets.
The dual-zone configuration enables the simultaneous but distinct management of precursor availability and reaction kinetics. By maintaining independent thermal profiles, it ensures the controlled nucleation and growth necessary to produce high-quality, ultrathin MnSe structures.

The Mechanics of Zone Separation
Independent Thermal Management
The fundamental advantage of a dual-zone furnace is the ability to maintain the upstream and midstream sections at different temperatures.
This separation prevents the thermal requirements of one material from dictating the conditions of another.
Establishing the Thermal Gradient
By setting different temperatures in each zone, the system creates a specific thermal gradient along the tube.
This gradient acts as the driving force for the transport of vaporized materials, ensuring precursors migrate correctly from the source zone to the deposition zone.
Specific Function in MnSe Synthesis
Upstream Zone: Se Precursor Control
In the synthesis of MnSe nanosheets, the upstream temperature zone is dedicated to managing the Selenium (Se) powder.
Its specific function is to precisely control the sublimation rate of the Se.
By fine-tuning this temperature, you determine exactly how much selenium vapor is introduced into the gas stream at any given moment.
Midstream Zone: MnCl2 Regulation
The midstream zone is responsible for regulating the reaction conditions for the metal precursor, specifically Manganese Chloride (MnCl2).
This zone ensures the MnCl2 is at the optimal temperature to react with the incoming selenium vapor.
It creates the necessary thermodynamic environment for the chemical interaction between the two distinct precursors.
Downstream: Controlled Nucleation
The interplay between the upstream and midstream zones dictates the conditions at the downstream substrate location.
This precise control allows for the controlled nucleation and growth of the material.
The result is the formation of MnSe with a specific "ultrathin" nanosheet morphology, rather than bulk crystals or irregular films.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity of Optimization
While a dual-zone system offers superior control, it introduces complexity in finding the "sweet spot" for two interacting variables.
You must optimize not just one temperature, but the ratio and timing between the sublimation zone and the reaction zone.
Sensitivity to Gradient Drifts
The quality of the nanosheets is highly sensitive to the stability of the gradient between the zones.
If the upstream zone fluctuates, the Se concentration changes; if the midstream fluctuates, the reaction kinetics shift.
Inconsistent control in either zone can lead to uneven nanosheet thickness or uncontrolled nucleation rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To effectively utilize a dual-zone furnace for MnSe nanosheets, align your thermal strategy with your specific morphological targets:
- If your primary focus is Nanosheet Thickness: Prioritize the precision of the upstream zone temperature to limit Se vapor concentration, as lower precursor saturation often yields thinner sheets.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality/Stoichiometry: Focus on optimizing the midstream zone to ensure the MnCl2 reaction kinetics are thermodynamically favorable for pure crystal formation.
Success in LPCVD relies not just on heating materials, but on orchestrating the precise thermal difference between where the vapor is born and where the crystal grows.
Summary Table:
| Zone Location | Primary Precursor | Key Function | Impact on Nanosheet Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream Zone | Selenium (Se) Powder | Controls sublimation rate | Regulates vapor concentration and sheet thickness |
| Midstream Zone | Manganese Chloride (MnCl2) | Regulates reaction kinetics | Ensures thermodynamic favorability and crystal purity |
| Downstream | Substrate | Site for deposition | Facilitates controlled nucleation and morphology formation |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Ready to achieve unmatched precision in your LPCVD processes? Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of advanced nanomaterial synthesis. Whether you are growing MnSe nanosheets or developing complex thin films, our dual-zone and multi-zone tube furnaces provide the stable thermal gradients essential for your success. Our systems are fully customizable to fit your unique laboratory needs.
Take control of your research—Contact KINTEK today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Ye Zhao, Xiaohong Xu. Magnetic exchange coupling and photodetection multifunction characteristics of an MnSe/LaMnO<sub>3</sub> heterostructure. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra06719c
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace in pp-fiber production? Master Precise Carbonization Control
- What are the standard and customizable options for tube furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab's Needs
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in CVD synthesis of carbon nanotubes? Achieve Precision Thermal Control
- Why is a Tube Furnace required for the heat treatment of carbon fiber cloth? Master Surface Activation
- What does uniform length refer to in a tube furnace? Ensure Precise Thermal Control for Reliable Results
- What is the function of an industrial tube furnace in NdFeB recycling? Unlock Efficient Rare Earth Recovery
- What critical conditions does a high-precision tube furnace provide? Optimize Catalyst Reduction & Particle Control
- How can the uniform length of a tube furnace be improved? Boost Temperature Uniformity with Proven Methods



















